Effective supply chain planning is more vital than ever in today’s fast-paced business world. It plays a crucial role in streamlining the production and delivery of products, all while ensuring supply and demand are in equilibrium.
With this comprehensive article, we’ll dive deep into the complexities of supply chain planning. We’ll also cover indispensable factors that supply chain experts must weigh carefully when helping companies prepare to compete globally.
Finally, we’ll show how you can understand supply chain planning holistically with a tool that helps global companies save money daily.
An effective supply chain plan is essential for companies to deliver products and services efficiently to customers. By optimizing the flow of goods and information, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction while reducing costs and inventory needs.
This article provides a step-by-step guide to developing a robust supply chain plan tailored to your operations. We’ll cover key factors to consider at each stage and strategies to create alignment across the end-to-end supply chain.
Steps to Build a Strategic Supply Chain Plan
Follow these key steps to develop a comprehensive tactical and strategic supply chain plan:
1. Define Objectives and Metrics
First, determine the key objectives your supply chain plan aims to achieve Typical goals include
- Improving customer service levels
- Reducing inventory costs
- Increasing supply chain visibility
- Mitigating disruptions and risk
- Leveraging emerging technologies
Identify quantitative metrics aligned to each objective to track progress Common metrics include fill rates, perfect order rates, inventory turnover, and days of supply in inventory
2. Map the Current State
Next, visualize your current supply chain from end-to-end and identify all key processes, stakeholders, flows of goods and information loops.
Document elements like:
- Tier 1, 2, 3 suppliers
- Manufacturing sites
- Warehouses and distribution centers
- Transportation modes and lanes
- Planning processes like S&OP
- Order management approach
- Inventory policies
- IT systems and data flows
This mapping illuminates interconnections and constraints to address.
3. Forecast Demand
Develop forecasts for demand by product and channel based on statistical models, market intelligence, and input from sales and marketing.
Factor in elements like seasonality, promotions, market trends, and product life cycles. Use rolling forecasts with different horizons to balance accuracy and agility.
4. Plan Supply Requirements
Compare demand forecasts with current and projected inventory levels to determine raw material, component, and finished goods requirements.
Factor in parameters like:
- Lead times
- Batch sizes
- Inventory holding policies
- Space constraints
- Shelf life
The result is future-looking time-phased supply plans.
5. Identify Gaps and Opportunities
Compare required future supply with current capabilities and constraints. Look for mismatches between demand and supply at product, facility, and regional levels.
Determine root causes of gaps, such as:
- Production capacity shortfalls
- Material shortages
- Long production lead times
- Inflexible transportation
- Low sourcing redundancy
Brainstorm supply chain changes to close gaps, reduce costs, and improve flexibility.
6. Define Strategic Initiatives
Based on the gaps identified, outline key strategic supply chain initiatives to pursue. Examples include:
- Increasing supplier base – Reduces risk and provides flexibility
- Adding production locations – Improves responsiveness and stability
- Implementing postponement strategies – Allows customization closer to demand
- Using dynamic discounting – Lowers procurement costs
- Upgrading transportation fleet – Speeds delivery times
Prioritize the initiatives based on feasibility, costs, risks, and alignment with objectives.
7. Develop Tactical Plans
Translate strategic initiatives into detailed execution plans with assigned owners, resources, timelines, and performance indicators.
Tactical plans specify how you will actually implement changes to policies, technology, facilities, and daily S&OP and order fulfillment processes. They make the strategy actionable.
8. Optimize Plans Dynamically
Build in regular cycles to gather updated data on demand, inventory, and supply risks and run planning models to identify new disconnects or opportunities.
Rerun optimization models and use sensitivity analysis to support decisions on dynamic course corrections in purchasing, production, distribution, and inventory. This enables agility.
9. Collaborate on Ongoing Improvements
Keep cross-functional teams engaged through regular meetings to review KPIs, address recurring problems proactively, brainstorm innovations, and support change management.
Nurture culture of ownership, flexibility, and data-driven decision making. Continuously refine plans based on lessons learned.
Key Components of a Supply Chain Plan
To maximize robustness and alignment, the integrated supply chain plan must include details on:
1. Demand
- Statistical forecasting models
- Customer segmentation
- Promotions plan
- Seasonality patterns
2. Supply
- Sourcing plans per tier
- Production plans per facility
- Inventory policies per SKU
- Distribution plans
3. Logistics
- Carrier contracts
- Transportation mode optimization
- Routing guides
- Shipment consolidation logic
4. S&OP Processes
- Demand/supply review cadence
- Collaborative planning events
- Executive review procedures
- Change management processes
5. Technology
- TMS, WMS, and ERP systems
- Optimization engines
- Data interchange protocols
- Analytics capabilities
6. Contingency Plans
- Risk assessment and monitoring
- Sourcing redundancy
- Inventory buffers
- Crisis response scenarios
Together these elements synchronize demand with supply across partners, facilities, and geographies.
Key Features of Effective Supply Chain Plans
The best supply chain plans have these critical characteristics:
- Cross-functional – Procurement, production, logistics, sales all contribute unique insights
- Datadriven – Leverages statistically robust demand forecasts and inventory data
- Dynamic – Gets frequently updated based on new projections, outcomes, constraints
- Integrated – Aligns plans across departments, suppliers, and global entities
- Collaborative – Involves robust input and buy-in across stakeholders
- Risk-aware – Incorporates contingency plans for disruptions
- Customer-centric – Focuses on profitably meeting customer needs
- Flexibility-focused – Builds in agility to adjust course rapidly
- Innovative – Embraces new technologies, processes, partnerships
- Continuously improving – Refines approaches and shares learnings
With these characteristics, supply chain plans can manage complexity while enabling responsiveness and outstanding customer service.
Keys to Successful Supply Chain Planning
Follow these best practices to build world-class supply chain planning capabilities:
-
Invest in forecasting expertise – The quality of statistical demand forecasts drives downstream supply plans. Hire data scientists and equip planners with demand analytics skills.
-
Map interconnectivity – Understand how each network node and process impacts others to manage tradeoffs holistically.
-
Test scenarios – Model different demand spikes, supply shocks, and contingencies to stress test plans.
-
Colocate teams – Break down functional silos by having procurement, production, inventory, and logistics planners work side-by-side.
-
Build transparency – Share projections across partners and functions to align expectations and actions.
-
Run what-if analysis – Assess multiple supply configurations to optimize inventory, capacity, transportation, and costs.
-
Automate where possible – Use optimization engines for granular tradeoff analysis impossible manually.
-
Institutionalize S&OP governance – Ensure executive commitment and cross-functional accountability.
With rigorous processes, advanced analytics, and strong collaboration, companies can enact supply chain plans that create real competitive advantage.
Developing an aligned supply chain strategy involves analyzing demand signals, supply capabilities, logistics networks, and risks. Companies must translate insights into integrated strategic and tactical plans focused on profitably delivering outstanding customer service.
By regularly updating projections and plans, securing broad collaboration, and embracing innovation, businesses can optimize their end-to-end supply chains. The reward is increased agility, reduced costs, and resilience in the face of disruptions. With sound supply chain planning, companies can master demand volatility and intensifying customer expectations.
What is a Supply Distribution Network Design?
The supply distribution network design is a framework that determines the flow of goods, the locations of warehouses and distribution centers, and transportation routes.
An effective distribution network design ensures that goods are transported from the point of production to the end of consumption most efficiently and cost-effectively.
What to Consider in Designing an Efficient Supply Distribution Network?
- Geographical coverage of the distribution network should reach a wide geographical area to ensure products can get customers efficiently.
- Customer demand patterns must be understood to determine the number and location of distribution centers to optimize product availability.
- Transportation costs must be considered in the distribution network design, including shipping, fuel, and maintenance, to minimize overall supply chain expenses.
- Lead time requirements of different products
- Inventory positioning within the distribution network must ensure that products are available when and where needed, reducing stockouts and excess inventory.
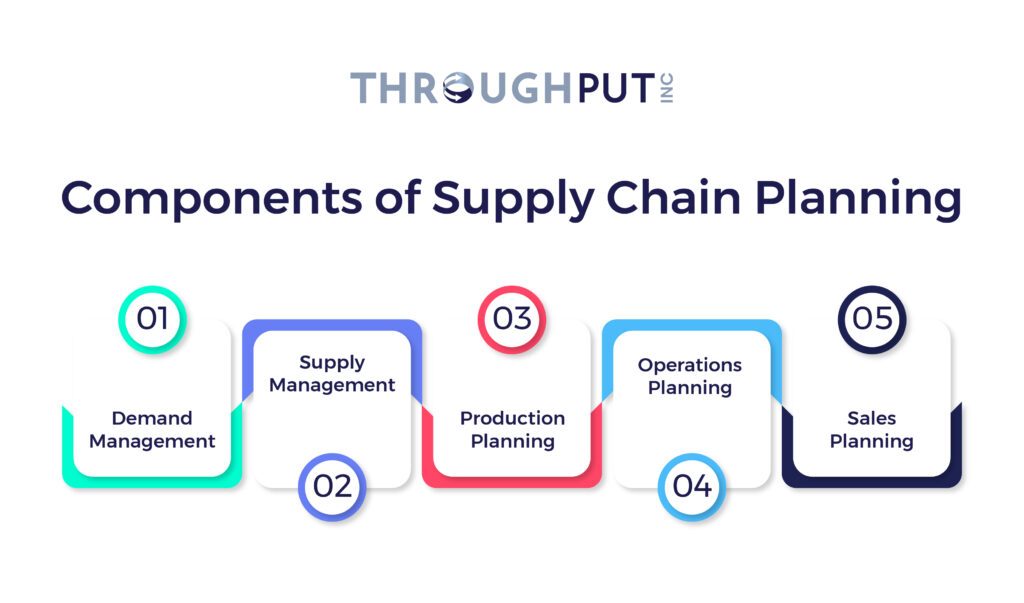
What are the Key Elements of Effective Supply Chain Planning?
The key elements of demand planning are production planning, demand and supply planning, inventory management, logistics management, supplier management, risk management, and sales and operations planning.
The planning process needs to optimize the delivery of goods, services, and information from suppliers to customers. It involves coordinating the mentioned elements of the supply chain.
Production planning aligns production capacities with customer demand to ensure optimal efficiency and customer satisfaction.
There are several important points when it comes to production planning:
To ensure that the production capacities are in sync with the forecasted customer demand, companies must analyze historical data, observe market trends, and include customer feedback to predict future demand and accurately adjust production.
When this alignment of production and customer data is in place, companies avoid issues such as stockouts or excess inventory that often lead to financial losses and dissatisfaction in the market value chain.
To optimize production planning, companies employ various strategies, such as implementing lean manufacturing principles, utilizing advanced scheduling tools, and adopting just-in-time (JIT) production techniques.
The correct strategies result in minimizing waste, reducing lead times, and improving operational efficiency.
Resource management and optimization involve effectively allocating resources such as labour, machines, and materials to ensure smooth production processes.
With the correct resource utilization, operational efficiency meets customer demand within the desired time frame. As a result, companies minimize idle time, reduce production bottlenecks, and increase productivity.
Supply Chain Management In 6 Minutes | What Is Supply Chain Management? | Simplilearn
How do I create a supply chain plan?
Here are six steps to consider when creating your supply chain plan: 1. Review company goals Reviewing your company’s revenue and production goals can help you determine inventory levels and daily production output. It also helps your company create marketing and sales strategies that can aid them in reaching revenue goals.
What is a supply chain plan?
A supply chain plan is the process of companies determining the ideal manufacturing and sales volume to achieve profit or revenue-related goals. This plan usually involves specific steps a company can take to achieve profit goals. These plans often factor supplies, production, market demand and sales into the steps.
How to create a successful Supply Chain Strategy?
In this section, we will cover the five essential steps to creating a successful supply chain strategy. From setting goals to keeping an eye on how things are going, these steps will make sure that your strategy works and is efficient. So, sit back, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into each step.
What are the basic principles of Supply Chain Planning?
Here are seven basic principles that leading supply chain planners adopt: Synchronize supply chain planning and execution, how often you update your data and planning horizons—or how far into the future your company will project.