In economics, the concepts of elastic and inelastic demand describe how sensitive the quantity demanded for a good or service is to changes in price. Understanding the factors that make demand more elastic or inelastic is key for both consumers and producers when making economic decisions. This comprehensive guide will explain the key distinctions between elastic and inelastic demand using clear examples and analysis.
What is Elastic Demand?
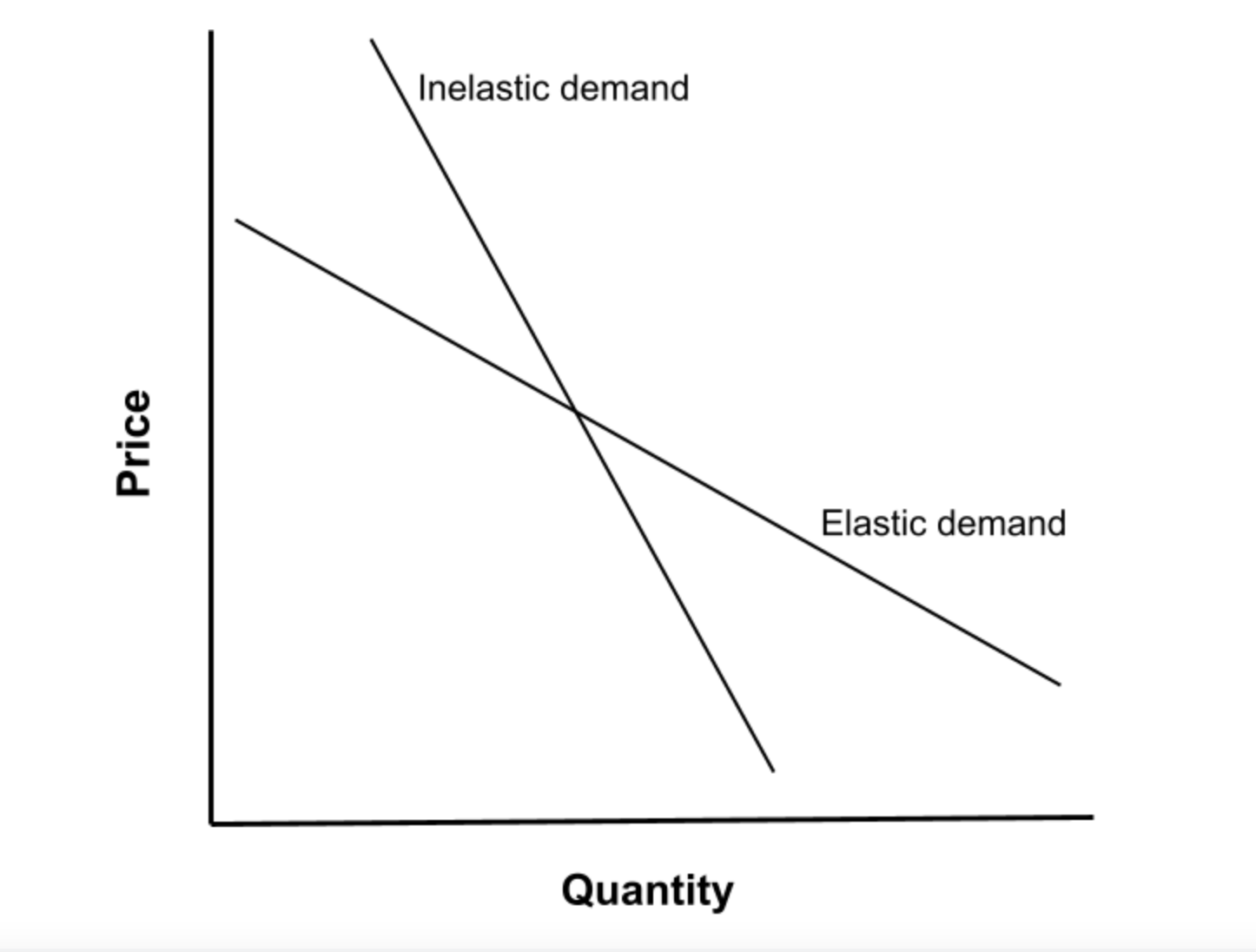
Elastic demand refers to when the quantity demanded for a good or service changes significantly in response to changes in price. Products that have elastic demand are usually more discretionary items that consumers can easily do without if the price rises. Some examples include restaurant meals new clothing, vacation travel and luxury vehicles.
The formula for calculating price elasticity of demand is:
% Change in Quantity Demanded% Change in Price
If this formula results in a number greater than 1, demand is considered elastic. For example, if a 10% price increase causes a 15% drop in quantity demanded, the elasticity would be 1.5 (15%/10%) showing relatively elastic demand.
Some key traits of elastic demand:
- Many close substitutes are available
- The product represents a small portion of the consumer’s budget
- The product is not an essential item
- Consumers can postpone or reduce purchases
- Brand loyalty is low
Since consumers are sensitive to price hikes for elastic products sellers have less power to raise prices without impacting revenues.
What is Inelastic Demand?
Inelastic demand is when the quantity demanded does not change much in response to price changes. Consumers continue buying inelastic products even with higher prices. Examples include gasoline, utilities, food staples, medications, and cigarettes.
If the formula above results in a number less than 1, demand is considered relatively inelastic. For instance, a 10% price increase causing just a 5% decrease in quantity demanded would equal 0.5 elasticity (5%/10%), indicating inelastic demand.
Some key traits of inelastic demand:
- No close substitutes are available
- The product is a necessity
- The product represents a large portion of the consumer’s budget
- Consumers cannot easily reduce their usage
- Brand loyalty is strong
Since buyers of inelastic goods are not very price sensitive, producers can often raise prices without harming demand much.
What Makes Demand More Elastic vs. Inelastic?
There are several key factors that tend to make demand more elastic or inelastic:
Availability of Substitutes
-
Elastic – Many substitutes exist like store brand vs. name brand foods. Consumers can easily switch to alternatives.
-
Inelastic – No close substitutes exist like electricity from the public utility. Consumers have few options.
Necessity vs. Luxury
-
Elastic – The product is discretionary like a vacation. Consumers can live without it.
-
Inelastic – The product is a necessity like groceries. Consumers cannot eliminate this expense.
Budget Share
-
Elastic – The product is a small part of the consumer’s budget like movie tickets. A price change has little impact.
-
Inelastic – The product represents a large part of the budget like housing. Consumers are very price sensitive.
Time Horizon
-
Elastic – Consumers can plan ahead and delay purchases if prices rise, like appliances.
-
Inelastic – Consumers cannot easily delay purchases, like emergency medical care.
Examples of Elastic vs. Inelastic Products
To better understand the differences, let’s look at some examples of goods with relatively elastic demand versus relatively inelastic demand:
Elastic Products
- Restaurant meals
- New cars
- Air travel
- Electronics
- Furniture
- Toys
If prices rise for these discretionary items, consumers will likely buy less. Many substitutes exist as well.
Inelastic Products
- Gasoline
- Electricity
- Tap water
- Bread
- Milk
- Insulin
If prices rise for necessities like these, the demand will remain relatively steady. Few close substitutes exist.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The concepts of elasticity and inelasticity have important implications for both businesses and consumers:
For businesses:
-
Elastic demand – Limited power to raise prices, or revenues may fall. Need to keep prices competitive.
-
Inelastic demand – More power to raise prices without impacting revenues much. Captive audience of buyers.
For consumers:
-
Elastic demand – More options to adjust buying if prices increase. Can reduce quantity or find substitutes.
-
Inelastic demand – Harder to make adjustments if prices rise. May have to pay higher prices for necessities.
Key Takeaways on Elastic vs. Inelastic Demand
-
Elastic demand is when the quantity demanded changes significantly with price changes. Inelastic is when the quantity demanded remains relatively constant despite price changes.
-
Products with close substitutes and discretionary purchases tend to have elastic demand. Products with few substitutes that are necessities tend to have inelastic demand.
-
Consumers have more ability to adjust their purchases for items with elastic demand. But businesses have less power to raise prices.
-
For inelastic products, consumers cannot easily adjust demand if prices rise. However, businesses often have more pricing power without impacting revenues much.
Understanding these fundamental economic principles allows both producers and consumers to make better pricing and buying decisions.
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for High School Physics
A car travelling at
collides with another
car that is at rest. The two bumpers lock and the cars move forward together. What is their final velocity?
This is an example of an inelastic collision, as the two cars stick together after colliding. We can assume momentum is conserved.
To make the equation easier, lets call the first car “1” and the second car “2.”
Using conservation of momentum and the equation for momentum, , we can set up the following equation.
Since the cars stick together, they will have the same final velocity. We know the second car starts at rest, and the velocity of the first car is given. Plug in these values and solve for the final velocity.
Example Question #4 : Understanding Elastic And Inelastic Collisions
A ball moving at
strikes a second ball at rest. After the collision the
ball is moving with a velocity of
and the second ball is moving with a velocity of
. What is the mass of the second ball?
This is an example of an elastic collision. We start with two masses and end with two masses with no loss of energy.
We can use the law of conservation of momentum to equate the initial and final terms.
Plug in the given values and solve for .
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand?
The differences between elastic and inelastic demand can be drawn clearly on the following grounds: Elastic Demand is when a small change in the price of a good, cause a greater change in the quantity demanded. Inelastic demand means a change in the price of a good, will not have a significant effect on the quantity demanded.
What are elasticity and inelastic goods?
Elastic goods include luxury items and certain food and beverages, as price changes can have an impact on demand to a great extent. Inelastic goods may include items such as tobacco and prescription drugs, as demand often remains constant despite price changes. The elasticity of demand measures how demand responds to a change in price or income.
What is the difference between perfect elastic and inelastic?
Perfectly elastic means the response to price is complete and infinite: a change in price results in the quantity falling to zero. Perfectly inelastic means that there is no change in quantity at all when price changes. If . . . It Is Called . . .
Is the price elasticity of demand perfectly inelastic?
The numerator of the formula given in Equation 5.2 for the price elasticity of demand (percentage change in quantity demanded) is zero. The price elasticity of demand in this case is therefore zero, and the demand curve is said to be perfectly inelastic.