This guide will cover everything you need to know about ultrasound technicians, the types of ultrasound technicians, and how much you can make.Â
There will always be a high demand for jobs in the medical field. Especially in the U.S., where the healthcare industry is the largest employer in the country.Â
There are many careers in the healthcare field that are in demand that dont require a person to become a nurse or a doctor. These careers also dont require many years of education compared to nursing and physician careers.
An ultrasound technician is one of those careers in the medical field with great potential. According to U.S. News, diagnostic medical sonographers are ranked #6 in best healthcare support jobs and #64 in best jobs.Â
Keep reading if youre curious about this fantastic career and want to learn more about it!
So you’re interested in becoming an ultrasound technician, but aren’t sure where to start or how long the process takes? This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the process, from education requirements to finding a job after graduation
An Overview of Ultrasound Techs
Ultrasound technicians, also known as diagnostic medical sonographers or ultrasonographers, use special imaging equipment that directs sound waves into a patient’s body to assess and diagnose various medical conditions. The reflections of these sound waves create images that allow technicians to examine a patient’s body.
Common responsibilities of ultrasound techs include:
- Preparing patients for procedures by explaining how they work and answering any questions
- Operating ultrasound equipment to obtain diagnostic images
- Identifying abnormal images and bringing them to the attention of a physician
- Recording medical history and diagnostic information
- Maintaining and calibrating diagnostic equipment
Ultrasound techs often specialize in abdominal, breast, cardiologic, obstetric, gynecologic, or ophthalmic imaging. They work in various medical settings like hospitals, doctors’ offices, and diagnostic imaging centers. The job typically involves significant patient interaction and collaboration with other healthcare professionals.
Education Requirements
To become an ultrasound technician, you’ll need a postsecondary degree or certificate in the field There are a few options
-
Associate’s degree: This is the most common educational path and takes 2 years to complete. Look for programs accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). Coursework covers areas like anatomy, physics, instrumentation, patient care, and medical ethics.
-
Bachelor’s degree: You can also obtain a 4-year bachelor’s degree in diagnostic medical sonography or radiologic sciences. This provides a more in-depth foundation and opens up leadership roles.
-
Certificate program For those with prior healthcare experience a 12-24 month certificate program may be sufficient. Common backgrounds include nursing radiologic tech, EMT, or paramedic training. Programs focus just on sonography topics.
No matter which option you choose, look for a program with plenty of hands-on clinical training. This allows you to get comfortable with ultrasound equipment and gain real-world experience. Clinical rotations often take place at hospitals, clinics, or imaging centers.
Obtaining Your Credentials
After finishing your ultrasound program, there are a few key credentials needed to start working:
-
ARDMS certification: The primary certification is through the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). You’ll need to pass a Sonography Principles and Instrumentation exam, as well as a specialty exam in abdominal, OB/GYN, or another focus area.
-
State licensure: A handful of states require ultrasound technicians to be licensed. Check your state’s requirements. In most places it isn’t mandatory.
-
Basic Life Support (BLS) certification: Most employers require BLS/CPR certification to provide emergency care to patients if needed. Many schools include this as part of the curriculum.
Holding the proper credentials is crucial for finding work as an ultrasound tech. Start the application processes for certification and licensure as you near graduation.
Finding a Job
Once you’ve completed an accredited program and obtained your credentials, you’ll be ready to start applying for ultrasound technician jobs. Here are some tips:
-
Look for openings at hospitals, medical imaging clinics, doctor’s offices, and other healthcare facilities. Larger practices and urban settings often provide the most job opportunities.
-
Highlight your hands-on clinical experience in your resume and cover letter. This sets you apart from other new graduates.
-
Be prepared to apply to multiple openings, interview, and possibly relocate for the best position. Competition can be stiff. Patience and persistence are key!
-
Joining industry groups like the Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography (SDMS) can aid your job search through networking, mentors, and access to job boards.
-
Consider completing a vascular or echo specialty program to increase marketability down the road. This can lead to higher-paying advancement opportunities.
How Long Does it Take?
Now that we’ve reviewed the steps to become an ultrasound tech, how long will it realistically take you from start to finish? Here are some estimates:
-
Earning your associate’s degree or completing a certificate program will take 2 years at minimum. Allow extra time if attending school part-time.
-
Obtaining your ARDMS certification generally takes 3-6 months after graduation to prep for exams and receive results.
-
Securing your first job could take 2-4 months once you begin applying. The job hunt time varies.
-
Therefore, the total timeline is approximately 2.5-3 years from starting your ultrasound program to landing your ideal job.
This assumes attending school full-time with some summer courses. Taking prerequisites or gaps between steps extends the process. But the investment is well worth it for this rewarding, in-demand medical career!
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Do I need a college degree to become an ultrasound tech? While no specific undergrad degree is required, you do need a postsecondary degree or certificate in diagnostic medical sonography. Most technicians hold an associate’s degree.
-
Which ultrasound specialty has the highest salary? According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, ultrasound techs specializing in vascular sonography and echocardiography tend to be the highest earners. They work with cardiac patients.
-
Is being an ultrasound tech stressful? While the job does involve being on your feet and interacting with many patients daily, ultrasound techs enjoy lower stress levels than many other healthcare occupations. It provides good work-life balance.
-
How long will my ultrasound certification last? ARDMS certifications are valid for 3 years initially, then renewed every 10 years through continuing education credits and practice requirements. State licenses also need periodic renewal.
-
Can I work part-time as an ultrasound tech? While full-time schedules are most common, part-time ultrasound tech jobs definitely exist. Large hospitals, busy clinics, or temp staffing agencies can provide part-time flexibility.
Start Your Ultrasound Technician Career Path Today
If you’re motivated to help patients through medical imaging, a career as an ultrasound technician may be ideal for you. It offers great job stability and satisfaction, without the extensive time and cost of becoming a physician.
With a focused ultrasound program taking 2 years or less, you can begin working in this growing field relatively quickly. Just be prepared to study hard, get certified, and spend time searching for that first position. Your efforts will pay off!
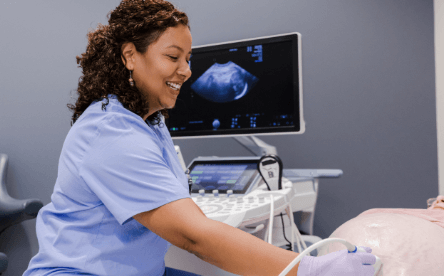
Types of Ultrasound Technicians
There are several types of ultrasound technicians, each specializing in a particular area of the body. Below are some common types of ultrasound technicians.Â
A medical sonographer aids physicians in diagnosing patients who experience symptoms that need to be internally examined. Theyâre also referred to as ultrasound technicians because they use ultrasound equipment to take medical imaging.Â
These ultrasound technicians use specialized ultrasound equipment to produce detailed s of the heart.Â
They may also use ultrasound equipment to visualize the blood vessels, including the aorta, carotid arteries, and peripheral vessels. Cardiovascular sonographers often use 2D and 3D s of the heart to examine its structure and find irregularities.Â
Abdominal sonographers take diagnostic s of organs within the abdominal cavity, including the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and kidneys.Â
They often work in hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities. Abdominal sonographers undergo extensive training in different areas of the abdomen to aid physicians in diagnosing patients medical conditions.Â
This type of ultrasound technician specializes in taking s of fetuses during pregnancy. Obstetric sonographers evaluate the growth of a fetus and track its development. They can also take s of the uterus to see if someone is pregnant and predict the patients due date.
A musculoskeletal sonographer takes s of the muscles, bones, and joints and is used to diagnose musculoskeletal disorders. They often use the s to identify medical conditions that affect the patients mobility. Musculoskeletal sonographers look for conditions such as broken bones, sprains, strains, inflammation, cysts, and hernias.
Musculoskeletal sonographers frequently work in medical facilities, hospitals, and emergency rooms because they focus on diagnosing injuries or accidents.Â
Breast sonographers use specialized ultrasound equipment to create detailed s of the breast tissue, which can help identify any abnormalities indicative of breast cancer or other breast health conditions.Â
Breast sonographers work closely with radiologists or other healthcare professionals to interpret the s and provide guidance on further testing or treatment options.
A neurosonographer is a medical professional who uses ultrasound imaging to produce detailed s of the brain and other parts of the nervous system.Â
Neuro sonographers typically work closely with neurologists and other medical professionals to diagnose and treat conditions that affect the brain and nervous systems, such as strokes, brain tumors, and aneurysms.Â
Neuro sonographers may also perform and interpret the results of other diagnostic tests, such as electromyography (EMG) and electroencephalography (EEG).
In recent reports, the average annual ultrasound technician salary in the U.S. is $88,220 a year. Below is a chart of the monthly, weekly, and hourly wages of various earners in this field.
| Annual Salary | Hourly Wage | |
|---|---|---|
| Top Earners | $146,500 | $70 |
| 75th Percentile | $127,000 | $61 |
| Average | $98,273 | $47 |
| 25th Percentile | $63,500 | $31 |
âThe job outlook for ultrasound technicians is projected to grow 10 percent from 2021 to 2031. Its estimated that there will be 10,100 job openings for ultrasound technicians each year.
If you still have any inquiries, check out these frequently asked questions and answers.Â
Consider a Specialty
Ultrasound technicians specialize in specific fields in the healthcare industry. Before pursuing a certification, you must choose a specialty. Here are some specialties you can consider.
- Vascular or cardiac
- Abdominal
- Neuro
- Breast
- ObstetricÂ
You also have the option to specialize in more than one field. You must earn your certification for the various fields you plan on practicing in.
There are three pathways you can choose to complete your ultrasound technician certification. They are the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS), Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI), and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Each of those programs has its requirements and timeline, heres more information about each of the programs.
Offers five certification courses that focus on different areas of sonography. Below are the following certificates they offer.
- Midwife Sonography Certificate
- Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer (RDMS)
- Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer (RDCS)
- Registered Vascular Technologist (RVT)
- Registered Musculoskeletal Sonographer (RMSKS)
Itâs important to note that youâll need to reapply for this certification after six years and pay a fee annually.Â
Here are the following certificates the CCI offers.
- Advanced Cardiac Sonographer (ACS)
- Certified Cardiographic Technician (CCT)
- Certified Rhythm Analysis Technician (CRAT)
- Registered Congenital Cardiac Sonographer (RCCS)
- Registered Cardiac Electrophysiology Specialist (RCES)
- Registered Cardiovascular Invasive Specialist (RCIS)
- Registered Cardiac Sonographer (RCS)
- Registered Phlebology Sonographer (RPhS)
- Registered Vascular Specialist (RVS)
To maintain certification, you must pay a fee after your first year and show proof of your continuing education every three years.Â
This pathway allows you to earn advanced certification. To maintain your certification, you must pay an annual fee and show proof of completion of the required coursework every two years.Â