This article has been vetted by University of Phoenixs editorial advisory committee. Read more about our editorial process.
This article has been reviewed by Kathryn Uhles, MIS, MSP, Dean, College of Business and IT
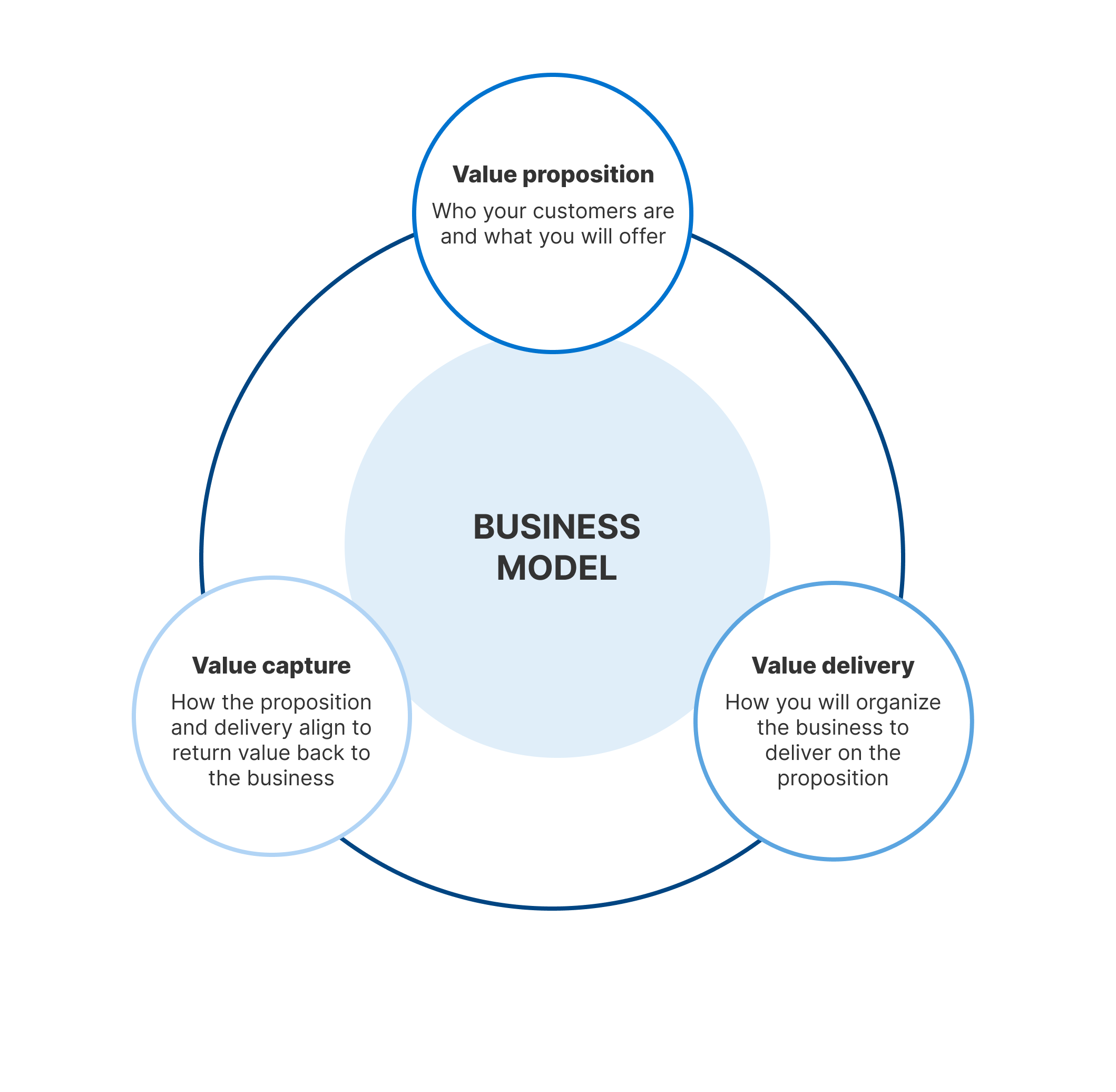
A business model is a framework for how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. The model outlines the company’s products, services, target customers, costs, revenue streams, and more. While there are many variations, most business models contain these 8 core components:
Value Proposition
The value proposition is the primary reason customers choose one product or service over another, It highlights the unique benefits and competitive advantages a company offers,
Strong value propositions solve a customer problem or satisfy a need. For example Uber’s value proposition is providing quick and convenient urban transportation through its ride-hailing app.
Companies should continually refine their value proposition as customer needs evolve Value propositions can leverage factors like price, quality, convenience, design, experience, and brand prestige.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams represent the various ways a company generates income from its value proposition. Some examples include:
- Product or service sales
- Usage or subscription fees
- Licensing or leasing
- Advertising
- Transaction fees
- Sponsorships
Diversified revenue streams provide financial stability and growth potential. Companies may utilize multiple streams like selling products and services plus subscriptions.
Cost Structure
The cost structure outlines the company’s monetary obligations to operate its business model. Costs typically include:
- Fixed costs – Expenses that remain consistent like rent, utilities, and salaries.
- Variable costs – Expenses that fluctuate with production like materials, shipping, and marketing.
Understanding the cost structure allows companies to identify opportunities to become more efficient. It also enables effective pricing strategies that cover costs while remaining competitive.
Market Segments
Market segmentation involves dividing potential customers into groups with common needs, behaviors, or other attributes. Key segmentation criteria include:
- Demographics like age, income, and education level
- Geographical factors like country, city, or climate
- Psychographics based on attitudes, values, interests
- Behaviors like purchase history, usage, or desired benefits
Companies tailor product designs, pricing, promotions, and customer service to match key segments. This targeted marketing allows businesses to attract and retain customers more effectively.
Distribution Channels
Distribution channels get a company’s products or services to its customers. Traditional channels include:
- Direct sales like door-to-door salespeople
- Physical retail stores
- Wholesalers that supply products to retailers
- Distributors that provide logistics and warehousing
Digital channels are increasingly important, such as:
- E-commerce sites and marketplaces
- Mobile apps
- Social media platforms
Utilizing the optimal distribution channels allows businesses to minimize costs while making buying efficient and accessible for customers.
Customer Relationships
This component examines how companies interact with customers through the buyer’s journey. The goal is to build lasting relationships that promote loyalty and brand advocacy.
Strategies for nurturing customer relationships include:
- Providing excellent customer service
- Developing loyalty programs
- Personalizing communications and offers
- Engaging through social media
- Creating online communities and user forums
Positive customer relationships can boost referrals, upselling, cross-selling, and brand reputation.
Key Partnerships
Partnerships with other businesses can optimize operations and reduce risks. Common types of partnerships include:
- Suppliers and vendors
- Channel partners like retailers and resellers
- Technology partners that provide services or integrate systems
- Strategic alliances between non-competitors
- Joint ventures to collaborate on major projects
Partnerships allow companies to acquire capabilities beyond their capacity and expand into new markets. This enables businesses to deliver their value proposition more efficiently.
Key Resources
Resources are the assets required to create and deliver the value proposition. Resources fall into four categories:
- Physical – Infrastructure, equipment, locations, and transportation
- Financial – Cash, credit, equity, and funding sources
- Intellectual – Patents, trademarks, copyrights, databases
- Human – Staff, leadership, skills, and knowledge
A company’s business model depends on optimally managing these resources. For example, a manufacturer will rely heavily on physical resources while a consultancy depends more on human resources.
Key Activities
This component identifies the crucial things a company must do to make its business model work. Examples include:
- Research and development
- Manufacturing or service delivery
- Platform development and maintenance
- Sales, marketing, and distribution
- Partnership management
- Supply chain coordination
By recognizing key activities, businesses can prioritize their operations, processes, and workflows to maximize value.
Aligning the Components
An effective business model harmonizes these components into a value-creating system. Product designs, target customers, distribution methods, and revenue approaches all need to fit together.
If components become misaligned, the business model can quickly become unsustainable. For example, a company may promise exceptional customer service in its value proposition but fail to train staff adequately on relationship skills.
To prevent misalignments, companies should regularly evaluate how components interact and make adjustments as needed. This helps ensure the model adapts to market changes over time.
Types of Business Models
While these 8 elements provide the core framework, there are many types of business models out there. Models differ based on various factors like target customers, value delivery, or revenue generation. Here are some of the most common models:
Product Business Model
This model focuses on selling products, whether physical goods, digital downloads, or packaged software. Companies like Apple and Microsoft exemplify product models. Pricing strategies and distribution channels are two important considerations.
Service Business Model
Service companies derive income by providing expertise, experiences, access, or other intangible offerings. Examples include accountants, restaurants, hotels, and transportation services. The key resources are typically human capital and specialized skills.
Subscription Model
This model charges customers a recurring fee, often monthly or annually, to access products/services. Netflix and gym memberships operate on subscription models. The value comes from ongoing access versus outright ownership.
Advertising Model
Companies utilizing this model generate revenue by selling advertising space on their platforms. Media sites, search engines, and social networks monetize through ads. The value stems from free content supported by relevant, targeted advertising.
Freemium Model
Freemium combines free basic services with premium paid features. Products like games, apps, and cloud software use this model. The free tier acts as a marketing tool to upsell customers to the paid version.
E-Commerce Model
E-commerce businesses sell products and services through online channels versus physical retail stores. Amazon is the dominant player, but small e-commerce businesses thrive in niche markets. The value propositions emphasize selection, convenience, and savings.
Evolving the Business Model
Markets shift rapidly, so companies must continually reassess their business models. Leaders should ask questions like:
- Is our value proposition still relevant to customers?
- Do our revenue streams and costs align with market realities?
- How are customer needs, preferences, and behaviors changing?
- Are there new partnerships or technologies we should leverage?
- What new competitors or disruptions threaten our position?
Adapting the business model for changing conditions is key to sustained growth and profitability. Remaining static can lead to declining sales, loss of competitive edge, and potential failure.
Designing a New Business Model
When developing a new business model, founders and leaders should follow these steps:
- Identify target customers and understand their needs.
- Determine a value proposition that solves those needs better than competitors.
- Define key activities and resources to deliver that value.
- Establish cost structure and revenue streams that yield profitability.
- Select market segments, customer relationships, and channels that optimize reach.
- Assess partnerships that can supplement capabilities.
- Validate assumptions through market research and testing.
- Continually refine the model based on customer feedback and market dynamics.
Avoid copying existing business models. Instead, leverage the core elements to create innovative models positioned for growth and differentiation.
Benefits of a Strong Business Model
Crafting a robust, sustainable business model delivers tangible benefits:
-
Attracts investment – A logical, scalable model gives investors confidence. Over 40% of startup pitches get rejected due to model flaws.
-
Fuels growth – Efficient models create competitive advantage and operating leverage to rapidly grow market share.
-
Boosts profitability – Optimized models maximize income while minimizing expenses and waste.
-
Withstands competition – Defensible models maintain value propositions and cost positions that rivals cannot easily replicate.
-
Adapts to change – Agile models pivot to meet shifting customer expectations, technologies, and market conditions.
-
Enhances decision-making – Models provide a clear framework for strategic choices on products, pricing, partnerships, and more.
Without a solid business model, companies lack direction and face significantly higher risks. But well-designed models map a path to sustainability and success.
Key Takeaways on Business Model Components
-
Business models outline how companies deliver value to customers and generate profits.
-
Core components include value proposition, revenue streams, cost structure
Understanding business models
Your business model is meant to serve as a comprehensive guide — one that leads your business toward success. The best business models and plans also help companies navigate their market while identifying potential risks and avoiding setbacks.
Put simply, your company’s business model outlines the ways you plan to add value or grow and maintain a business. You’ll likely include details like employees, available resources, price points, competition, customer behaviors and potential expenses in your business model — all to help you forecast how your company might perform in the future.
If you’ve completed a business degree, you can use your business experience to help inform your company’s business model. In addition, earning an MBA can give you the tools to handle investments and high-level decisions that come with deciding on or switching up your business model. However, whether you’re a business management student or an experienced executive, it’s important to consistently evaluate your company’s progress and discover new business models that could propel that growth.
Learn more about online business degree programs!
I would not be able to go back to school if it were not for the fact that I can sign in at my convenience to complete my assignments.”
Save time and money
The Explainer: What is a Business Model?
What are the components of a business model?
The various components of a business model are interconnected and influence each other. It is essential to align all elements to ensure a coherent and effective approach. A successful business model aligns with the company’s overall goals and objectives. It should support the organization’s mission, vision, and values.
How do I create a business model?
The first component of your business model is a basic description of your strategy. Your vision can be as short as a few sentences long and can ultimately be part of your company’s mission statement. When creating a vision, be sure to clearly state the industry your business is in and use positive language.
Why is it important to follow all the components of a business model?
It’s important to follow all the components of a business model because they provide you with a guide to making your company profitable while also creating value for your customers. Each component relates to a key aspect of your company’s infrastructure, operations, relationships with customers and products or services.
What is a business model example?
A business model determines what products make sense for a company to sell, how it wants to promote its products, what type of people it should try to cater to, and what revenue streams it may expect. What Is an Example of a Business Model? Best Buy, Target, and Walmart are some of the largest examples of retail companies.