As workforces are moving out of physical offices in favor of remote work environments, cloud services — which allow employees to access corporate applications, data, and resources from any location using any device — have become increasingly essential. Businesses now have several different cloud service options to choose from when managing hybrid and remote workers:
Each business must make a comparison among DaaS vs. SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS to decide which cloud-based solution is ultimately most appropriate to help streamline the remote workforce. Company goals, culture, and line of business are all important considerations when weighing cloud-service options. But first, it’s important to take a closer look at what each of these four services are.
The rise of remote and hybrid work has made cloud services an essential part of doing business today. With more employees working outside of traditional office environments, companies must provide access to data, applications, and resources from anywhere. This has led to an explosion in cloud computing services that enable this flexible work model
As a business leader, you now face the challenge of navigating the various cloud service options available and determining which ones meet your specific needs. The four main types of cloud services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
In this article, I’ll explain what each of these cloud service models entails and the key differences between SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS vs DaaS. I’ll also provide guidance on how to select the right cloud solutions for your business based on your goals, resources, and use cases.
Defining the Main Types of Cloud Services
Before determining which type of cloud service is best for your company, it’s important to understand what each one is at a fundamental level:
SaaS: Software Delivered Through the Cloud
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. With SaaS, users access software applications over the internet through a web browser. The applications are hosted and managed by the SaaS provider on their own infrastructure. Users don’t need to install, maintain or update the software themselves.
Examples of SaaS applications include Salesforce CRM, Microsoft Office 365, Box, and Google Workspace.
PaaS: Development Platforms Hosted in the Cloud
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. PaaS provides a cloud-based environment for developers to build, test and deploy applications without having to maintain the underlying infrastructure. The PaaS provider manages the servers, storage, networking, operating systems, and middleware required to run the platform.
Examples of PaaS providers include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk, and Google Cloud Platform App Engine.
IaaS: IT Infrastructure Provided as a Service
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. With IaaS, fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, networks and operating systems are hosted on the cloud. Businesses can rent cloud infrastructure on-demand rather than having to purchase and manage physical servers themselves.
Leading IaaS providers include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
DaaS: Desktops Hosted and Managed in the Cloud
DaaS stands for Desktop as a Service. DaaS providers host virtual desktops in the cloud and deliver them to users on-demand. This allows workers to access desktop environments and business applications from any internet-connected device.
Prominent DaaS solutions include Amazon WorkSpaces, Microsoft Windows 365, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, and VMware Horizon Cloud.
Comparing the Pros and Cons of Each Cloud Service Model
Now that we’ve defined SaaS, PaaS, IaaS and DaaS, let’s do a detailed comparison of the major advantages and disadvantages of each option:
SaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- No need to install, update or maintain software. The SaaS provider handles this.
- Access applications from any device with an internet connection.
- Scales flexibly based on usage and number of users.
- Payment is usually subscription-based operating expense rather than large upfront capital expense.
Cons:
- Functions are limited to what the specific SaaS app provides. Less flexibility to customize.
- Reliant on vendor for security, uptime and performance.
- Limited integration capabilities with on-premises systems.
PaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Developer productivity is increased by automating infrastructure management.
- Easy for development teams to collaborate on apps in the cloud.
- Built-in scalability and high availability.
- Access to advanced tools and services for app development and deployment.
Cons:
- Potential vendor lock-in – migrating apps can be difficult.
- Securing applications and data is the responsibility of the user.
- Platform functionality depends on capabilities of provider.
IaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Only pay for what you use. Usage can scale up or down.
- No large upfront investment in physical infrastructure.
- Global availability and resilience of resources.
- Fast access to vast compute and storage capacity.
Cons:
- Responsible for managing applications, runtimes, middleware, data and OS.
- Security and compliance controls are your responsibility.
- Reliant on internet connectivity for all infrastructure.
DaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Improved security since data isn’t stored locally.
- Hardware independence – accessible from any internet-enabled device.
- Easier to scale desktops up or down as business needs change.
- Shifts IT resources from desktop maintenance to strategic initiatives.
Cons:
- Performance is dependent on internet connection bandwidth.
- Licensing costs for virtual desktops and applications.
- Limited offline access in case of network disruptions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cloud Service
Clearly there are trade-offs involved with each type of cloud service. Certain models will be better suited for specific business goals and use cases. Here are the most important factors to consider when deciding between SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS vs DaaS:
Business Goals – What are you hoping to achieve by moving to the cloud? Reduced costs and improved efficiency? Faster innovation and time to market? Greater workforce mobility and continuity? Each model lends itself to different priorities.
Resources and Capabilities – Do you have in-house technical skills and expertise to manage infrastructure and applications yourself or would you rather offload these tasks to a provider? What are your budget constraints?
Security and Compliance Needs – Are you bound by regulations like HIPAA or PCI that require strict data protections? Who handles security controls varies across service models.
Integration Requirements – Do you need to interconnect cloud capabilities with your existing on-premises systems and data? Some models make this easier than others.
Agility and Scalability – How dynamic are your workload demands and capacity needs? Can you easily scale up or down based on changes in the business?
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS vs DaaS: Making the Optimal Choice
In many cases, businesses will utilize a mix of SaaS, PaaS, IaaS and DaaS rather than adopt a single model. You might leverage multiple SaaS apps with a PaaS that integrates them while also using IaaS for handling peak workloads and spillover storage. DaaS can provide your workforce secure access to desktops and apps across various environments.
Here are a few examples of how you can align each cloud service approach with specific business scenarios:
-
SaaS – Best suited for turnkey business applications like email, CRM, project management, HR systems etc. Makes it easy to provide key apps to end users quickly.
-
PaaS – Ideal for developers and IT teams that want to build custom cloud-native applications rapidly without infrastructure headaches.
-
IaaS – Most flexible for workloads that have fluctuating resource demands like analytics, web apps, gaming, ecommerce etc. Pay-as-you-go model optimizes costs.
-
DaaS – Enables workforce mobility by allowing desktop access from any device secured by the cloud provider. Simplifies desktop management for distributed teams.
Making the optimal cloud choices requires a clear assessment of your true requirements. The various service models each have their own strengths and tradeoffs. With the right strategic approach, you can leverage SaaS, PaaS, IaaS and DaaS synergistically to maximize the business value of cloud computing and support your organization’s evolving needs.
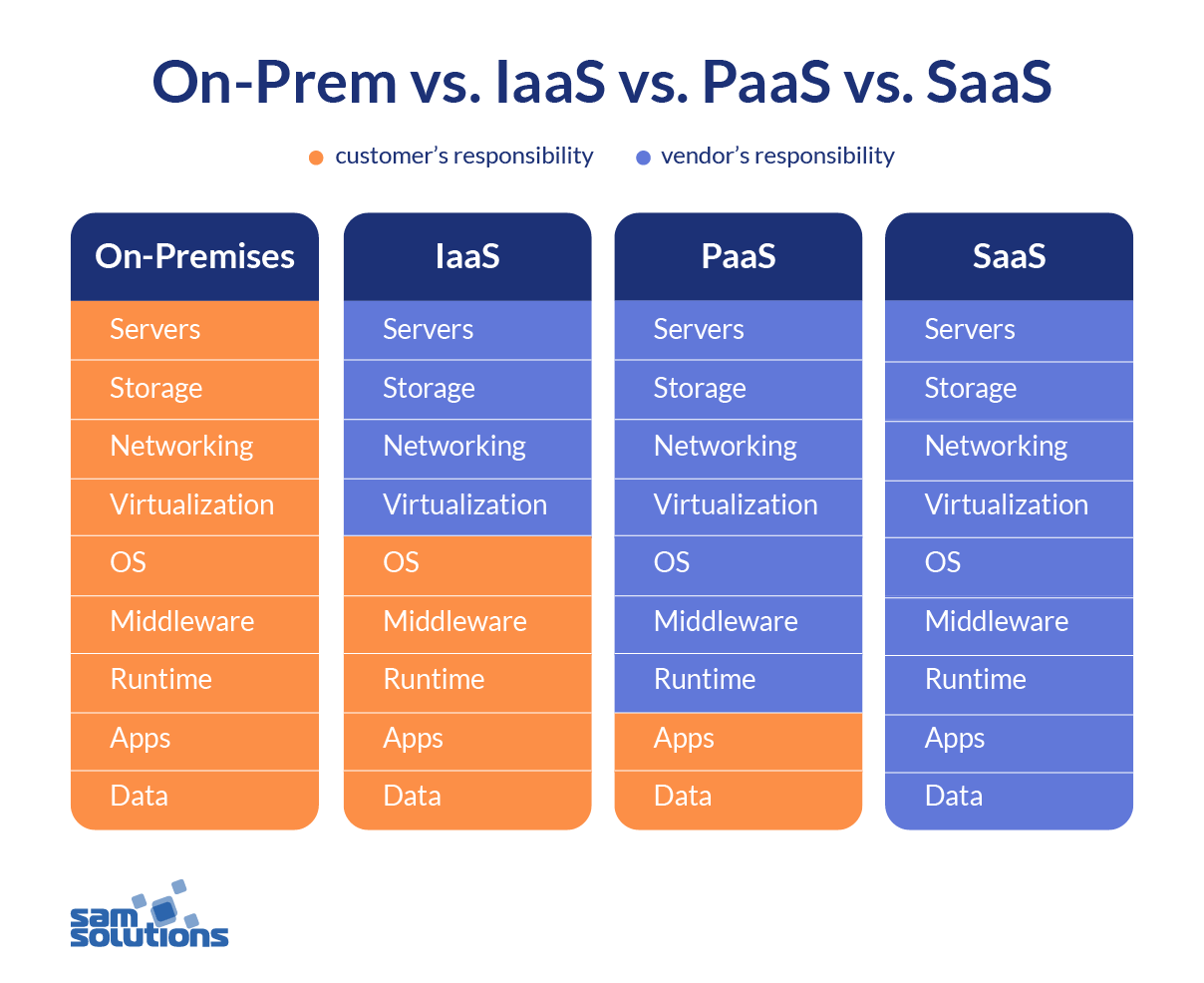
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Defined
IaaS moves vital storage, networking, and computing resources to the cloud. Organizations using IaaS platforms can reduce the amount of money spent on buying and managing on-premises servers and datacenters. IaaS services are offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing organizations to scale their infrastructure up and down as needed. When considering SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS vs. DaaS, companies that are looking to take advantage of virtualized resources should pay close attention to what IaaS solutions offer.
Which cloud service option should I choose for my business?
Cloud-based network infrastructures offer several advantages over traditional on-premises infrastructures, but there’s still the matter of deciding between PaaS vs. SaaS vs. IaaS vs. DaaS. The decision will ultimately be based on the size and type of organization you are a part of and what problems you need to solve. To start, let’s look at some pros and cons for each type of service.
The main DIFFERENCES between IaaS, SaaS and PaaS explained…
FAQ
Is Gmail SaaS or PaaS?
|
Platform
|
Examples
|
|
PaaS
|
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and Adobe Commerce
|
|
SaaS
|
Gmail, Slack, and Microsoft Office 365
|
|
IaaS
|
Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine
|
What is the difference between Saas & Paas?
The three cloud service models mainly differ in what they offer out of the box. SaaS is cloud-based software that companies can buy from cloud providers and use. PaaS helps developers build customized applications via an application programming interface ( API) that can be delivered over the cloud.
Which is better SaaS or IaaS?
For individuals looking for a wide variety of capabilities and customization, service models such as IaaS, DaaS and PaaS are often preferred over SaaS. This is because SaaS usually provides only a small number of online applications, unlike DaaS, which offers an entire virtual desktop to the user.
What is the difference between IaaS & PaaS?
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are all different options for cloud delivery models. They each have their own pros and cons, and the difference between them is the level of abstraction they offer the end-user. IaaS offers the lowest level of abstraction.
Should you choose a SaaS or a Daas cloud service?
Organizations looking to choose between SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS vs. DaaS must be sure to have a clear understanding of the advantages of cloud services over traditional, on-premises datacenters. There are five key advantages cloud services offer: Scalability: Cloud servers can scale up or down as your business grows and your needs change.