Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error (WMAPE) is a measure of forecasting accuracy used to evaluate the accuracy of a model’s predictions against actual values. It is used in a variety of forecasting models and is commonly used in business, finance, and economics. It is an important metric to consider when evaluating the efficacy of forecasting models, as it provides a useful measure of the difference between the predicted values and the actual values. WMAPE is also often used to compare various forecasting models to determine which one is most accurate. In this blog post, we will explore what WMAPE is, how it is calculated, and why it is important for forecasting accuracy. We will also discuss some best practices for using WMAPE to evaluate the accuracy of forecasting models.
Mean Absolute Percentage Error
Example: Weighted MAPE in Excel
The following actions can be taken in Excel to calculate Weighted MAPE:
Step 1: Add the forecasted values and actual values to two different columns.
Step 2: Calculate the weighted error for each row.
Remember that the weighted error is determined by the following formula: |actual-forecast| / |actual| * 100 * actual This formula will be used to determine the weighted error for each row.
The weighted error is shown in Column D, and the formula is shown in Column E:
We will repeat this formula for each row:
Step 3: Find the sum of actual values.
Step 4: Calculate the Weighted MAPE.
The Weighted MAPE will then be calculated by dividing the total weighted errors by the total of the actual values:
The Weighted MAPE turns out to be 5.92%.
The Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error (WMAPE)
The Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error (WMAPE) is the absolute error multiplied by a scalar value (i) and normalized by the sum of the realized values. e. , weight).
Formula WMAPE:
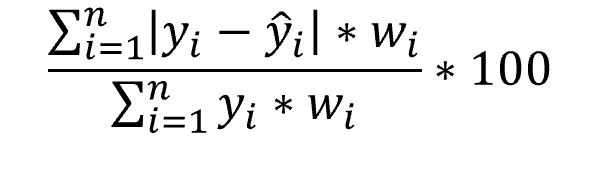
, where:
Therefore, the WMAPE by definition places a greater emphasis on some errors than others (i e. , the difference between realized and predicted values). Each error’s significance is determined by multiplying the realized value by its weight.
The accuracy of a forecasting system is measured by the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), also known as the mean absolute percentage deviation (MAPD). It can be calculated as the average absolute percent error for each time period less actual values divided by actual values to represent this accuracy as a percentage.
Since the variable’s units are scaled to percentage units, which makes it easier to understand, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) is the most frequently used measure to forecast error [1]. The data should not have any extremes (including zeros) for the best results. In regression analysis and model evaluation, it is frequently used as a loss function.
Another method for predicting accuracy is called Weighted Mean Absolute Percentage Error, or WMAPE. Since the sum of the actual value in the denominator can never equal zero, the issue of infinite error (divide by zero) is eliminated in this case. While the error is calculated using weights, the MAPE error was determined using average values. Therefore, WMAPE is more trustworthy and provides accurate results than MAPE.
Therefore, one of the most popular techniques for determining forecasting accuracy is MAPE, also known as Mean Absolute Percentage Error. Seeing the MAPE value alone makes it simpler to interpret the accuracy, making it a more efficient and practical method. When the Actual value of any entity is zero, we are faced with an infinite error problem.
2. Calculate the subpart of the summation’s formula known as the weighted error.
The weighted error for the first entry in the data set will be determined using the formula above. To obtain the weighted error for the remaining entries, drag the Auto Fill Options button at this time.
In statistics, forecasting accuracy is a term used to describe how closely a quantity matches its actual value. The actual value is also known as the true value. It essentially refers to the degree of proximity or a verification procedure that is heavily utilized by business professionals to keep track of their sales and exchanges in order to maintain the demand and supply mapping each year. There are various methods to calculate Forecasting Accuracy.
FAQ
What is MAPE and how is it calculated?
The mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), which is a statistical indicator of forecasting system accuracy It can be calculated as the average absolute percent error for each time period less actual values divided by actual values to represent this accuracy as a percentage.
What is the difference between MAPE and Wmape?
WMAPE and MAPE are different measures. Mean Absolute Percent Error (MAPE) is the simple average of the percent errors. WMAPE, which stands for Weighted Mean Absolute Percent Error, weighs the errors according to volume, making it more accurate and dependable. The calculation is unaffected by negative errors because this is all absolute error.
How do you calculate mean absolute percentage error in time series?
One of the most frequently used error metrics in time series forecasting is the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). It is calculated by dividing the actual values by the average (mean) of the absolute difference between the actual values and the predicted values.
How do I calculate percentage error?
Percentage Error = ((Estimated Number – Actual Number)/ Actual number) x 100 summarizes all of the above.