Creating more value for customers is a core business strategy. With more technologies being developed, companies have been optimizing their technology delivery to get the best value out of their products or services.
Instead of focusing on individual functions, companies are now developing interest in the end-to-end value chain.
Software has become so ingrained in our society that company leaders and management have taken an active role in making sure the process is both driving value for the business and keeping it profitable. In a way, every organization has become a software company.
Unfortunately, businesses have found that even after investing considerable time and resources in transforming their technology capabilities, they struggle to achieve these goals.
While methodologies such as Agile and DevOps may have been implemented, there is often still a disconnect between software delivery and the overall business value.
How can we make introducing change more successful? The answer may be identifying and managing value streams.
The value stream is the series of steps taken from the concept to delivery of the product or service to a customer. For example, if we want to provide a refreshing drink we might source the ingredients, a glass, make the drink, deliver it to the customer, and receive payment. The steps in the value stream are:
By this definition, if we stop at step 2 our value stream is incomplete. We need to complete production and delivery of the product to complete the value stream.
As this states, you need to optimize more than just the software delivery process. You need to understand how end-to-end flow creates value for your customers. Businesses that can identify their value streams will be able to focus on strengthening value-added activities and minimizing nonessential ones. The practices of value stream mapping and value stream management can help with this. To create an even more holistic view we can further enhance our understanding using other Flow Engineering practices, such as outcome, dependency, and capability mapping. Flow Engineering addresses how to improve flow over the next 3-6 months, and value stream mapping is a core practice.
Both value stream mapping and value stream management stem from lean philosophies aimed at increasing operational efficiency while reducing risk and waste. They maximize customer value by helping companies see and improve their value stream thereby optimizing flow. Focusing on taking a customer-centric approach will generate higher returns for the company.
The question now is: what are value stream mapping and value stream management? Both have the acronym VSM, are they the same thing? If not, how do we differentiate one from the other?
Value stream management and value stream mapping are two important concepts and tools used in lean management approaches to improve efficiency and eliminate waste. While they sound quite similar and are related, there are some key differences between value stream management and mapping.
What is Value Stream Management?
Value stream management is the process of continuously monitoring measuring and improving the end-to-end flow of value through an organization or process. The goal is to optimize the value stream to maximize customer value while eliminating waste.
Value stream management involves:
-
Mapping out the current value stream through the organization
-
Identifying constraints, bottlenecks and waste
-
Developing metrics to monitor the value stream
-
Using data to continuously improve the value stream
-
Aligning processes to optimize value flow
Value stream management provides a data-driven way to improve the flow of value from idea all the way through to customer delivery. It focuses on making value flow fast, smooth and free of constraints.
What is Value Stream Mapping?
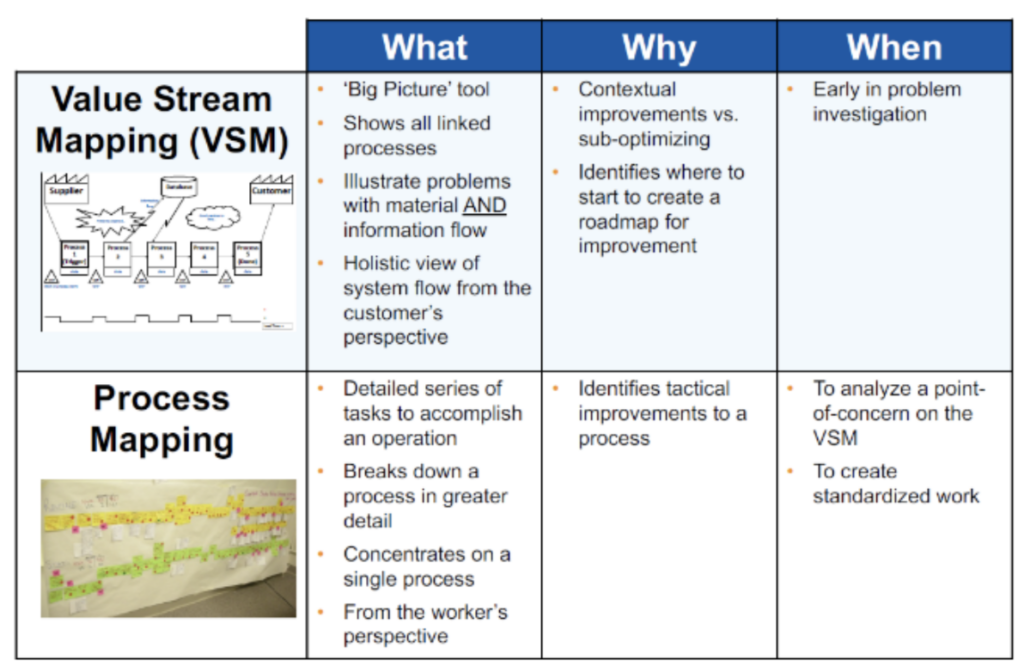
Value stream mapping is a lean tool used to document, visualize and analyze the current state of the value stream through an organization or process. It is often the first step in value stream management.
The key elements of value stream mapping include:
-
Mapping out all process steps from beginning to end
-
Identifying value-added vs. non value-added activities
-
Pinpointing waste and inefficiencies
-
Analyzing process flow and cycle times
-
Developing a future state vision for improvement
Value stream mapping provides a bird’s eye view of the current value stream and highlights areas for improvement. It is a foundational tool used before optimizing the stream.
The Relationship Between VSM and VMM
Value stream management and value stream mapping are complementary concepts that work together:
-
Value stream mapping comes first to understand and document the current state value stream.
-
Value stream management then uses data to continuously monitor and improve the stream.
Value stream mapping provides the visualization and analysis. Value stream management provides the metrics and governance to drive improvement.
You can think of value stream mapping as a one-time project to map things out. Value stream management is an ongoing practice and mindset for continuous optimization.
The following image shows how they fit together:
![vsm-vmm][]
Key Differences Between Value Stream Mapping and Management
While value stream mapping and management are complementary, there are some important differences:
Scope
- Mapping – Focuses on current state visualization and analysis of the value stream.
- Management – Ongoing practice for optimizing the entire lifecycle of value delivery.
Approach
- Mapping – Manual process of documenting and analyzing each step in the value stream.
- Management – Data-driven approach using metrics to monitor and improve the stream.
Output
- Mapping – Current state map, future state vision, improvement plan.
- Management – Dashboards, metrics, governance processes for continuous improvement.
Mindset
- Mapping – Project focused on fixed analysis and recommendations.
- Management – Way of thinking focused on constant improvement and optimization.
Similarities Between Value Stream Mapping and Management
While having differences, value stream mapping and management also share some key similarities:
- Customer-focused – Centered on improving customer value by removing waste.
- End-to-end view – Looks at the full value stream from start to finish.
- Lean principles – Based on lean concepts like eliminating waste and optimizing flow.
- Data-driven decisions – Leverages data to drive improvement.
- Cross-functional – Requires involvement across departments.
- Continuous improvement – Not one time initiatives but ongoing processes.
Deciding Which Approach to Use
How do you know whether to focus on value stream mapping, management or both? Here are some guidelines:
When value stream mapping is most helpful:
- Getting an initial high-level view of current processes
- Identifying obvious areas of waste or bottlenecks
- Bringing teams together to visualize the end-to-end flow
- When starting a lean or process improvement initiative
When value stream management is most helpful:
- When you already have a baseline map and analysis
- To continually monitor and improve the stream long term
- To track performance and progress through metrics
- To break down silos and align on optimizing flow
When to use both together:
- When starting a new improvement program – map then manage
- Periodically remapping the current state while still managing
- Any major process change – remap then realign management
Value Stream Management Best Practices
Here are some tips for effectively implementing value stream management:
- Take an enterprise view – Look at value flow across your entire organization not just IT or individual departments.
- Focus on cross-functional flow – Avoid siloed thinking. Map and manage flows across departments.
- Design meaningful metrics – Quantify value flow, quality, speed, waste etc. to provide visibility.
- Automate data collection – Manual data gathering is tedious. Use tools to automate where possible.
- Make metrics visible – Display VSM metrics on dashboards, scorecards etc. Make them visible throughout the org.
- Create a culture of flow – Drive mindset shifts focused on improving end-to-end flow vs. functional silos.
- Develop people’s capabilities – Train employees in value stream principles, problem solving and improvement skills.
Getting Started With Value Stream Management
Follow these steps to begin implementing value stream management:
1. Create current state value stream maps
Document all steps in key processes end-to-end. Identify waste and constraints.
2. Define metrics and KPIs
Determine metrics to track value, quality, time, waste, cost etc.
3. Collect and display baseline data
Gather current benchmarks for the metrics. Display using graphs, dashboards etc.
4. Analyze data and identify improvement opportunities
Dig into the data to find ways to improve flow and reduce waste.
5. Develop improvement plans and governance
Create Kaizen plans. Establish governance model and meetings to drive continued improvement.
6. Develop capabilities
Train employees in value stream skills, metrics, A3 thinking etc.
7. Continuously improve
Keep optimizing processes through daily kaizen and finding new ways to improve flow.
Value Stream Management Tools
There are a variety of software tools that enable organizations to better visualize and manage value streams:
- Visual mapping tools – Lucidchart, Microsoft Visio, Miro
- Work management platforms – Jira, Trello, Asana
- Business intelligence software – Tableau, Power BI, Looker
- Specialized value stream tools – CloudBees, Plutora, ConnectALL
Look for tools that make it easy to map processes, build dashboards, visualize data flows and bottlenecks, and collaborate across teams.
Driving More Business Value
In today’s competitive business environment, improving value streams is essential for delivering greater value to customers faster.
Value stream mapping gives you visibility. Value stream management enables you to turn that visibility into action.
By combining value stream mapping and management practices, organizations can improve flow, reduce waste, slash lead times and costs, and exceed customer expectations.
Adopting value stream management and mapping provides a proven approach for building more efficient, lean and customer-centric delivery pipelines to gain competitive advantage.
Featured in Architecture & Design
-
Decentralizing Decision Making with Shawna Martell & Dan Fike
In this episode, Thomas Betts talks with Shawna Martell and Dan Fike, about the Navigators program at Carta and how they are finding ways to decentralize decisions and empower individual contributors. The quality of technical decisions is improved, and decisions are reached more quickly because the people involved are close to the relevant context.
Featured in AI, ML & Data Engineering
-
Reach Next-Level Autonomy with LLM-Based AI Agents
Tingyi Li discusses the AI Agent, exploring how it extends the frontiers of Generative AI applications and leads to next-level autonomy in combination with enterprise data.
What is Value Stream Management?
What is value stream mapping & value stream management?
He is highly experienced in accelerating delivery practices and is equally comfortable talking about business strategy as he is talking about IT. Value stream mapping and value stream management are powerful tools. They complement one another to provide clarity into an organization’s delivery systems. They both enable decision-making.
Why is value stream management important?
For example, value stream management can help a company identify the steps they can take to develop a new software product, consider which people on a team might be involved in the project and determine which processes lead to the fastest delivery to customers. For value stream mapping, the focus is often simpler.
How do I perform value stream mapping?
To perform value stream mapping, teams collaborate to create the following components: Current state map: the current method by which products or services are produced for customers. Future state map: the target state of value stream we are looking to create.
What is value-stream mapping?
Value-stream mapping (VSM) is a fundamental lean practice that involves diagraming a value stream, which includes all the actions (value-creating and nonvalue-creating) needed to move a product or service from raw material to the arms of the customer, including the material and information flow.