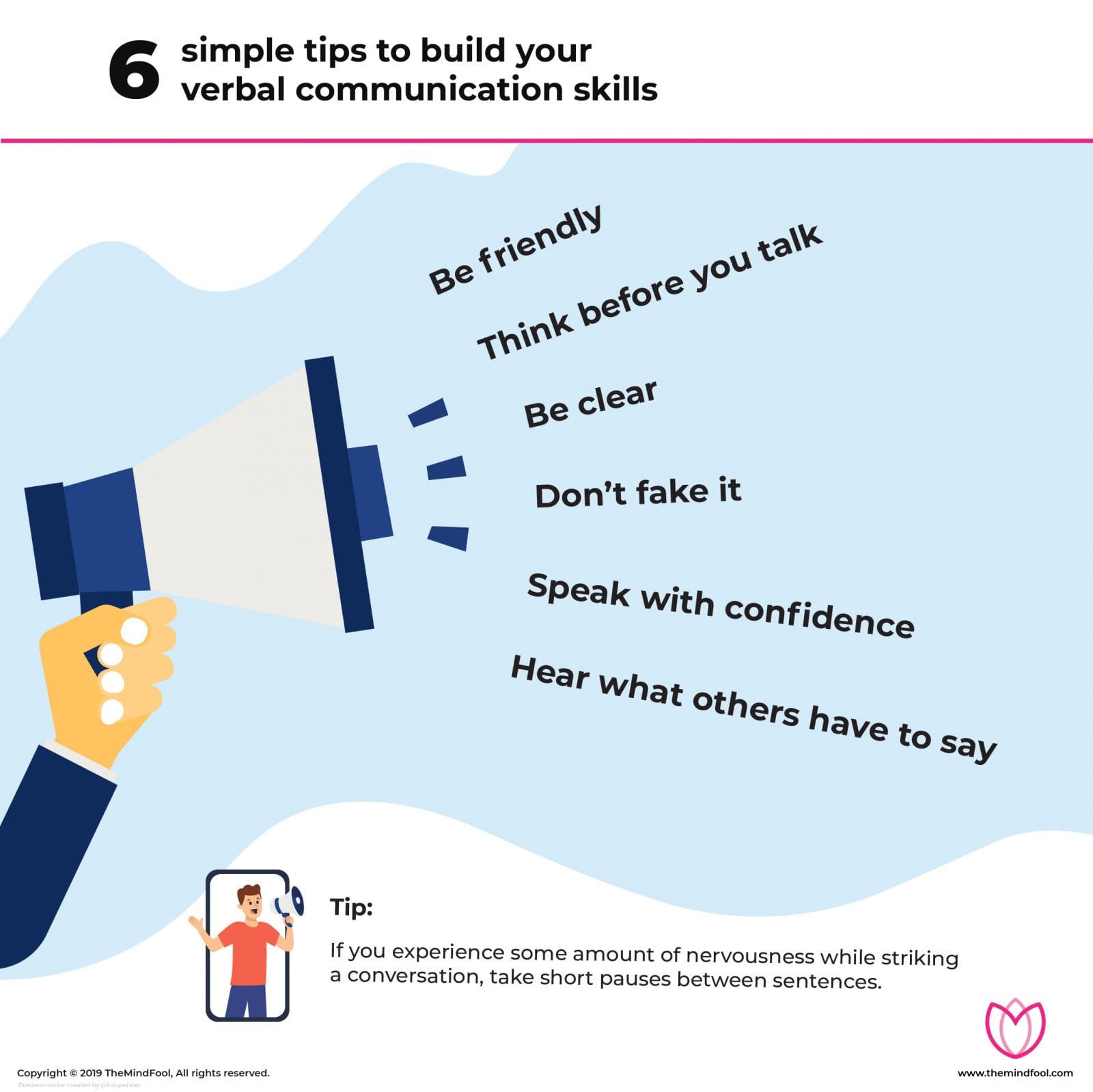
Effective verbal communication abilities are essential for succeeding in both personal and professional realms The capacity to express ideas, give clear instructions, build rapport, persuade and motivate others largely relies on strong communication skills
While some people are naturally more adept verbally, anyone can enhance their verbal skills with practice and strategy. This 10-step guide reveals techniques to significantly improve verbal communication and interpersonal interactions.
1. Think Before Speaking
Most people are eager to respond immediately when spoken to. The problem is blurting things out without forethought. This leads to excessive filler words, rambling sentences, and miscommunication.
Instead, make it a habit to take a brief pause before responding in conversations. Consider your words carefully. Mentally organize key points you want to convey.
This simple act of pausing to gather your thoughts results in much clearer, more intentional communication. You avoid rambling and stay focused.
2. Speak Concisely
Concise verbal communication eliminates fluff and gets right to the point. To speak more concisely:
-
Remove unnecessary filler words like “um”, “like”, “you know”, etc.
-
Avoid lengthy run-on sentences. Break ideas into shorter sentences.
-
Cut out off-topic tangents and details that detract from your message.
-
Summarize points upfront instead of meandering to them.
Concise communication demonstrates confidence and respect for the listener’s time.
3. Vary Tone for Emphasis
Words alone convey limited meaning without vocal inflection and emphasis. Monotone speaking bores listeners.
Inject energy by emphasizing important text and varying tone:
-
Stress key words and phrases by speaking forcefully when uttering them.
-
Raise or lower volume at strategic points to highlight ideas.
-
Adjust pace and add dramatic pauses for effect before pivotal concepts.
-
Use animation and enthusiasm when appropriate to stimulate engagement.
This nonverbal emphasis makes your verbal message more dynamic and compelling.
4. Listen Actively
Communication flows two ways. Speaking skills falter without active listening abilities. When others speak, focus completely on comprehending:
-
Maintain eye contact. Nod along. Mirror body language.
-
Avoid interrupting or mentally formulating your next speech. Stay present.
-
Paraphrase content back to confirm understanding. Ask clarifying questions.
-
Observe nonverbal cues that add context like facial expressions and gestures.
Active listening ensures you fully absorb information being conveyed so you can respond accordingly.
5. Master Nonverbal Communication
What you say accounts for less than half of communication effectiveness. Nonverbal cues like eye contact, smiling, posture, gestures, and tone of voice impact meaning and connections.
Align nonverbal signals with your words. For example, maintaining eye contact and an open posture when speaking conveys confidence and trustworthiness.
Observing others’ nonverbal cues also provides insight into their unspoken perspective. Note cues that reinforce or contradict the spoken message.
6. Adjust for the Audience
Communication must be tailored to the specific audience. The language, tone, and approach used with close friends differs greatly from that of senior executives, for example.
Consider demographics, knowledge level, culture, goals and interests of the audience. Aim to speak on their level in a way that resonates.
Adapting your style establishes better rapport and ensures your message lands effectively.
7. Avoid Jargon and Acronyms
Technical terms, industry jargon, buzzwords, and acronyms confuse external audiences unfamiliar with them. This applies even when speaking to savvy audiences outside your niche.
Define any specialty terms and acronyms on first use:
-
“Facial recognition AI (artificial intelligence) scans….”
-
“KPIs, or key performance indicators…”
Sticking to simple, universally understood language ensures broader comprehension.
8. Open With Impact
First impressions matter greatly in communication. How you initiate an interaction sets the tone. Begin strongly by:
-
Starting with a compelling statement, question, story, quote or statistic.
-
Introducing yourself warmly with context to build connection.
-
State the purpose or objective upfront to frame the conversation.
-
Referencing common connections like mutual contacts.
A thoughtful opening line or two makes an instantly strong verbal impression.
9. Close Communications
Ending a verbal exchange well is equally important as opening it. To wrap up effectively:
-
Summarize key points and next steps.
-
Offer to follow up with any additional information.
-
Express gratitude for the person’s time.
-
Conclude with a single call-to-action statement if applicable.
Strong closings provide resolution and leave the listener clear on what happens next.
10. Seek Feedback
Ask trusted contacts for constructive feedback on your verbal communication skills. Specifically what you do well and areas to improve.
Feedback from peers, managers and mentors provides objective insights you can implement. You may detect blind spots.
A feedback loop fuels continuous improvement of verbal abilities.
Advanced Techniques and Training
Once you master essential verbal communication principles, consider further developing skills through:
-
Public speaking courses – Build presentation abilities through local classes or sites like Udemy.
-
Improv classes – Improv comedy trains quick thinking and smooth speaking skills.
-
Joining toastmasters – This organization provides mentoring for public speaking and leadership communication skills.
-
Reading body language guides – Books like What Every Body is Saying provide deeper expertise interpreting nonverbal communications.
-
Speech therapy – Work with a professional if you have a speech impediment affecting verbal skills.
-
Recording speeches – Record yourself and analyze areas needing improvement.
Keep enhancing verbal talents over time through deliberate education and practice. Communication is a career-long skillset.
Key Takeaways for Improving Verbal Communication
-
Think carefully before responding. Don’t just blurt things out.
-
Speak concisely. Remove fluff and rambling from your speech.
-
Remember nonverbal cues like eye contact and tone. Don’t rely on words alone.
-
Listen attentively without interrupting when others speak. Reflect back key points.
-
Gauge audience demographics and interests to adapt your style and language for maximum impact.
-
Open and close each communication smoothly. Start strong and end deliberately.
Applying these verbal communication best practices leads to greater clarity and persuasion in any industry role relying on interpersonal interaction.
Enhance your communication skills
Discover tailored coaching to master effective communication for professional growth.
Communication Skills: How to Improve Verbal Communication Skills
How do I improve my verbal communication skills?
Here are some tips for improving your verbal communication skills, both spoken and written: 1. Consider your message Decide what you want to convey during your next conversation, presentation or written communication. This might involve brainstorming or outlining a list of key points you’d like to make.
How can one overcome speech blockages and stammering?
Speech block is when someone gets caught on a particular word, which makes it difficult to continue speaking. It can be due to problems with fluency too. It can be avoided by using prolonged speech, like stretching out the whole sentence. Soft contacts and easy onset are beneficial too. Certain stressful situations can increase stuttering and fatigue and pressure contribute to it. So doing some breathing exercises, being mindful and reducing stress can help. Avoiding triggers, using brief pauses in between sentences avoids stuttering. Taking treatment from childhood helps to overcome this condition and builds confidence, and improves speech fluency.
How do I use my verbal communication skills in a work setting?
Here are a few tips for using your verbal communication skills in a work setting: Be observant: Nonverbal cues can be extremely communicative, so if possible, practice being aware of how both you and your coworkers are using body language.
What are verbal communication skills?
Verbal communication skills represent more than speaking abilities—they demonstrate how you deliver and receive messages in both speaking and written interactions. These skills focus on how you communicate rather than what you say. Because of this, you can utilize nonverbal techniques such as body language to enhance your interactions.