Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that provides proven tools and techniques to help businesses streamline operations and provide customers with higher quality products and services.
Its primary focus is on eliminating defects and variation from organizational processes. Part of what helps make that happen is the human element. Education and training is key to successful implementation of Six Sigma.
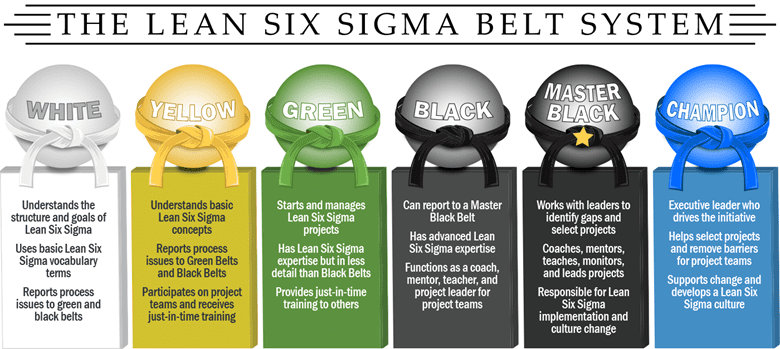
Because of the complexities of the methodology, Six Sigma offers training at distinct levels that are specified by color-coded belts. The belts range in ascending order, from White to Yellow, Green, Black and Master Black Belt. The belts offer increasingly higher knowledge and expertise in Six Sigma strategies and techniques.
Two of the most common and important levels are green and black. Though differences exist between the two, Green Belts and Black Belts often work very closely together.
Six Sigma has become an increasingly popular methodology for quality improvement across various industries. Professionals can demonstrate their expertise in Six Sigma tools and techniques through certifications such as Green Belt and Black Belt. But what exactly is the difference between these two levels?
In this comprehensive guide, we will examine the key distinctions between Six Sigma Black Belts and Green Belts including roles, responsibilities, requirements, and benefits. Whether you are considering Six Sigma training or currently hold a Green Belt, understanding these differentiators is essential for career development
Overview of Six Sigma Belts and Levels
Six Sigma utilizes a martial arts-inspired belt system to designate expertise Here is a quick overview of the different belt levels
- White Belt: Beginners with limited Six Sigma knowledge
- Yellow Belt: Possess basic tools training, assist on projects
- Green Belt: Proficient in DMAIC, lead small-scale projects
- Black Belt: Master of tools/methods, lead major projects
- Master Black Belt: Elite experts who coach and mentor Black Belts
As you progress from White to Master Black Belt, the expected level of proficiency and responsibility increases significantly This article will focus specifically on distinctions between Green and Black Belts
Green Belt Role and Responsibilities
Green Belts are trained in Six Sigma methodologies and equipped to lead small-scale improvement projects. Typical responsibilities include:
- Leading hands-on quality improvement projects utilizing DMAIC.
- Collecting and analyzing data relevant to projects.
- Identifying root causes and implementing solutions.
- Managing small project teams including Yellow Belts.
- Reporting on progress to Black Belts and key stakeholders.
- Contributing process expertise from daily work experience.
- Completing the required certification exam.
Green Belts are part-time Six Sigma agents, applying their skills while maintaining their normal job duties. They bring process knowledge from the frontlines to achieve tangible results.
Black Belt Role and Responsibilities
Black Belts are full-time change agents guiding large strategic projects. Responsibilities include:
- Leading high-impact Six Sigma projects aligned to key business goals.
- Coaching and mentoring Green Belts and project teams.
- Combining process expertise with statistical analysis to drive optimal outcomes.
- Designing and implementing training programs across the organization.
- Communicating project findings and recommendations to executives.
- Overseeing programs enterprise-wide while reporting to Master Black Belts.
- Passing a rigorous exam demonstrating advanced proficiency.
Black Belts possess extensive training in statistical tools and are often involved in developing core company processes and initiatives. They identify opportunities and ensure processes are sustainable.
Distinctions in Requirements and Training
Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certifications have different training and requirement standards:
Green Belt Requirements
- Typically complete 2 weeks of training
- Work on 1 Six Sigma project from start to finish
- Pass a written exam demonstrating comprehension of Six Sigma and DMAIC
Black Belt Requirements
- 4-6 months of intensive training
- Work full time as a Six Sigma specialist for 2 years
- Lead 2 Six Sigma projects from start to finish
- Complete 1 year of mentoring under a Master Black Belt
- Pass a comprehensive written exam proving mastery of tools/concepts
- Develop expertise applying statistical software like Minitab
- Demonstrate leadership abilities and change management skills
As shown above, Black Belt necessitates significant advanced training, leadership capabilities, and a time commitment to earning the certification. The requirements reflect the responsibility entrusted to Black Belts to be Six Sigma authorities driving enterprise-wide transformation.
Key Differences in Skills and Abilities
Given their distinct roles, Green Belts and Black Belts require different skill sets:
Green Belts:
- Working knowledge of process improvement methodologies
- Familiarity with data collection and basic statistical analysis
- Ability to lead small teams and projects effectively
- Skills to present findings and recommendations
Black Belts:
- Expert-level knowledge of statistical analysis and Six Sigma tools
- Highly adept in quantitative process analysis and optimization
- Extensive training in process design, control, and improvement
- Experienced leading multifunctional process improvement initiatives
- Exceptional change management and leadership capabilities
- Skilled training and mentoring other Six Sigma practitioners
Black Belts possess deep expertise and experience applying Six Sigma at a strategic level. Their comprehensive abilities allow them to identify complex organizational challenges and drive innovative solutions.
Career Advancement and Salary Impacts
Both certifications confer advantages for career growth and salary:
-
Green Belts can expand their responsibilities and act as project leaders. Some may transition into full-time Black Belt roles. Average salary increase is 5-10%.
-
Black Belts attain expertise that prepares them for leadership positions like quality engineering directors. Average salary increase is 15-25%.
-
Other Benefits:
- Enhanced technical and leadership skills
- Understanding of process improvement
- Project management and communication abilities
- Professional prestige and recognition
Investing in Six Sigma skills clearly provides value for professionals and organizations seeking process excellence. Employees with advanced certifications can step into key quality improvement positions with proven expertise.
Should You Pursue Black Belt or Green Belt Certification?
If deliberating between Green and Black Belt training, consider your career goals:
-
For part-time improvement skills, Green Belt is ideal for process owners.
-
Black Belt develops experts to drive enterprise excellence full time.
-
Many pursue Green then Black Belt sequentially as proficiency increases.
Discussing needs with your employer can provide direction on whether Green or Black Belt aligns better with personal and organizational objectives. Both offer pathways for professional enrichment in quality assurance and leadership.
Key Takeaways on Six Sigma Belts
-
Six Sigma Green and Black Belts serve differentiated roles based on proficiency.
-
Green Belts lead smaller initiatives part time, while Black Belts guide major programs full time.
-
Black Belt requires extensive advanced training, experience, and leadership capabilities.
-
Certification at either level improves technical qualifications, career prospects, and salary potential.
-
Determining the most suitable level is based on personal and company goals for Six Sigma expertise.
In an environment where process excellence is paramount, Six Sigma skills offer professionals and employers powerful competitive advantages. Investing in Green or Black Belt certification demonstrates commitment to quality and equips talent to spearhead impactful improvements.
What a Green Belt Does
By the time someone earns Six Sigma Green Belt status, they have in-depth knowledge of the tools and techniques involved in implementing Six Sigma. This includes an understanding of how to leverage the Six Sigma methodology DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control). DMAIC is used when optimizing an existing operation to reduce defects or variation.
To earn Villanova University’s Green Belt certification, you must meet the following requirements:
- Successfully complete Villanova’s Six Sigma Green Belt coursework and unit exams
- Pass a 100-question multiple choice exam
Green Belts often do much of the heavy lifting on project teams, leading the data collection and analysis efforts. They also oversee much of the testing of new strategies and analyzing the results. In some cases, a Yellow Belt will assist with the data-related work, under a Green Belt’s supervision.
Green Belts generally function on a Six Sigma project part-time and typically work closely under the supervision of a Black Belt.
What is the difference between Green Belt and Black Belt?
What does a Six Sigma green belt mean?
Six Sigma green belt signifies that an individual has passed the Six Sigma greenbelt certification exam. They can solve quality problems, improve processes, and analyze them using Six Sigma. An interest in professional development is demonstrated by a Six Sigma green belt.
What is a black belt in Six Sigma?
At the project level, there are master black belts, black belts, green belts, yellow belts, and white belts. These people conduct projects and implement improvements. Master Black Belt: Trains and coaches Black Belts and Green Belts. Functions more at the Six Sigma program level by developing key metrics and the strategic direction.
What are the different types of Six Sigma belts?
The belts range in ascending order, from White to Yellow, Green, Black and Master Black Belt. The belts offer increasingly higher knowledge and expertise in Six Sigma strategies and techniques. Two of the most common and important levels are green and black.
What is the difference between Lean Six Sigma green belt and black belt?
Choosing between Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification depends on your career goals. Green Belt focuses on smaller projects, while Black Belt offers advanced expertise for leading large, strategic initiatives.