Decision support systems (DSS) are powerful tools that can help businesses analyze data and make more informed decisions As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, using DSS is becoming increasingly important for organizations of all sizes This comprehensive guide will explain what decision support systems are, the main components and types of DSS, key benefits, and provide actionable tips on how to select and implement the right DSS for your business needs.
What is a Decision Support System?
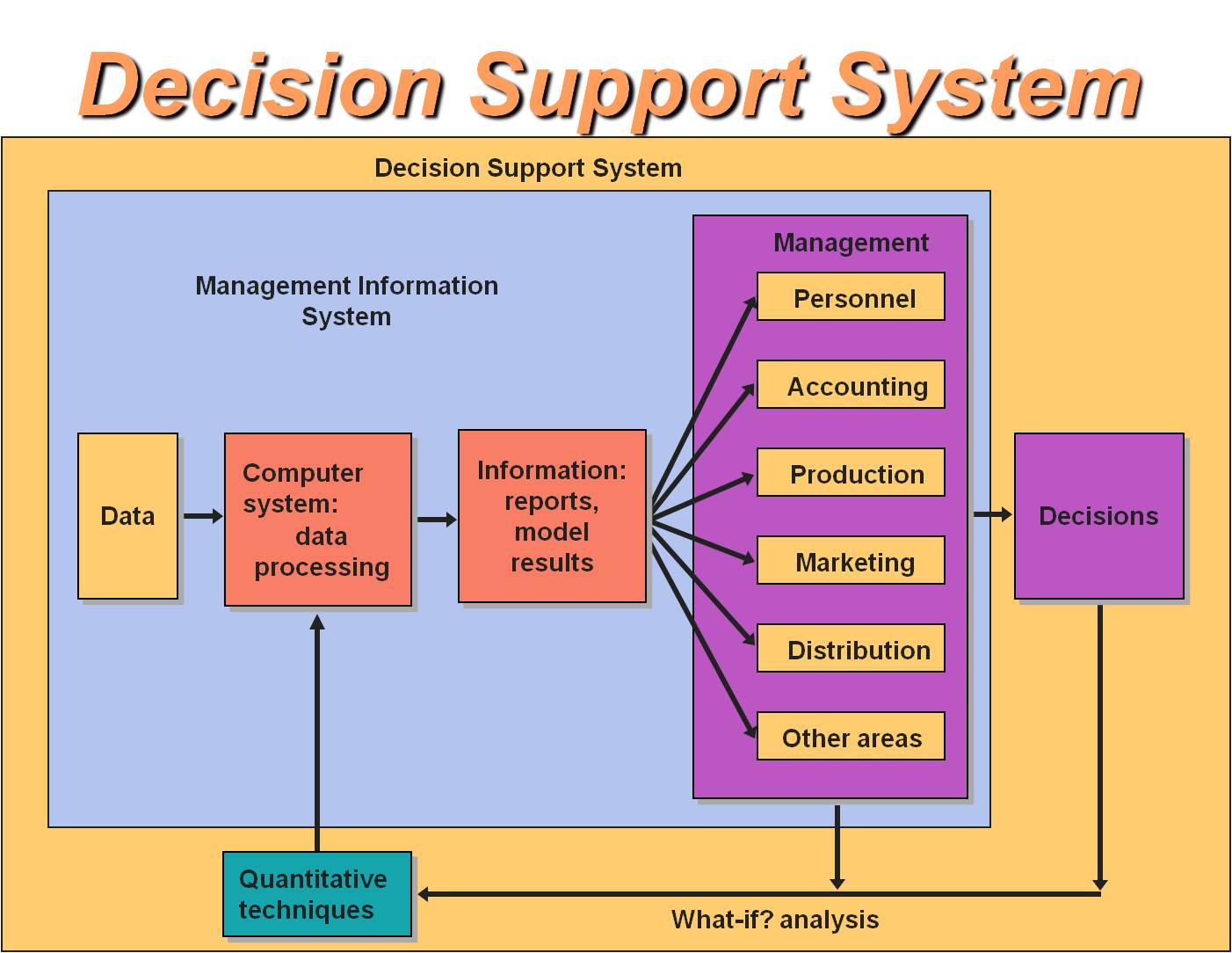
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that helps organizations make better decisions by gathering organizing, and analyzing large amounts of data. DSS tools go beyond traditional business intelligence software by incorporating advanced analytics data mining, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence to not only report on past performance but also predict future outcomes.
While traditional business software focuses on transaction processing and record keeping, DSS emphasizes analysis and visualization of information to support strategic and tactical decision making. From forecasting sales to optimizing supply chains, DSS enables organizations to leverage data-driven insights for a competitive advantage.
Main Components of a Decision Support System
An effective decision support system is made up of three key components:
-
Data Management: This module integrates data from multiple sources, transforms data into a unified format, stores data in a centralized data warehouse or database, and prepares data for analysis. Data management ensures consistent, high-quality data.
-
Model Management: The model management component applies quantitative and statistical models to analyze data. Different analytic models include optimization, simulation, predictive modeling, machine learning, and data mining. This module automates complex analyses.
-
User Interface: The user interface presents information to users in an easy-to-understand visual format such as dashboards, charts, graphs, and reports. This component allows interactive queries, report generation, and visualization.
Types of Decision Support Systems
There are five main types of decision support systems, each designed to address different business needs:
-
Data-Driven DSS: Analyzes large databases to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. Helps organizations summarize vast amounts of data.
-
Model-Driven DSS: Uses financial, predictive, or optimization models to simulate “what-if” scenarios. Useful for sensitivity analysis.
-
Knowledge-Driven DSS: Offers specialized problem-solving expertise stored as rules, procedures, or similar constructs. Does not require a large database.
-
Document-Driven DSS: Searches unstructured information in documents or websites to retrieve answers to queries. Helps find content relationships.
-
Communications-Driven DSS: Facilitates collaboration and information sharing between decision makers in an organization. Enables group decision making.
Key Benefits of Using a Decision Support System
Implementing an enterprise-wide DSS delivers many benefits for businesses:
-
Improved Decision Making: DSS enhances decision quality by enabling data-driven analysis rather than reliance on gut feel. This leads to increased revenues, lower costs, and reduced risks.
-
Increased Productivity: Automated analytics save time compared to manual analysis. DSS also quickly delivers insights to decision makers company-wide.
-
Enhanced Reporting: User-friendly visualization through dashboards, charts, and interactive reports improves clarity and understanding.
-
Competitive Advantages: Data mining uncovers hidden patterns and relationships that can lead to better products, pricing, logistics, and customer service.
-
Future Planning: Predictive analytics and modeling forecast future demand, identify emerging trends, and simulate scenarios for more informed planning.
-
Consistent Analytics: Standardizes analysis across the organization and integrates analytics into business processes. Promotes fact-based decisions.
How to Select the Right Decision Support System
Choosing the optimal DSS depends on your business requirements, existing infrastructure, and budget. Follow these steps for a successful DSS implementation:
1. Define Your Objectives
First, determine your key business objectives, problems areas, and metrics for success. This focuses DSS selection on your specific needs.
2. Assess Internal Capabilities
Review your current analytics skills, data sources, and technical readiness. This identifies any gaps the DSS must fill.
3. Create System Requirements
Outline your functional and technical requirements. Requirements may include predictive analytics, OLAP, big data integration, cloud vs. on-premise, and ease of use.
4. Evaluate Leading DSS Solutions
Research DSS vendors like SAP, SAS, IBM, and Oracle. Compare capabilities, tools, and reviews. Consider ease of use, TCO, scalability, and vendor viability.
5. Select the Best Solution
Choose the DSS that closest matches your key requirements and has the right mix of features, flexibility, and affordability. Focus on long-term value over upfront cost.
6. Start with a Pilot Project
Initially implement the DSS for a targeted, high-impact business process. The pilot demonstrates value and allows testing before enterprise-wide rollout.
Tips for Successful DSS Implementation
Following best practices will ensure your organization fully leverages its investment in a decision support system:
-
Secure Executive Buy-In: Gain leadership support by quantifying the business case and tying DSS to strategic goals.
-
Establish Data Governance: Institute data standards, quality processes, security policies, and access controls. Quality data leads to quality analysis.
-
Involve Key Stakeholders: Get user input when defining needs and designing reports. Ensure tools match workflows and requirements.
-
Consider Change Management: New technology often faces user resistance. Promote adoption through training and communication.
-
Start with High-Impact Areas: Initially focus DSS on the highest payback applications to demonstrate benefits and build support.
-
Leverage External Data: Supplement internal data with relevant external data sources for richer insights and benchmarking.
-
Review and Refresh Models: Continuously verify model accuracy and relevance. Tune, retrain, or replace models to sustain value.
-
Expand System Usage: After early successes, roll out DSS to new applications, users, and organizational levels to maximize its impact.
DSS Use Cases
Here are just a few examples of how organizations employ decision support systems:
-
Retail: Retailers use DSS for sales forecasting, pricing optimization, inventory management, and supply chain optimization. DSS enables data-driven decisions on merchandise planning and operations.
-
Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics apply DSS for clinical decision support, resource allocation, appointment scheduling, length of stay prediction, and readmission risk assessment. This improves quality of care and patient flow.
-
Financial Services: Banks use DSS for credit scoring, fraud detection, investment analysis, risk management, and compliance processes. DSS enhances risk models and complements human judgement.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturers integrate DSS with supply chain and production systems for improved demand forecasting, production scheduling, inventory control, and delivery logistics. This increases efficiency.
-
Government: Government agencies employ DSS for functions like tax collection, public transit planning, utilities demand forecasting, infrastructure project selection, and social welfare programs.
As data volumes continue exploding, decision support systems provide the analytical power organizations need to gain strategic insights and predictive intelligence from their data assets. By investing in the right DSS technology and following best practices, companies can leverage data-driven decisions to improve all aspects of business performance. Mastering big data through decision support systems is becoming an essential competency for successful management in the information age.
Decision support system components
A typical DSS consists of three different parts: knowledge database, software and user interface.
Knowledge base. A knowledge base is an integral part of a decision support system database, containing information from both internal and external sources. It is a library of information related to particular subjects and is the part of a DSS that stores information used by the systems reasoning engine to determine a course of action.
Learn about knowledge base uses in customer service and call centers.
Software system. The software system is composed of model management systems. A model is a simulation of a real-world system with the goal of understanding how the system works and how it can be improved. Organizations use models to predict how outcomes will change with different adjustments to the system.
For example, models can be helpful for understanding systems that are too complicated, too expensive or too dangerous to fully explore in real life. Thats the idea behind computer simulations used for scientific research, engineering tests, weather forecasting and many other applications.
Models can also be used to represent and explore systems that dont yet exist, like a proposed new technology, a planned factory or a businesss supply chain. Businesses also use models to predict the outcomes of different changes to a system — such as policies, risks and regulations — to help make business decisions.
User interface. The user interface enables easy system navigation. The primary goal of the decision support systems user interface is to make it easy for the user to manipulate the data that is stored on it. Businesses can use the interface to evaluate the effectiveness of DSS transactions for the end users. DSS interfaces include simple windows, complex menu-driven interfaces and command-line interfaces.
What is a decision support system (DSS)?
A decision support system (DSS) is a computer program application used to improve a companys decision-making capabilities. It analyzes large amounts of data and presents an organization with the best possible options available.
Decision support systems bring together data and knowledge from different areas and sources to provide users with information beyond the usual reports and summaries. This is intended to help people make informed decisions.
Typical information a decision support application might gather and present include the following:
- comparative sales figures between one week and the next;
- projected revenue figures based on new product sales assumptions; and
- the consequences of different decisions.
A decision support system is an informational application as opposed to an operational application. Informational applications provide users with relevant information based on a variety of data sources to support better-informed decision-making. Operational applications, by contrast, record the details of business transactions, including the data required for the decision-support needs of a business.
Understanding Decision Support Systems
How does decision support software work?
Below, we explain how decision support software works and how it can help you run your business better. What is a decision support system? A decision support system (DSS) is a computer-based information system that organizes, collects and analyzes business data.
What is a decision support system?
Decision support system s are designed to assist decision-makers by providing them with relevant information, data analysis, and tools to enhance the quality of their decisions. DSS offers interactive interfaces that allow users to manipulate data, explore scenarios, and perform “what-if” analyses, fostering more informed decision-making.
What is a decision support system (DDS)?
A decision support system (DDS) is a tool professionals use to help them make informed and intelligent business decisions. DDSs can have various functions and focuses depending on the industries and the professionals employing them. Most DDSs comprise three key components: databases, models and user interfaces. What is a decision support system?
What is a decision support user interface?
The user interface is the access point for those who use the decision support system. Successful decision support systems use flexible and intuitive user interfaces that allow professionals to access the information they need and operate the system without extensive technological knowledge.