Every virtual private network (VPN) uses protocols that impact its speed, stability, and security. VPN protocols help you to reach the desired result from your VPN connection, be it a faster VPN speed or tougher encryption. Let’s review the most popular VPN protocols and the types of VPNs so you can choose a combination that best fits your needs.
Virtual private networks (VPNs) have become an essential tool for protecting privacy and securing connections to the internet At the core of any VPN service is the protocol it uses to tunnel traffic and encrypt data There are a variety of protocols, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the key VPN protocols enables selecting the right one for specific use cases.
Below we compare the pros, cons and typical use cases of the most common VPN protocols – WireGuard, OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPSec and L2TP/IPSec.
WireGuard
WireGuard is a new open source VPN protocol that has gained widespread popularity in the last few years Some key highlights
Pros
- Extremely simple and lean implementation, yet secure.
- Much faster speeds than older VPN protocols.
- Uses state-of-the-art cryptography like Curve25519 for key exchange.
- Easy to set up and manage.
- Effective firewall blocking unwanted traffic.
- Available for all major platforms.
Cons
- Still relatively new with limited evaluation so far.
- Implemented by fewer VPN services as yet.
- Limited configuration options compared to OpenVPN.
Use Cases
WireGuard is great for
- Getting extremely fast VPN speeds.
- Clients that need lightweight, simple VPN access.
- General purpose VPN use for both desktops and mobiles.
Its new design provides secure connections while being much faster than alternatives. This makes WireGuard suitable for VPN use cases requiring top speeds.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is currently the most widely used VPN protocol.
Pros
- Extremely secure design and strong encryption.
- Extensively audited and evaluated over the years.
- Highly configurable with abundant options.
- Available for all platforms.
- Open source for community review.
- Customizable with plugins.
Cons
- Slower speeds than WireGuard.
- Complex configuration with steeper learning curve.
Use Cases
The robustness and configurability of OpenVPN make it ideal for:
- Business or enterprise VPN use.
- Connecting across restrictive networks.
- Use cases demanding highly customized setups.
- Maximizing VPN security above all else.
OpenVPN is the gold standard for VPN protocol security and customization.
IKEv2/IPSec
IKEv2/IPSec is a secure VPN protocol widely supported natively on mobile devices.
Pros
- Native integration with iOS, Android, Windows, MacOS and more.
- Seamless switching between WiFi and mobile networks.
- Fast speeds on mobile networks.
- Strong security with encryption.
Cons
- Complex protocols harder to manually configure.
- Must support IKEv2 and IPSec.
Use Cases
IKEv2 excels in:
- Native mobile VPN clients on phones and tablets.
- Frequent switching between WiFi hotspots and mobile data.
- VPN use while traveling when roaming between networks.
It’s the standard VPN protocol for mobile use cases.
L2TP/IPSec
L2TP/IPSec builds on PPTP to create a more secure VPN protocol.
Pros
- Better security, privacy and reliability versus dated PPTP.
- Supported by all major platforms.
- No configuration required on some client platforms.
- Faster than OpenVPN.
Cons
- Less secure than OpenVPN or IKEv2.
- No encryption by default unless using IPSec.
Use Cases
L2TP is good for:
- Simple VPN setup without advanced configurations.
- Clients with native L2TP support like Windows, MacOS, iOS and Android.
- Transition from older PPTP based VPN access.
It provides a better alternative to PPTP with wider support and improved security.
Key Factors When Selecting a VPN Protocol
With an understanding of the popular VPN protocols, the right one can be selected based on key factors:
-
Speed – WireGuard provides the fastest speeds.
-
Security – OpenVPN offers best-in-class VPN encryption and security.
-
Mobile use – IKEv2 excels for mobile devices with native support.
-
Simplicity – L2TP/IPSec allows simple setup on some clients.
-
Customization – OpenVPN enables extensive configuration options.
-
New systems – WireGuard is ideal for modern network deployments.
-
Legacy support – L2TP/IPSec supports older clients.
The “best” protocol depends on the specific needs and priorities for accessing the VPN.
Key Considerations for VPN Protocols
Beyond the protocol, additional factors impact VPN effectiveness:
-
The overall VPN service’s security, logging policies and reliability.
-
Server availability and speeds in required geographic locations.
-
VPN client software capabilities, OS support and configuration options.
-
Local network restrictions that may block protocols or require specific ones.
The VPN protocol is just one piece – albeit an important one – that determines overall VPN quality.
Understanding VPN protocols enables selecting the ideal one for a particular use case:
-
WireGuard – Fast, simple and secure general purpose VPN.
-
OpenVPN – Heavy duty VPN security and customization.
-
IKEv2 – Native VPN for mobile devices.
-
L2TP – Basic VPN with wide legacy client support.
Rather than a single “best” protocol, different ones excel in certain deployment scenarios. By matching use case needs with the right protocol, users can maximize VPN security, performance and reliability.
Summary of VPN Protocol Pros and Cons
| Protocol | Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| WireGuard | Extremely fast speeds<br>Very simple to configure<br>Cutting-edge cryptography | Less evaluation so far<br>Fewer implementations currently | General purpose VPN<br>Fast performance needed |
| OpenVPN | Best-in-class security<br>Highly audited and customizable | Slower speeds<br>Complex to configure fully | High security applications<br>Enterprise use |
| IKEv2/IPSec | Native integration with mobile<br>Seamless switching between networks | Complex protocols<br>Both IKEv2 and IPSec required | Mobile VPN on phones/tablets<br>Frequent network switching |
| L2TP/IPSec | More secure than PPTP<br>Simple setup on some clients | Slower than WireGuard<br>Less secure than OpenVPN | Transition from older PPTP VPNs<br>Basic VPN needs |
The variety of VPN protocols means there’s one suited for every use case – you just need to select the right solution for your needs.
6 common VPN protocols
Though there’s a variety of VPN protocols in the market, we’ll review the six most popular ones widely used within the VPN industry.
OpenVPN is a very popular and highly secure protocol many VPN providers use. It runs on either the TCP (transmission control protocol) or UDP (user datagram protocol) internet protocol. The former guarantees that your data is delivered in full and in the right order, while the latter focuses on faster speeds. Many VPNs, including NordVPN, will let you choose between the two.
Pros
- Open source, meaning it’s transparent. Anyone can check the code for hidden backdoors or vulnerabilities that might compromise your VPN’s security.
- Versatility. It can be used with an array of different encryption and traffic protocols, configured for different uses, or be as secure or light as you need it to be.
- Security. Since OpenVPN is an open source protocol, it’s compatible with additional features that can enhance the protocol’s security.
- Bypasses most firewalls. Firewall compatibility isn’t an issue when using NordVPN, but it can be if you ever set up your own VPN. Fortunately, with OpenVPN, you’ll be able to bypass your firewall easily.
Cons
- Complex setup. Its versatility means that most users may be paralyzed by choice and complexity if they try to set up their own OpenVPN server.
When to use it. OpenVPN is a good choice when you need comprehensive security and stable connections, especially when browsing on unsecure public Wi-Fi.
IKEv2/IPsec establishes an authenticated and encrypted connection. Microsoft and Cisco developed it to be fast, stable, and secure. As part of the IPsec internet security toolbox, IKEv2 uses other IPsec tools to provide comprehensive VPN coverage.
Pros
- Stability. IKEv2/IPsec uses a tool called the Mobility and Multi-homing Protocol, which supports a VPN connection as you move between internet connections. This makes IKEv2/IPsec a dependable and stable protocol for mobile devices.
- Security. As part of the IPsec suite, IKEv2/IPsec works in combination with other secure algorithms, making it a secure VPN protocol.
- Speed. It takes up little bandwidth when active, and its network address translation (NAT) traversal makes it connect and communicate faster. It also helps to get through firewalls.
Cons
- Complex Configuration. Setting up IKEv2/IPsec is more complex compared to other protocols. Its configuration requires good knowledge of networking concepts and might be too complicated for a beginner VPN user.
When to use it. With IKEv2/IPsec, you won’t lose your VPN connection when switching from Wi-Fi to mobile data, so it is a good choice when you’re on the move. It also quickly bypasses firewalls and can offer high speeds online.
WireGuard is the newest and fastest tunneling protocol the entire VPN industry is talking about. It uses state-of-the-art cryptography that outshines the current leaders – OpenVPN and IKEv2/IPsec. However, it’s still considered experimental, so VPN providers need to look for new solutions (like NordLynx by NordVPN) to overcome WireGuard’s shortcomings.
Pros
- Free and open source. Anyone can look into its code, which makes it easier to deploy, audit, and debug.
- Modern and extremely fast. It consists of only 4,000 lines of code, making it “the leanest” protocol of them all. In comparison, OpenVPN code approximately has 100 times more lines.
Cons
- Room for improvement. WireGuard seems to be the “next big thing,” but its implementation is still in its growing stages with some room for improvement.
When to use it. Use WireGuard whenever speed is a priority: Streaming, online gaming, or downloading large files.
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a fairly secure and capable VPN protocol created by Microsoft. It has its upsides and downsides, meaning that each user has to decide for themselves whether this protocol is worth using. Despite being primarily a Microsoft product, SSTP is available on other systems besides Windows.
Pros
- Secure. Similarly to other leading VPN protocols, SSTP supports the AES-256 encryption protocol.
- Bypasses firewalls. SSTP can get through most firewalls without interrupting your communications.
Cons
- Owned by Microsoft, meaning that the code isn’t available to security researchers for testing. Microsoft has been known to cooperate with the NSA and other law-enforcement agencies, so some suspect that the system may have backdoors. Many VPN providers avoid this protocol.
When to use it. SSTP is generally good for enhancing privacy while browsing the internet.
Layer 2 tunneling protocol (L2TP) doesn’t actually provide any encryption or authentication – it’s simply a VPN tunneling protocol that creates a connection between you and a VPN server. It relies on other tools in the IPsec suite to encrypt your traffic and keep it private and secure. This protocol has a few convenient features, but certain issues prevent it from being a leading VPN protocol. (L2TP is not among supported NordVPN protocols.)
Pros
- Security. Ironically, L2TP not offering any security at all makes it fairly secure. That’s because it can accept a number of different encryption protocols, making the protocol as secure or lightweight as you need it to be.
- Widely available. L2TP is available on almost all modern consumer systems, meaning admins will have no trouble finding support and get it running.
Cons
- Slow. The protocol encapsulates data twice, which can be useful for some applications but makes it slower compared to other protocols that only encapsulate your data once.
- Has difficulties with firewalls. Unlike other VPN protocols, L2TP has no clever ways to get through firewalls. Surveillance-oriented system administrators use firewalls to block VPNs, and people who configure L2TP themselves are an easy target.
When to use it. It’s beneficial to use L2TP when you want to connect several company branches into one network.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) was created in 1999 and was the first widely available VPN protocol designed to tunnel dial-up traffic. It uses some of the weakest encryption ciphers of any VPN protocol on this list and has plenty of security vulnerabilities. (PPTP is not a supported NordVPN protocol.)
Pros
- Fast. It doesn’t require a lot of resources to be run, so modern machines operate PPTP very efficiently. It’s fast but offers minimal security.
- Highly compatible. In the years since it was made, PPTP has become the bare minimum standard for tunneling and encryption. Almost every modern system and device supports it, which makes it easy to set up and use.
Cons
- Insecure. Numerous vulnerabilities and exploits have been identified for PPTP. Some, though not all, have been patched, but even Microsoft has encouraged users to switch to L2TP or SSTP.
- Cracked by the NSA. The NSA is said to decrypt this protocol as a matter of course regularly.
- Blocked by firewalls. As an old, outdated, bare-bones protocol, PPTP connections are easier to block via a firewall. If you’re using the protocol at a school or business that blocks VPN connections, this can disrupt your service.
When to use it. Since PPTP is an old protocol, it’s considered not secure and is better to be avoided.
| VPN protocol | Speed | Encryption | Streaming | Stability | P2P | Available in NordVPN app |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Fast | Very good | Good | Good | Good | |
| IPsec/IKEv2 | Fast | Very good | Good | Very good | Good | |
| Wireguard* | Very fast | Very good | Good | Very good | Good | |
| SSTP | Medium | Good | Medium | Medium | Good | |
| L2TP/IPsec | Medium | Medium | Poor | Good | Poor | |
| PPTP | Fast | Poor | Poor | Good | Poor |
* Our NordLynx protocol is built around WireGuard and you can find it on the NordVPN app.
What is a VPN protocol?
A VPN protocol is a ruleset determining how data is encrypted and online traffic moves between a device and a VPN server. VPN providers use these protocols to deliver stable and secure connections for their users. Typically, each protocol focuses on a specific combination of features, for instance, compatibility and high speed or robust encryption and network stability.
However, no VPN protocol is perfect. Each may have potential vulnerabilities, documented or yet to be discovered, that may compromise your online security. Let’s look into each protocol’s pros and cons.
VPN Protocols Explained – PPTP vs L2TP vs SSTP vs OpenVPN
What makes a good VPN?
The right combination of VPN protocols is at the heart of any good VPN. Norton Secure VPN lets you choose between VPN protocols like WireGuard, OpenVPN, Mimic (Norton’s proprietary VPN protocol), or an automatic option to help give you the VPN experience you want.
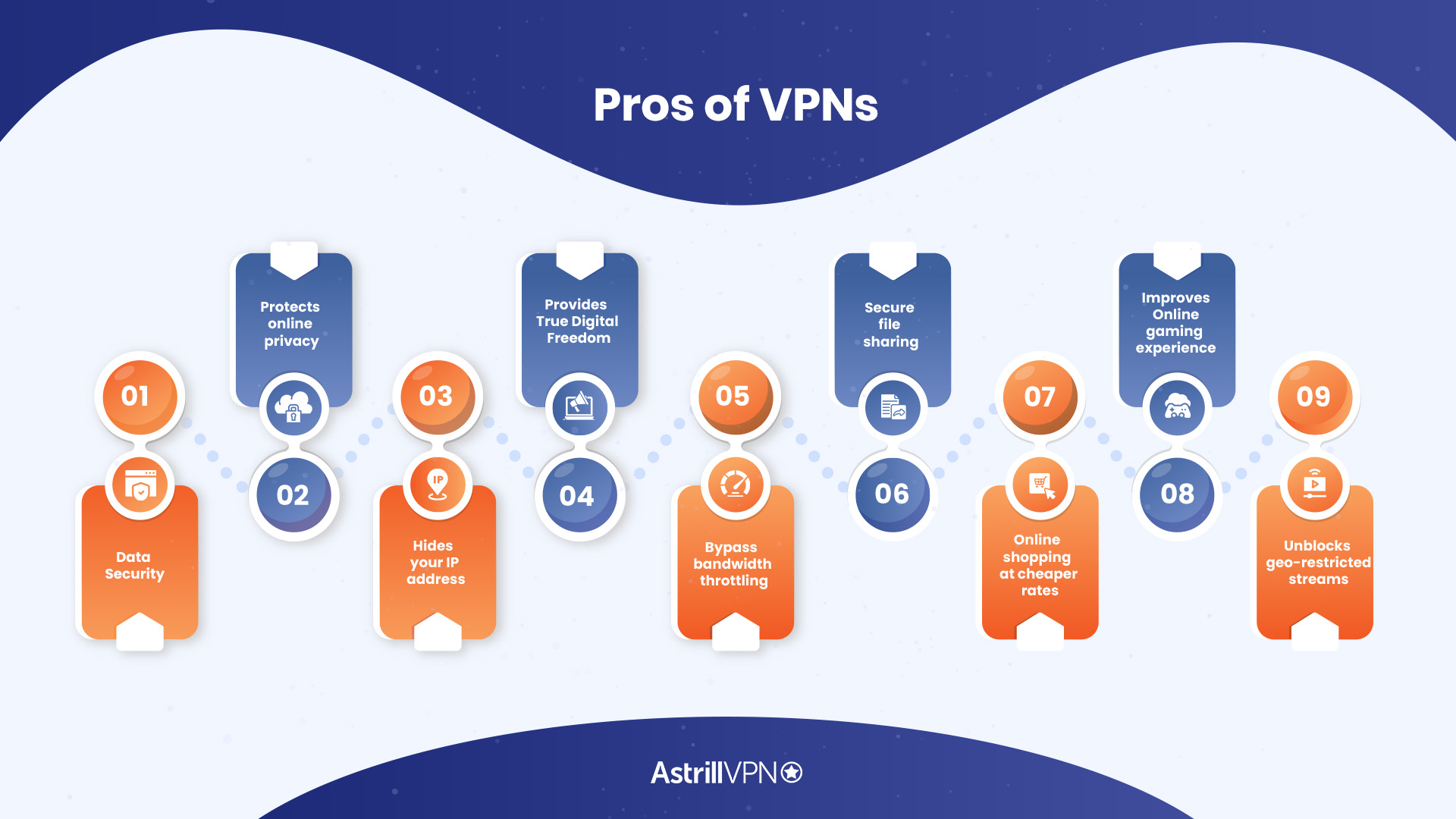
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a VPN?
Although certain VPNs may have their drawbacks, it is evident that the advantages outweigh the disadvantages. By utilizing a VPN, not only can you enjoy unrestricted access to desired content at your convenience, but you can also have the peace of mind that your private information remains truly confidential.
What are the performance and security characteristics of a VPN protocol?
The performance and security characteristics of a VPN protocol may vary depending on the VPN provider and its custom configuration. There are six major VPN protocols used in VPN applications today: OpenVPN is widely regarded as one of the most secure and versatile VPN protocols, with robust encryption and authentication methods.
How does a VPN protect your data?
Standard tunneling protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec and IKEv2, which can shield your data from potential threats. Other than encryption, VPNs have protocols to ensure data integrity. If data routed across the server is tampered with, the VPN connection can detect and prevent the altered data from being accepted.