As a business owner or aspiring entrepreneur, having a solid grasp of basic accounting and financial terminology is critical. Three of the most fundamental concepts are revenue, income, and profit. While these terms are related and influence each other, they have distinct meanings. This article will clearly explain the key differences between revenue, income, and profit.
What is Revenue?
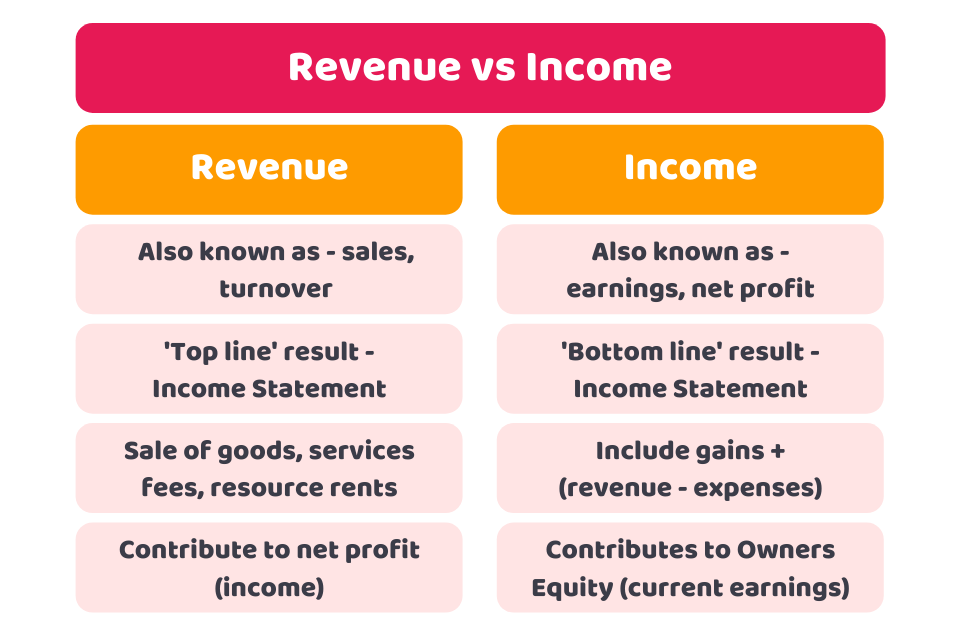
Revenue represents the total amount of money a company brings in during a specific time period through its core business activities. For example, if a clothing retailer sells $5 million worth of merchandise in a year, its annual revenue is $5 million.
A company’s revenue appears as the top line on its income statement. Revenue is often referred to as sales or the “top line.” It encompasses all sources of sales including cash, credit, and other forms of payment. Revenue is a crucial metric since it reveals the total income generated before any costs or expenses are deducted.
While revenue showcases earning potential, it does not account for the cost of conducting business. Revenue simply tracks total sales. Subtracting costs and expenses from revenue produces a company’s profit.
Key Things to Know About Revenue:
-
Revenue is the total money received from sales of products and services.
-
It is calculated as the number of units sold multiplied by the price per unit
-
Reported on the top line of the income statement.
-
Increases when production and sales volume expand.
-
Provides insight into sales performance but not profitability.
What is Income?
Income represents the money a company retains after deducting the costs directly associated with generating revenue. These costs include things like the costs of goods sold, operating expenses, depreciation, interest, and taxes.
Income, often called net income or net profit, appears on the last line of the income statement. It is also referred to as the “bottom line.” Net income measures profitability after subtracting all expenses required to operate the business. This gives a clear snapshot of how much the company actually earned or lost during the period.
Income is a critical metric both for internal financial planning and assessing the company’s fiscal health. It reveals how efficiently management is running the business. High net income means the company was effective in managing expenses while growing revenue.
Key Things to Know About Income:
-
Income is revenue minus total costs and expenses.
-
Also called net profit or net income.
-
Appears on last line of income statement.
-
Measures profitability after deducting operating costs.
-
Directly impacts retained earnings on balance sheet.
-
Used to calculate earnings per share (EPS).
What is Profit?
In financial terminology, profit represents the money left after subtracting all business expenses from revenue. So profit is synonymous with net income. Profit appears on the income statement and directly feeds the retained earnings account on the balance sheet.
However, in a general sense, the term profit is sometimes used interchangeably with revenue. The assumption is that if a company has revenue, they are profitable. But again, revenue does not guarantee profitability since it only accounts for sales, not the cost of generating those sales.
Profit and revenue are directly correlated, but increased revenue does not always mean increased profit. For example, a company might sell more products, boosting revenue. But if the extra sales volume leads to a proportional rise in expenses, profit could stay flat or even decrease.
When assessing a company’s profitability, net income gives the real picture whereas revenue alone can be misleading.
Key Things to Know About Profit:
-
In accounting, profit means net income.
-
In general usage, profit is sometimes used synonymously with revenue.
-
For clarity, net income should be used to denote profit.
-
Revenue does not equal profit.
-
Profit is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue.
The Relationship Between Revenue, Income, and Profit
Revenue, income, and profit are all vital metrics that work together to measure a company’s financial performance from different perspectives. Here is an example income statement to showcase their interactions:
Fictional Company Income Statement
| Revenue | $1,000,000 |
|-|-|-|
| Cost of Goods Sold | $600,000 |
| Gross Profit | $400,000 |
| Operating Expenses | $100,000 |
| Depreciation | $50,000 |
| EBIT (Earnings Before Interest & Taxes) | $250,000 |
| Interest | $20,000 |
| Pretax Income | $230,000 |
| Income Taxes | $60,000 |
|Net Income|$170,000|
In this example:
-
Revenue is $1 million. This represents total sales.
-
After deducting Cost of Goods Sold ($600K), Gross Profit equals $400K.
-
Operating Expenses and Depreciation are also subtracted, leaving EBIT of $250K.
-
Interest and taxes are deducted, resulting in Pretax Income of $230K.
-
Finally, after income taxes, Net Income (profit) equals $170K.
This example illustrates the connections between revenue, expenses, and profit. Revenue comes first, then costs are deducted in stages to calculate the company’s bottom line net income.
Tracking trends in all three metrics over time provides a comprehensive window into the company’s financial operations and health. Revenue highlights sales growth. Net profit measures fiscal strategy success. And all activity ultimately flows through to the retained earnings on the balance sheet.
Key Takeaways:
-
Revenue represents total sales. It reveals income potential.
-
Net Income is revenue minus total expenses and costs. It measures profit after operations.
-
Profit means net income in accounting terminology. Informally, profit is mixed up with revenue.
-
Revenue only looks at sales volume. Net profit factors in costs.
-
Monitoring all three metrics together provides a complete performance picture.
For business managers, clearly distinguishing between revenue vs. income vs. profit is vital. Each one provides unique insights. Mastering the differences takes financial understanding to the next level. Whether starting a new venture or analyzing an established company, being able to accurately interpret revenues, profits, and their relationship is an indispensable skill.
Can Income Be Higher Than Revenue?
In general, income can never be higher than revenue because income is derived from revenue after subtracting all costs. Revenue is the starting point while income is the endpoint. In cases where income is higher than revenue, the business will have received income from an outside source that is not operating income, such as a specific transaction or investment.
Revenue vs. Income
To really grasp how significant the difference between revenue and income can be, consider Apple, one of the largest tech companies on the market. It had a $294.5 billion difference between revenue and net income for its 2022 year. From a net sales (total revenue) of $384.3 billion, Apple deducted its:
- Total cost of sales: $223.5 billion
- Total operating expenses: $21.3 billion
- Other income (expense), net: $334 million
- Income taxes: 19.3 million
Which gave the company a net income of $99.8 billion for its 2022 year.
Revenue vs. Gross Income/Profit/Earnings vs. Net Income/Profit/Earnings (Bottom Line) in One Minute
What is the difference between profit and revenue?
Profit, which is typically called net profit or the bottom line , is the amount of income that remains after accounting for all expenses, debts, additional income streams, and operating costs. Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods or services related to the company’s primary operations.
What is the difference between net income and revenue?
Income (net income) is the amount of money a company retains after subtracting all expenses associated with operations. Therefore, net income is known as the bottom line of a company’s income statement. Earnings and net income are commonly used as synonyms. Revenue is the total amount of money a company generates from its core operations.
What is the difference between income vs Profit?
Understanding the differences between profit vs revenue vs income vs gross profits is crucial for financial literacy. While revenue represents total sales, profit is what remains after expenses are deducted. Income, on the other hand, refers to an individual’s earnings.
What is the difference between annual revenue and revenue?
Revenue is the total income generated by the business before any expenses. If you add up all of the business’s sales from the year, that is the company’s annual revenue. More formally put, revenue is the total of all money generated from the sales of goods or services. This only includes revenue from regular business operations.