IT is adapting to new business pressures by adopting new practices and technologies. What impact is this having on infrastructure and operations management? Written by
IT infrastructure and operations (I&O) teams are under intense pressure to rapidly adapt to changing business models, leveraging new technologies, processes and workflows to optimize their digital transformation. In this article, we’ll provide an insightful overview of how I&O teams are managing this transformative journey, considering the latest advancements in API integration, cloud infrastructures and their impact on business outcomes for end-users.
For many, the distinction between IT operations and IT infrastructure is blurry Though related, these two domains play different roles in enabling technology to support business goals In this article, we’ll clearly define IT operations vs. IT infrastructure and highlight how they work together to keep companies running smoothly.
IT Operations: An Overview
IT operations refers to the execution monitoring and management of technology systems and services. The IT operations team ensures that hardware, software, networks, and related infrastructure operate optimally on a day-to-day basis.
IT operations responsibilities include:
- Deploying and configuring systems
- Managing updates and patches
- Monitoring performance
- Conducting troubleshooting and repairs
- Maintaining continuity through backups and disaster recovery
Essentially, IT operations focuses on the daily activities involved in running IT systems and services. The overarching goal is to provide stable, seamless technology delivery so that employees can perform their jobs efficiently.
Common IT Operations Roles
IT operations teams comprise various roles collaborating to support the design implementation and care of technology systems.
Typical IT operations roles include:
- Systems administrators who install, configure, and maintain servers and systems.
- Network engineers who oversee communication networks like LANs and VPNs.
- Database administrators who ensure optimal database performance and availability.
- IT security specialists who protect systems and data from threats.
- Desktop support technicians who troubleshoot endpoint devices issues.
Importance of Streamlined IT Operations
Smooth IT operations are crucial for companies relying on technology to conduct business. System downtime can negatively impact productivity and revenue. The stakes are especially high for e-commerce companies, healthcare organizations, and financial institutions.
That’s why monitoring, preventive maintenance, capacity planning, and uptime optimization are imperative. Efficient IT operations safeguard against disruptions that affect internal and external stakeholders.
IT Infrastructure Defined
The physical technology components that store, process, and transmit data are collectively known as IT infrastructure. This infrastructure enables the delivery of IT services and powers business operations.
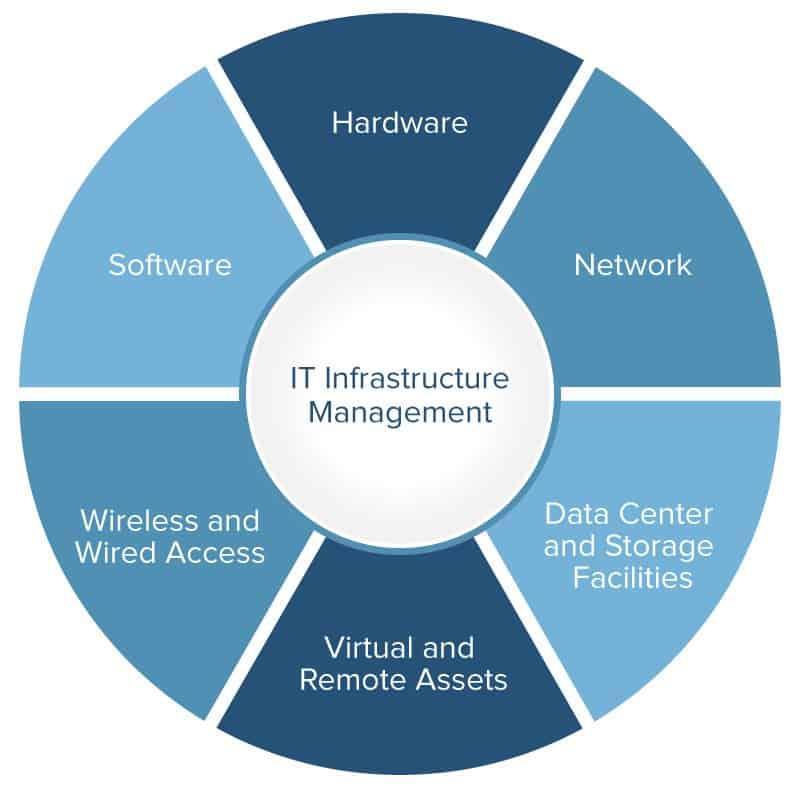
IT infrastructure comprises:
- Hardware – servers, computers, mobile devices, networking gear
- Software – operating systems, business applications
- Networks – LANs, WANs, wireless networks, network services
- Data centers – dedicated facilities housing critical IT equipment
- Cloud services – on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet
Hardware, software, networks, data centers, and cloud platforms provide the foundation on which IT operations and business processes run.
IT Infrastructure Components
IT infrastructure includes a wide array of technologies working in tandem:
Hardware
- Servers act as dedicated computers for hosting applications, databases, websites, and more.
- Storage infrastructure consists of disk arrays, SAN (storage area network) devices, tape libraries, and storage software.
- Networking hardware like routers, switches, and firewall appliances connect devices and enable communication.
- Endpoints refer to user devices like desktop PCs, laptops, tablets, and mobile phones.
Software
- Operating systems manage hardware resources and provide a platform for applications to run.
- Database management systems organize and store data, allowing for efficient querying and manipulation.
- Middleware facilitates integration and communication between software programs and systems.
- Virtualization software enables the creation of virtual machines that act as abstracted hardware.
Network Services
- DNS (Domain Name System) translates human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses to locate devices on a network.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses to network devices.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network) extends a private network over public infrastructure like the internet.
- Load balancing distributes network traffic across multiple servers to optimize performance.
Data Centers and Cloud
- Data centers are specialized facilities containing racks of servers and supporting infrastructure like power, cooling, and physical security.
- Cloud computing provisions IT services over the internet, often via public cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
IT Operations Rely on IT Infrastructure
Clearly, IT operations and IT infrastructure are distinct but heavily interdependent. Smooth IT operations are only possible with a robust IT infrastructure foundation.
IT infrastructure provides the raw ingredients for delivering IT services and applications. IT operations brings expertise to leverage that infrastructure to enable and enhance business processes through technology.
For example, a company may decide to implement a new cloud-based ERP system. The IT infrastructure team would architect and deploy the necessary servers, storage, and networking hardware in their cloud environment to support the ERP system.
Once the infrastructure is provisioned, the IT operations team would install, configure, and customize the ERP software for the specific business requirements. They would also handle ongoing administration, monitoring, troubleshooting, and system upgrades.
The infrastructure provides the flexible foundation for operations to build upon. Operations, in turn, ensures the infrastructure is maintained and leveraged to deliver business value through stable IT services.
Streamlining IT Ops and Infrastructure with Jira Service Management
Jira Service Management (JSM) streamlines IT management processes, including enhanced IT operations and infrastructure capabilities.
For optimizing IT infrastructure deployment and configuration, JSM offers:
- ITSM Templates – pre-built templates for standard ITIL workflows
- CMDB – centralized configuration management database
- Automated workflows – standardize and automate repetitive tasks
For monitoring and managing ongoing IT operations, JSM provides:
- Incident management – ticket tracking for issues resolution
- Problem management – root cause analysis and prevention of incidents
- Change management – minimize risk and disruption from system changes
- Service level agreements – define and meet performance goals
With robust capabilities supporting both optimized infrastructure and IT operations, Jira Service Management enables high-velocity yet stable IT services delivery.
Key Takeaways: IT Operations vs IT Infrastructure
-
IT operations focuses on the daily activities involved in managing IT services and systems.
-
IT infrastructure comprises the core physical and virtual technology components that enable IT operations.
-
While distinct, IT operations and infrastructure work hand-in-hand to deliver business technology. Smooth IT operations rely on a solid infrastructure foundation.
-
Jira Service Management enhances both IT operations and infrastructure via features like CMDB, automated workflows, and mature ITIL-aligned processes.
-
Clearly understanding the difference between operations and infrastructure roles leads to efficient collaboration and IT management.
In today’s tech-driven business climate, high-performing IT operations and infrastructure provide a competitive advantage. With a powerful platform like Jira Service Management supporting your IT teams, you can achieve technology excellence.
The Scope of IT Operations Management
IT operations teams are responsible for applications, processes and platforms supporting IT and business functions. This encompasses software configuration, maintenance, database management, disaster recovery and the integration of new technologies. IT operations also extends to managing help desks and devices, ensuring comprehensive support for business needs.
Evolving I&O Teams for the Digital Future
The rapid evolution of technology impacts markets, consumer expectations and businesses, making it imperative for I&O teams to optimize digital experiences and application workloads. IT has become a central player in the organization’s value stream, contributing to product development, improvement and the maintenance of systems supporting the business’s value proposition.
To meet the demands of this evolving landscape, I&O teams must transition from traditional hierarchical approaches to collaborative efforts. The focus is on rapid design, deployment and improvement, moving beyond project management to deliver products continuously refined for end-users.
What is ITOps | ITOps Explained | IT Operations Explained In 3 Minutes | Intellipaat
What is the difference between IT operations and infrastructure?
IT operations have a higher-level view of an organization’s infrastructure and processes, so their leadership policy and workflow often determine how staff support and interact with IT infrastructure. Oppositely, infrastructure may demand IT operations to perform certain roles or processes for them.
What is it operations?
IT operations, or IT ops, is a term that encompasses all the activities involved in the setup, design, configuration, deployment and maintenance of the IT infrastructure that supports business services. It has moved to the forefront of service delivery and is a key driver of operational stability.
Why is it important to improve your IT Operations & Infrastructure Strategy?
Today’s IT ops teams need to provide a level of predictability that makes it possible to support frequent and rapid innovation without disruption to existing services and operations. Improving your IT operations and infrastructure strategy is easier said than done.
What is the primary role of IT operations?
The primary role of IT operations is to ensure the smooth performance of IT and business technologies so that business operations can proceed uninterrupted. The responsibilities of ITOps include: Managing resources: ITOps keeps IT infrastructure running.