Computer hardware refers to all the physical parts and components that make up a computer system. From the complex motherboard to external peripherals the various hardware components work together to run software and applications. Understanding the core components that comprise a computer is helpful for anyone using or operating these devices.
In this guide, we’ll provide an overview of the basic hardware components found in a typical computer, how they function, and why they are essential to the computer’s operation.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The central processing unit, or CPU, is considered the “brains” of the computer It carries out the instructions of a computer’s programs and processes data
The CPU is housed on a chip and located on the motherboard. It contains arithmetic logic units (ALU) that perform calculations and comparisons, as well as control units that fetch instructions from memory and decode them. The CPU retrieves program instructions, processes data, and transient results are stored within the CPU’s registers.
Modern CPUs contain multiple cores, allowing them to multitask and process multiple instructions simultaneously. More advanced CPUs also have larger caches and higher clock speeds. All of these enhancements combine to increase the CPU’s overall processing power.
When examining CPUs, important specs to look for include:
-
Number of cores – More cores allow for parallel processing of multiple tasks at once. Quad-core and octa-core CPUs are common in modern computers.
-
Clock speed – Expressed in gigahertz (GHz), the clock speed determines how fast the CPU executes instructions and completes cycles. Higher is better.
-
Cache size – Cache is high speed memory located directly on the CPU to store frequently used data. More cache improves performance.
-
Architecture – The overall CPU design and number of instructions it can process per cycle impacts performance. Common architectures include x86 and ARM.
Selecting the right CPU is crucial when building or configuring a computer. The CPU significantly impacts overall system performance.
Motherboard
The motherboard is the main printed circuit board in a computer that connects crucial hardware components together. It allows communication between connected devices and the CPU.
The motherboard contains connectors for attaching additional boards and typically includes built-in ports and interfaces like USB, HDMI, and Ethernet. It contains the BIOS/UEFI chip that stores firmware and system configurations.
Key elements of a motherboard include:
-
Chipset – The chipset manages data flow between the CPU and other components, impacting overall system performance. The chipset is embedded into the motherboard.
-
RAM slots – Hold the computer’s memory modules, with each slot supporting a specific generation and capacity of RAM.
-
Expansion slots – Allow you to install additional cards like video, audio, network adapters, etc. Common types are PCI and PCI Express.
-
Form factor – The size and shape of the motherboard impacts which type of case it fits into. ATX is the most common motherboard form factor.
When selecting a motherboard, you need one compatible with your chosen CPU and ensuring it has the necessary ports and connectors for your use case. The right motherboard ties everything together.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, or random access memory, stores data and instructions for the CPU to fetch while executing a program. It provides high-speed, temporary data storage and access during computation.
Information in RAM is volatile, meaning it is lost when the computer is powered off. The operating system, software applications, and data files being actively used are loaded from disk into RAM while the computer is on for optimized access.
Important RAM specs:
-
Memory speed – Faster RAM improves performance so look for DDR4 RAM with speeds of at least 3000 MHz.
-
Capacity – More RAM allows you to run more programs simultaneously. 8GB or 16GB is typical for most users.
-
Number of modules – Motherboards have multiple RAM slots. Use matching modules in each slot for best performance.
Having sufficient RAM capacity and speed ensures responsive system performance, especially when multitasking. Upgrading RAM provides an easy boost.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The graphics processing unit or GPU produces the images and visuals displayed on the computer screen. It offloads graphics rendering from the CPU to enable high-quality visuals when gaming or editing video and images.
Dedicated GPUs contain hundreds of cores optimized for graphical computations like 3D rendering. The GPU has its own dedicated video memory, with more VRAM enabling higher resolutions and graphics settings.
Key aspects of a GPU include:
-
Core count – More cores improve parallel processing of graphical operations. Gaming GPUs may have thousands of cores.
-
Clock speed – Faster GPU clock speeds measured in MHz can positively impact framerates.
-
Memory capacity – More VRAM lets you run games at higher settings. 4GB to 8GB is typical for most gaming needs.
-
Outputs – GPUs have outputs like HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI for connecting monitors at various resolutions.
-
Architecture – Nvidia and AMD have proprietary GPU architectures like CUDA, Stream, and RDNA.
The GPU is essential if you’ll be gaming, video editing, 3D modeling, or performing graphically intensive work. Pick a GPU suited for your needs.
Storage Drives
Computer storage drives hold your operating system, software applications, and data. There are two main types of storage drives:
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
- Use magnetic platters to store data.
- Less expensive per gigabyte compared to SSDs.
- Moving parts lead to slower read/write speeds.
- More prone to damage from drops or vibration.
- Common capacities range from 500GB to 6TB.
Solid State Drives (SSDs)
- Use flash memory with no moving parts.
- Much faster read and write speeds than HDDs.
- More expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs.
- Resistant to physical damage.
- Common capacities range from 128GB to 4TB.
For optimal performance, today’s computers use both – smaller SSDs to run the operating system and programs, and larger HDDs for mass data storage.
When selecting storage drives, consider the capacity needed, performance, form factor, and your budget. Pay attention to sequential read/write speeds and IOPS for the best experience. Faster drives load programs and transfer files quicker.
Power Supply
The power supply unit (PSU) provides the electricity and power needed to operate the PC components. It converts outlet AC voltage to the DC voltage used by PC components.
Key factors for power supplies:
-
Wattage – The PSU needs sufficient wattage for all components. 500W to 800W is typical for most desktops. Allow 100-300W extra as a buffer.
-
Efficiency rating – Look for 80+ Bronze or higher PSUs. Higher efficiency ratings waste less electricity as heat.
-
Modularity – Modular PSUs allow you to only connect the cables your build needs, aiding cable management.
-
Size – Ensure the PSU size matches your PC case, commonly ATX or SFX.
Selecting the proper power supply ensures stable power delivery. Buy from reputable brands and do not skimp on your PSU.
Computer Case
The computer case, also referred to as the tower or chassis, houses all the PC components in a metal enclosure. It includes drive bays to mount storage drives and external ports for connecting devices.
Factors to consider when selecting a PC case:
-
Form factor – The case must match the motherboard size, usually ATX or Micro ATX.
-
Drive bays – Cases with more bays support installing more storage drives if needed.
-
Expansion slots – Need enough rear slots to install add-on cards and GPUs.
-
Cooling – Look for ventilated cases with internal fan mounts to enable airflow.
-
Radiator support – Required if liquid cooling the CPU or GPU.
-
Power supply size – Make sure the case accommodates standard ATX or SFX PSU sizes.
The right case makes building and upgrading your rig easier. Consider size, cooling, cable management, aesthetics, and ease of access when selecting a case.
Input Devices
Input devices allow users to enter data and control applications on the computer. Common input devices include:
-
Keyboard – The most common input device, keyboards use mechanical switches or membranes under the keys to register input. Gaming keyboards feature special keys and ergonomic designs.
-
Mouse – Mice track movement via mechanical rollers or optical sensors to control the cursor. Gaming mice have high DPI sensors and extra buttons.
-
Trackpad – Found on laptops, trackpads use touch-sensitive surfaces users can swipe to move the cursor.
-
Touchscreen – Touchscreen monitors and tablets allow direct on-screen interaction through touch.
-
Microphone – Used to capture audio input and speech.
-
Webcam – Records video input from users for streaming, video ch
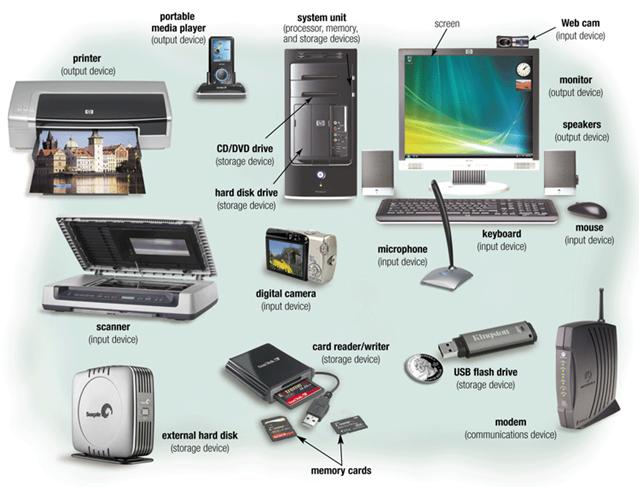
What are external hardware components?
External hardware components, also called peripheral components, are those items that are often externally connected to the computer to control either input or output functions. These hardware devices are designed to either provide instructions to the software (input) or render results from its execution (output).
Common input hardware components include the following:
- Mouse. A mouse is a hand-held pointing device that moves a cursor around a computer screen and enables interaction with objects on the screen. It may be wired or wireless.
- Keyboard. A keyboard is an input device featuring a standard QWERTY keyset that enables users to input text, numbers or special characters.
- Microphone. A microphone is a device that translates sound waves into electrical signals and supports computer-based audio communications.
- Camera. A camera captures visual s and streams them to the computer or through a computer to a network device.
- Touchpad. A touchpad is an input device, external or built into a laptop, used to control the pointer on a display screen. It is typically an alternative to an external mouse.
- USB flash drive. A USB flash drive is an external, removable storage device that uses flash memory and interfaces with a computer through a USB port.
- Memory card. A memory card is a type of portable external storage media, such as a CompactFlash card, used to store media or data files.
Other input hardware components include joysticks, styluses and scanners.
Examples of output hardware components include the following:
- Monitor. A monitor is an output device similar to a TV screen that displays information, documents or s generated by the computing device.
- Printer. Printers render electronic data from a computer into printed material.
- Speaker. A speaker is an external audio output device that connects to a computer to generate a sound output.
- Headphones, earphones, earbuds. Similar to speakers, these devices provide audio output thats audible only to a single listener.
Hardware refers to the computers tangible components or delivery systems that store and run the written instructions provided by the software. The software is the intangible part of the device that lets the user interact with the hardware and command it to perform specific tasks. Computer software includes the following:
- OS and related utilities;
- programs that control certain computer functions; and
- applications that usually perform operations on user-supplied data.
On mobile devices and laptop computers, virtual keyboards are also considered software because theyre not physical.
Since the software and hardware depend on each other to enable a computer to produce useful output, the software must be designed to work properly with the hardware.
The presence of malicious software, or malware, such as viruses, Trojan horses, spyware and worms, can have a huge effect on computer programs and a systems OS. Hardware is not affected by malware, though.
However, malware can affect the system in other ways. For example, it can consume a large portion of the computers memory or even replicate itself to fill the devices hard drive. This slows down the computer and may also prevent legitimate programs from running. Malware can also prevent users from accessing the files in the computers hardware storage.
While malware tends to directly affect software only, it can still have a profound impact on how a system and its components run.
What are internal computer hardware components?
Internal components collectively process or store the instructions delivered by the program or operating system (OS). These include the following:
- Motherboard. This is a printed circuit board that holds the central processing unit (CPU) and other essential internal hardware and functions as the central hub that all other hardware components run through.
- CPU. The CPU is the brain of the computer that processes and executes digital instructions from various programs; its clock speed determines the computers performance and efficiency in processing data.
- RAM. RAM — or dynamic RAM — is temporary memory storage that makes information immediately accessible to programs; RAM is volatile memory, so stored data is cleared when the computer powers off.
- Hard drive. Hard disk drives are physical storage devices that store both permanent and temporary data in different formats, including programs, OSes, device files, photos, etc.
- Solid-state drive (SSD). SSDs are solid-state storage devices based on NAND flash memory technology; SSDs are non-volatile, so they can safely store data even when the computer is powered down.
- Optical drive. Optical drives typically reside in an on-device drive bay; they enable the computer to read and interact with nonmagnetic external media, such as compact disc read-only memory or digital video discs.
- Heat sink. This is a passive piece of hardware that draws heat away from components to regulate/reduce their temperature to help ensure they continue to function properly. Typically, a heat sink is installed directly atop the CPU, which produces the most heat among internal components.
- Graphics processing unit. This chip-based device processes graphical data and often functions as an extension to the main CPU.
- Network interface card (NIC). A NIC is a circuit board or chip that enables the computer to connect to a network; also known as a network adapter or local area network adapter, it typically supports connection to an Ethernet network.
Other computing components, such as USB ports, power supplies, transistors and chips, are also types of internal hardware.
This computer hardware chart below illustrates what typical internal computer hardware components look like.
Click to expand and view a list of internal hardware components.
What Is Computer Hardware ? | Beginners Guide To Computer Hardware.
What are the basic components of computer hardware?
There are several basic components of computer hardware including: 1. Central processing unit (CPU) The CPU controls the computer processes and communicates with the other components of a personal computer. A computer’s CPU may be one of the most complicated parts of the computer because of its intricacies.
What is computer hardware?
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer. It refers to the computer system, especially those that form part of the central processing unit. Computer technicians should know the basic components of computer hardware and how to work with each part, including the motherboard, power supply, keyboard, mouse and monitor.
What are the parts of a computer?
Computer hardware comprises the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices such as a monitor, mouse, keyboard, and speakers.
What are the internal components of a computer?
Some important hardware devices known as the internal components are discussed below: 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) The CPU is also known as the heart of the computer. It consists of three units, generally known as the control unit, Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU), and the memory unit.