It is important to understand sales forecasting advantages and disadvantages to implement it in your growing business.
But, we must say that better understanding of sales forecasting will help you to raise your business with high profits. You can predict business costs and make better decisions with future plans. So, it’s essential to learn sales forecasting advantages and disadvantages.
In this blog, we will give you a comprehensive guide to learn what is sales forecasting, its pros and cons, and the sales forecasting process.
Find out both positive and negative effects of sales forecasting and then invest your time to implement in everyday’s techniques.
Accurate sales forecasting is crucial for effective business planning and growth. However, with so many methods available, it can be challenging to determine which techniques are best suited for your business. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into the top 10 sales forecasting methods, weighing up the pros, cons, and ideal use cases of each approach
Overview of the Top 10 Sales Forecasting Methods
Here is a quick overview of the sales forecasting methods we will cover
- Historical sales analysis
- Pipeline analysis
- Opportunity stage analysis
- Time series analysis
- Regression analysis
- Economic indicators
- Seasonality adjustment
- Causal models
- Subjective/judgemental forecasting
- AI-based forecasting
Now let’s explore each of these techniques in more detail.
Historical Sales Analysis
How It Works
Historical sales analysis examines previous sales data to identify trends and patterns. It assumes past performance can predict future outcomes.
Pros
- Simple and straightforward to implement
- Leverages readily available data
- Provides insight into sales cycles and seasonality
Cons
- Limited ability to account for market changes
- Not useful for new products/services or disrupted markets
Best Use Cases
- Stable, established products/services
- Industries with predictable cycles and minimal volatility
Pipeline Analysis
How It Works
Pipeline analysis evaluates current opportunities at various stages of the sales funnel to estimate closure rates.
Pros
- Provides visibility into near-term sales potential
- Helps prioritize sales efforts on likely deals
- Useful for short-term forecasting
Cons
- Relies on accuracy of pipeline data
- Limited view beyond immediate pipeline
Best Use Cases
- Quarterly or monthly forecasts
- Businesses with long sales cycles
Opportunity Stage Analysis
How It Works
This approach examines opportunities based on the defined stages and predicts closure rates for each stage.
Pros
- Granular, stage-specific predictions
- Quantifies progress through sales funnel
- Helps identify bottlenecks
Cons
- Requires robust process and stage definitions
- More complex to implement
Best Use Cases
- Businesses with clearly defined sales processes
-Complementary to pipeline analysis
Time Series Analysis
How It Works
Time series analysis identifies historical patterns and trends in data over time to predict future outcomes.
Pros
- Highlights seasonal/cyclical patterns
- Useful for long-term forecasts
Cons
- Requires extensive historical data
- Assumes past patterns continue
Best Use Cases
- Industries with seasonal cycles
- Long-range forecasts e.g. annual
Regression Analysis
How It Works
Regression analysis examines correlations between variables to model future outcomes. Useful for sales by assessing impact of investments, promotions etc.
Pros
- Quantifies impact of influencing factors
- Adaptable model based on new data
Cons
- Requires expertise in statistics/analysis
- Risk of overfitting models
Best Use Cases
- Planning marketing campaigns, pricing changes, promotions
- Businesses with many influencing variables
Economic Indicators
How It Works
Macroeconomic indicators like employment, inflation, GDP etc are used to predict sales, assuming link between economy and demand.
Pros
- Provides broader market context
- Useful for long-range predictions
Cons
- Not all businesses are highly correlated
- Significant lag between indicators and sales
Best Use Cases
- Industries heavily impacted by economic trends
- Annual forecasts
Seasonality Adjustment
How It Works
Sales data is modified to account for seasonal and cyclical fluctuations, revealing underlying trends.
Pros
- Normalizes temporary peaks/troughs
- Better determination of true growth
Cons
- Requires historical data
- Seasonal patterns may change over time
Best Use Cases
- Businesses with seasonal swings
- Often used to complement other methods
Causal Models
How It Works
Causal modeling combines elements of regression analysis and economic indicators to identify drivers of demand.
Pros
- Determines cause-and-effect relationships
- Adaptable to changing conditions
Cons
- Requires statistical expertise
- Significant data requirements
Best Use Cases
- Markets with multiple demand drivers
- Companies with resources for advanced analytics
Subjective/Judgemental Forecasting
How It Works
Experts provide estimates based on knowledge of products, customers, competitive landscape etc.
Pros
- Fast and inexpensive
- Leverages insights from experience
Cons
- Reliant on biased personal opinions
- Low accuracy and consistency
Best Use Cases
- New products or markets
- Quick estimates or supplementary method
AI-Based Forecasting
How It Works
AI algorithms continuously analyze data, identify patterns, learn from errors, and improve predictive accuracy.
Pros
- Automated, scalable predictions
- Rapidly adapts to new data
Cons
- Significant upfront investment
- Requires troves of quality data
Best Use Cases
- Data-rich companies
- Environment of rapid change
Key Considerations When Choosing a Sales Forecasting Method
While we’ve explored the pros and cons of each approach, the ideal method ultimately depends on your unique business conditions and objectives. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Data availability – the quantity and quality of historical data impacts options
- Sales cycle – short or long, level of variability
- Market maturity – new vs established, stable vs disrupted
- Resources – statistical expertise, data analytics capabilities
- Timeframe – short-term vs long-range predictions
- Influencing factors – complexity of demand drivers
- Industry patterns – degree of seasonality, economic sensitivity
Getting alignment on these elements will help guide you towards the techniques that are most relevant.
Best Practices for Sales Forecasting
While the chosen method is important, there are several best practices that apply across the board:
- Leverage multiple methods – using complementary techniques improves robustness
- Frequently revisit assumptions – past trends may not predict future
- Segment forecasts – by product, market, customer etc.
- Incorporate subjective insights – experience provides context
- Hold reviewers accountable – ensure thorough scrutiny of forecasts
- Implement continuous updates – real-time data improves accuracy
- Analyze variances – learn from past forecast errors
- Facilitate data accessibility – break down functional silos
- Integrate with workflows – embed forecasting in processes
Following these guidelines will help enhance the overall quality and value derived from sales predictions.
Key Takeaways and Next Steps
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to sales forecasting. The most effective solution involves:
- Determining the factors that apply to your business, from data availability to industry cyclicality
- Identifying the best methods based on your unique considerations
- Combining complementary forecasting techniques where appropriate
- Adopting best practices around continuous updates, variance analysis, and assumption validation
- Leveraging technology like AI and advanced analytics to enhance speed, scale, and sophistication
Now that you’re familiar with the pros and cons of the top sales forecasting methods, it’s time to assess your specific business context. Evaluating your internal capabilities, sales patterns, and data landscape will help determine the ideal forecasting approach to meet your needs. With the right solution in place, you’ll be well equipped to generate reliable predictions and make smart strategic decisions.
If you have any other questions on implementing sales forecasting in your organization, feel free to reach out! I’m always happy to chat more about optimizing processes and enhancing analytics capabilities.
Validate and Refine
Validate the accuracy of the forecasting models by comparing the forecasts with actual sales data from the past. Assess the forecast errors and identify any patterns or discrepancies.
If necessary, refine the models or adjust the forecast based on new information or changes in market conditions.
Choose Forecasting Methods
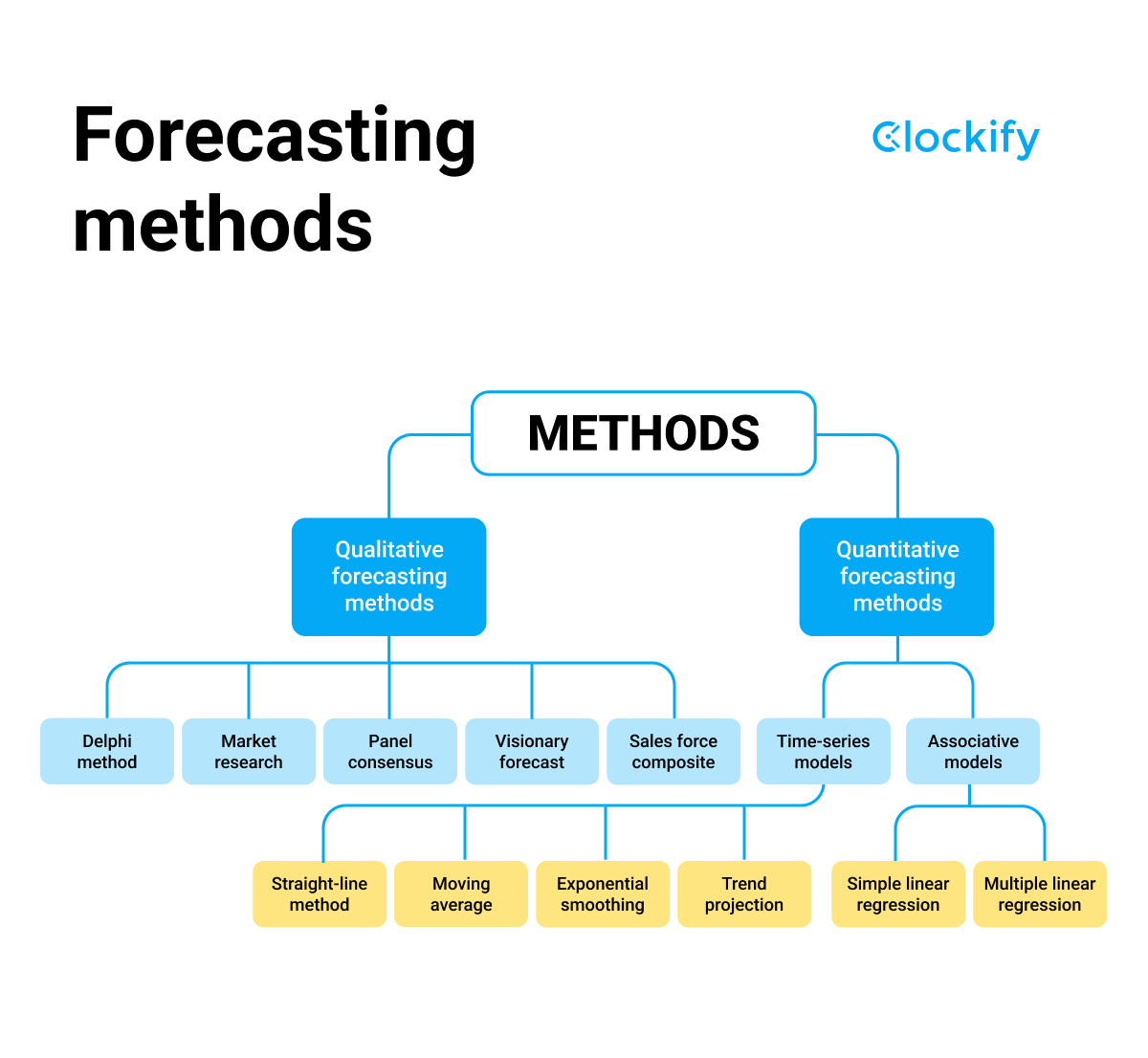
Select the appropriate forecasting methods based on the available data and the objective of the forecast.
Common methods include qualitative techniques (expert opinions, market research, surveys), quantitative techniques (time series analysis, regression analysis), and a combination of both (judgmental forecasting).
Forecasting Methods Overview
What are the pros and cons of sales forecasting?
Understanding sales forecasting can help you make better business decisions around costs, risks or future plans, so it’s important to use a method that aligns with your business practices. In this article, we discuss different sales forecasting methods and explore their pros and cons. Read more: Definitive Guide To Creating a Sales Forecast
How do you use sales forecasting?
Regardless of which sales forecasting method you choose, you’ll need to complete the following steps to effectively use it: Clarify the problem, outline how the information from the forecast will be used, identify who the findings are intended for, and determine how the forecasting project responsibilities will be divided up.
What are the different types of sales forecasting methods?
While there are a number of different forecasting methods, most will fall under two umbrella categories: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative Forecasts: These forecasts take a data-based approach to sales forecasting, relying on historical data of past sales revenue to help predict future trends.
Do sales forecasts need to scale?
If you aim to grow rapidly, your sales forecasts need to scale along with your business. 6. A Platform to Automate Sales Forecasting Processes On average, salespeople spend hours in forecasting every week. This time goes into entering the data and creating reports.