Expert Reviewed Editorial Note: We earn a commission from partner links on Forbes Advisor. Commissions do not affect our editors opinions or evaluations.
Employers are facing a widespread and growing shortage of cybersecurity professionals across the globe. Though the cybersecurity workforce has grown significantly in recent years, 4 million cybersecurity professionals are still needed to fill the field’s talent gap, according to research by ISC2.
This stark demand has made cybersecurity jobs virtually immune to cutbacks, so earning a cybersecurity degree can help you launch a lucrative career with lots of job security. In a cybersecurity degree program, you’ll learn how to protect valuable data from malicious actors online.
If you’re interested in cybersecurity, keep reading to learn about the various degree types and career paths available in this field.
Cyber security has become one of the most important issues facing organizations and governments around the world. As more and more sensitive data is stored and transmitted digitally, the need to protect that data has never been greater. This is why many educational institutions now offer cyber security degrees at the undergraduate and graduate levels But what exactly is a cyber security degree? In this comprehensive guide, we will examine everything you need to know about cyber security degrees, including an overview of the field, degree levels, coursework, career paths, salaries, and more
Cyber security refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access or attacks. The main objectives of cyber security include:
- Confidentiality – Ensuring that data remains private and is accessed only by authorized users
- Integrity – Safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of data
- Availability – Ensuring that authorized users can access networks and systems when needed
Some common cyber threats include malware, phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, denial of service, and data breaches. Cyber security professionals work to assess risks, implement safeguards, monitor systems, and respond to incidents Their goal is to allow organizations to take advantage of the benefits of technology while minimizing cyber risks
Why Get a Degree in Cyber Security?
There are several compelling reasons to pursue a cyber security degree
-
High demand – Cyber security is one of the fastest growing fields. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 32% growth in information security jobs between 2020 and 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations.
-
Good salaries – The median annual wage for information security analysts was $103,590 in 2021. Cyber security managers earned even more, with a median salary of $157,580.
-
Variety of roles – A cyber security degree prepares graduates for diverse roles such as security analyst, auditor, architect, engineer, consultant, and manager.
-
Career advancement – A degree combined with certifications such as the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) credential pave the way for advancement to senior and leadership positions.
-
Intellectual challenge – Cyber security requires a mix of hard and soft skills, presenting intellectually stimulating work. Professionals must stay on top of the constantly evolving threat landscape.
-
Meaningful work – Cyber security professionals help protect critical systems and data. They play a key role in national security, public safety, and organizational success.
Degree Levels
Cyber security degrees are available at the associate, bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degree levels. Each successive level of education provides additional skills and opens up more advanced career opportunities.
Associate Degrees
An associate degree in cyber security typically takes 2 years and 60 credits to complete. Coursework covers introductions to information security, networking, operating systems, and programming. Graduates may find entry-level work as security specialists, network technicians, or IT support professionals.
Bachelor’s Degrees
A bachelor’s degree is the most common credential for cyber security professionals. Majoring in cyber security, computer science, or information technology with a security focus equips students with skills in areas like:
- Cryptography
- Access controls
- Cyber defense
- Risk management
- Digital forensics
- Secure software development
- Ethics and compliance
Bachelor’s programs usually consist of around 120 credits taken over 4 years. Graduates can qualify for roles such as security analyst, engineer, consultant, and manager.
Master’s Degrees
A master’s degree in cyber security or information assurance provides further specialization. Coursework explores topics like software security, wireless security, and cloud security in greater depth. Programs typically require 30 to 60 credits and can be completed in 1-2 years. Professionals with a master’s degree are prepared for leadership roles managing cyber security strategy and teams.
Doctoral Degrees
A doctoral degree like a PhD focuses on research and scholarship. Doctoral students conduct original research and analysis to advance the field of cyber security. They take advanced coursework in areas like cryptography, data privacy, and network security. These programs generally take over 5 years to finish. Graduates pursue cyber security research and teaching positions in academia or research centers.
Typical Courses and Concepts
Cyber security curriculums are designed to build both technical expertise and soft skills. Here are some of the most common courses and concepts covered:
Technical Concepts
- Cryptography
- Digital forensics
- Incident response
- Network security
- Operating systems security
- Secure software development
Management/Policy Concepts
- Business continuity planning
- Compliance and auditing
- Cyber security law and ethics
- Information security management
- Risk assessment and mitigation
- Security policies and procedures
Tools/Skills
- Computer programming and scripting
- Data structures and algorithms
- Databases
- Malware analysis
- Penetration testing
- Statistics
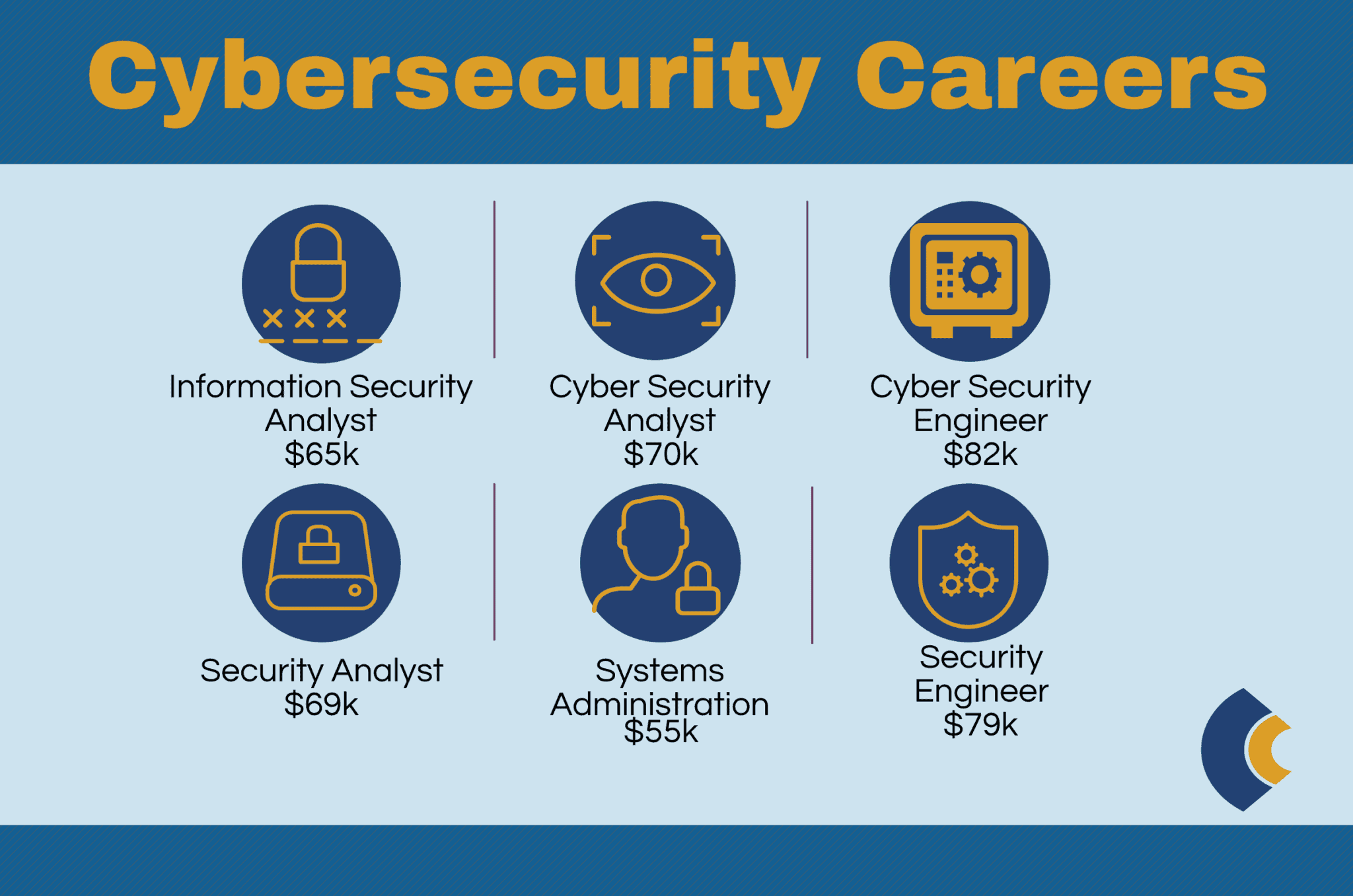
Career Paths and Job Titles
There are many different career paths open to those with cyber security degrees. Some top jobs include:
- Security Analyst – Identify vulnerabilities, recommend and implement controls
- Penetration Tester – Probe networks and systems to uncover weaknesses
- Incident Responder – Detect breaches, contain damage, and restore normal operations
- Security Engineer – Design and build secure networks, systems, and applications
- Security Architect – Develop overall security blueprints and integrations
- Security Manager – Lead teams and oversee strategy and operations
- Forensics Expert – Investigate cyber attacks through digital evidence recovery and analysis
- Security Consultant – Advise clients on assessing risks and implementing solutions
- Security Researcher – Explore new attack methods and defense techniques
Salary Information
According to PayScale, the average salary for cyber security professionals with a bachelor’s degree is $80,372 per year, while those with a master’s degree earn an average salary of $92,773. Salaries vary based on factors like location, experience, certifications, and specific job role. Some top salaries include:
- Security Analyst – $83,000
- Penetration Tester – $91,000
- Security Engineer – $106,000
- Security Architect – $130,000
- Security Manager – $141,000
The highest paid cyber security positions are Chief Information Security Officer and Vice President of Cyber Security, with average salaries of around $200,000.
Finding the Right Program
When researching cyber security degree options, keep the following criteria in mind:
- Specialized faculty and courses in cyber security
- Hands-on labs and projects
- Opportunities for internships and research
- Career counseling and job placement support
- Industry connections for networking
- Program alignment with certifications
- Accreditation
By considering these factors, you can identify cyber security degree programs that provide the knowledge, experience, and support to successfully launch your career. The high demand for cyber security professionals means that a degree in this field can lead to exciting, rewarding, and well-compensated work protecting the digital world we depend on.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cybersecurity Degrees
Yes, for many students, a cybersecurity degree is worth it. Earning a cybersecurity degree can lead to a rewarding career with a substantial salary. Moreover, most entry-level and mid-level cybersecurity positions require at least an undergraduate degree.
Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity
If you’ve already earned undergraduate training in computer science, you can narrow your area of focus by earning a specialized master’s in cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity master’s students typically take courses in cryptology, incident response and cyber threat environment. This advanced training prepares cybersecurity graduate students for positions such as penetration specialist, forensic analyst and cyber threat analyst.
Earning a master’s degree typically comprises 60 credits, which full-time learners can complete in two years. Admission usually requires a completed application, plus:
- A bachelor’s degree
- Transcripts demonstrating a minimum undergraduate GPA
- Prerequisite coursework
- A résumé or CV
- A college essay
- Letters of recommendation
A Doctor of Science, Doctor of Information Technology or Ph.D. in cybersecurity prepares candidates for high-level positions in academia or the IT field. Ph.D. students often complete coursework in applied cryptology, machine learning, cyber law and artificial intelligence alongside research components.
Depending on the institution, doctoral candidates need 50 to 70 credits to earn their degree. The process can last three to seven years. Admission requirements vary among programs but may include:
- A completed application
- A relevant bachelor’s degree
- A relevant master’s degree
- Transcripts from previous higher education
- A résumé or CV
- A personal statement
You don’t necessarily need a traditional college education to get into cybersecurity. If you’re a seasoned professional looking to switch careers, or if you’re not in a place to invest the time and money required to earn a full-time degree, you might consider a cybersecurity bootcamp instead. Bootcamps can help you launch your career in less time, at a lower cost.
Bootcamps are specialized, intensive training programs that equip learners with job-ready skills in a short timeframe. Depending on your schedule and preference, you can opt for fully online, in-person or hybrid bootcamps. Some online bootcamps even offer self-paced study options, allowing you to complete the coursework on your own time. No matter what format you choose, look for labs and other-hands on learning opportunities to practice and gain experience.
What Is Cyber Security | How It Works? | Cyber Security In 7 Minutes | Cyber Security | Simplilearn
What is a cybersecurity degree?
A cybersecurity degree is a program you can complete that helps you learn the skills necessary to begin a career in the network or information security field. As a type of computer science degree, a cybersecurity program can teach you how to protect computer systems, devices, networks and databases from digital attacks.
What courses are required for a cybersecurity bachelor’s degree?
While individual learning will vary depending on each cybersecurity bachelor’s degree program requirements, there are some universal curriculum trends. Undergraduate cybersecurity students can expect to take courses in: Computer science: Computer science theory and application is the bedrock of cybersecurity work.
How long does a cybersecurity degree take?
An associate degree in cybersecurity typically requires 60 credits and takes about two years to complete. A cybersecurity bachelor’s degree is another entry-level program, but this degree lasts four years instead of two and provides a more comprehensive foundation in cybersecurity.
What can I do with an undergraduate cybersecurity degree?
Many cybersecurity undergraduate degree programs focus on a combination of computer science with information and network security. The background and experience obtained during an undergraduate cybersecurity degree is also great preparation for the cybersecurity certification process, which is a core component of the cybersecurity field.