As a business owner or manager, understanding and tracking your labor productivity is critical. Labor productivity measures how efficiently your workforce converts inputs into outputs. By calculating and analyzing your labor productivity, you can identify opportunities to streamline processes reduce costs, and boost profitability.
In this comprehensive guide I will explain what labor productivity is why it matters, and provide step-by-step instructions on how to calculate and measure it for your business.
What is Labor Productivity?
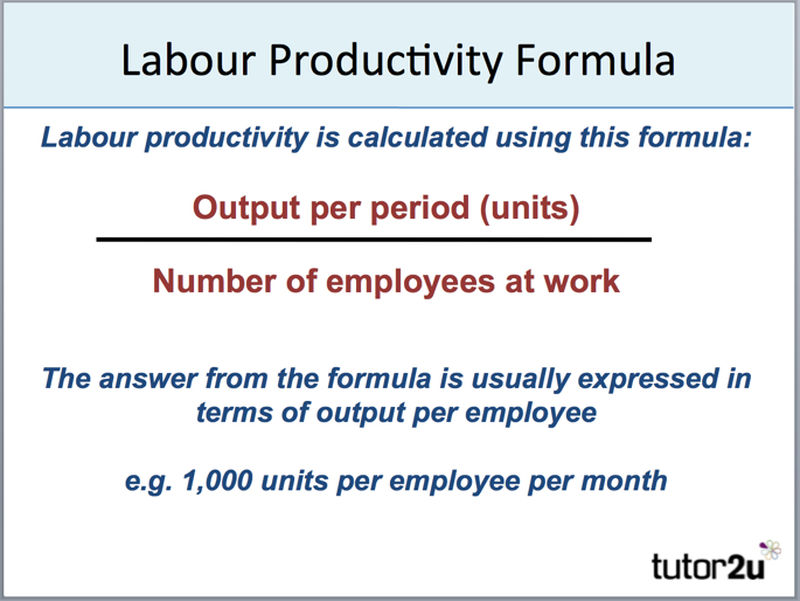
Labor productivity refers to how much output is produced per unit of labor input, It measures the efficiency of a workforce in converting labor time into goods or services,
Specifically, labor productivity is calculated as:
Total Output / Total Labor Hours
Output refers to the goods produced or services provided. Labor hours includes the time spent by employees directly involved in production. Higher productivity means more efficient utilization of labor to generate greater output.
For example, if your workers produce 100 widgets in 50 hours, your labor productivity is 2 widgets per hour. If they produce 200 widgets in 50 hours, your productivity has increased to 4 widgets per hour.
On a macroeconomic level, labor productivity measures the economic output per hour worked across an entire country. However, as a business manager you are likely more concerned with tracking productivity for your specific company or department.
Why Measure Labor Productivity?
There are several important reasons to measure and monitor labor productivity:
-
Evaluate efficiency – Productivity metrics show how well labor time is being used to produce outputs. This allows you to identify opportunities to streamline processes.
-
Compare performance – Productivity can be tracked over time to compare current performance vs past performance. You can also benchmark against industry competitors.
-
Identify issues – Decreasing productivity may indicate problems like deficient training, inadequate tools, or low worker morale.
-
Set goals – Establishing productivity goals creates focus for managers and employees. Progress can be tracked.
-
Reduce costs – Improving productivity reduces labor costs per unit of output. This directly impacts profit margins.
How to Calculate Labor Productivity
Figuring out labor productivity requires determining the total output produced and the total labor hours worked during a set time period. Here are the key steps:
1. Define Relevant Outputs
First, determine what outputs you want to measure. For a manufacturer this may be the number of widgets produced. For a restaurant it may be meals served. Choose outputs that align with your business goals.
Focus on measuring direct outputs from production processes. Services or support activities (e.g. accounting, HR) can be excluded.
2. Define Roles Included
Next, determine which job roles are directly involved in producing the measured outputs. This is your labor input.
For a restaurant, this may include cooks, servers, and busboys. Office staff not involved in serving customers would be excluded.
3. Establish Time Period
Decide what time frame you want to analyze productivity over – daily, weekly, monthly, etc. Longer periods show more overarching trends, while shorter periods can pinpoint temporary changes.
4. Track Outputs
Within your chosen time frame, track the quantity of outputs produced. Verify outputs match expectations and production records.
5. Track Labor Hours
Add up the total number of labor hours worked by employees in the defined roles. This may require tallying clocks-in/out, schedules, or timesheets.
Only count time directly involved in production – exclude breaks, trainings, etc.
6. Calculate Productivity
Divide total outputs by total labor hours to get productivity for the period.
For example:
- Outputs = 1,500 units produced
- Labor hours = 250 hours worked
- Productivity = 1,500/250 = 6 units per hour
7. Compare Over Time
Repeat the productivity calculation each period to identify trends and benchmark against past performance.
Significant changes in productivity warrant further investigation into root causes.
Tips for Measuring Productivity Accurately
When calculating labor productivity, keep these tips in mind:
-
Use consistent sources – Always rely on the same systems for output and hour tracking to ensure data reliability.
-
Focus on direct labor – Only include roles that directly produce the chosen output metric to prevent skewed results.
-
Account for quality – Weigh outputs based on quality standards met, not just pure quantity.
-
Consider labor skill level – Factor in the skill level required for different output units if vastly different.
-
Adjust for inflation – When comparing productivity over time, adjust old data for inflation to keep outputs comparable.
-
Look at longer horizons – Don’t make major conclusions based only on very short-term productivity changes, which can be misleading.
How to Improve Labor Productivity
Once you have productivity metrics established, you can take steps to improve your workforce efficiency:
-
Cross-train employees – Workers skilled in multiple roles can better adapt to changing business needs.
-
Implement technology – Automation and software can boost output while reducing manual labor time.
-
Standardize processes – Document procedures to ensure consistency across all employees.
-
Provide performance feedback – Let individual workers know how they are doing and involve them in optimizing their productivity.
-
Develop skills – Invest in employee training and education to enhance expertise.
-
Motivate your team – Offer rewards and incentives for meeting productivity goals.
-
Upgrade equipment – New tools and machinery can enable employees to work faster and more efficiently.
The bottom line is that monitoring and optimizing labor productivity should be an ongoing priority. Use the guidelines provided in this article to accurately measure productivity and make improvements over time. Your business revenues and profits will benefit!
How to Calculate Labor Productivity
To calculate a countrys labor productivity, you would divide the total output by the total number of labor hours.
For example, suppose the real GDP of an economy is $10 trillion and the aggregate hours of labor in the country is 300 billion. The labor productivity would be $10 trillion divided by 300 billion, equaling about $33 per labor hour. If the real GDP of the same economy grows to $20 trillion the next year and its labor hours increase to 350 billion, the economys growth in labor productivity would be 72 percent.
The growth number is derived by dividing the new real GDP of $57 by the previous real GDP of $33. Growth in this labor productivity number can sometimes be interpreted as improved standards of living in the country, assuming it keeps pace with labors share of total income.
What Is Labor Productivity?
Labor productivity measures the hourly output of a countrys economy. Specifically, it charts the amount of real gross domestic product (GDP) produced by an hour of labor. Growth in labor productivity depends on three main factors: saving and investment in physical capital, new technology, and human capital.
- Labor productivity measures output per labor hour.
- Labor productivity is largely driven by investment in capital, technological progress, and human capital development.
- Business and government can increase labor productivity of workers by direct investing in or creating incentives for increases in technology and human or physical capital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/labor-productivity.asp-final-2c0d23a4f3544122969aacf8ef94ed49.png)
Calculating Labor Productivity
How is labor productivity measured?
Growth in labor productivity is measured by the change in economic output per labor hour over a defined period. Labor productivity should not be confused with employee productivity, which is a measure of an individual worker’s output. To calculate a country’s labor productivity, you would divide the total output by the total number of labor hours .
What is the formula for labor productivity?
The formula for labor productivity is: Labor productivity = value of goods and services ÷ total number of hours worked Related: How To Measure Productivity and Increase Efficiency in the Workplace Here are some potential benefits of measuring labor productivity in your own organization:
How do you calculate a labor productivity index?
A labor productivity index can be calculated by dividing an index of output by an index of hours worked. When more than one index is included in a calculation, all the indexes must have the same base period. Average annual percent changes measure change over several periods stated at an average yearly rate.
How do you measure employee productivity?
You can measure employee productivity with the labor productivity equation: total output / total input. Let’s say your company generated $80,000 worth of goods or services (output) utilizing 1,500 labor hours (input). To calculate your company’s labor productivity, you would divide 80,000 by 1,500, which equals 53.