Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become an essential security tool for protecting online accounts, but how exactly does it work? In this article, we’ll explain in simple terms what multi-factor authentication is, how it adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password, and the different methods used for the second “factor” of authentication.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-factor authentication refers to requiring two or more forms of identity verification before granting access to an online account or service. The most common scenario is when you log into an account using your username and password (the first factor – something you know), and then you are prompted to provide an additional piece of information to confirm it’s really you.
This extra step adds important security because it requires something beyond just the password, which makes it much harder for hackers and cybercriminals to access your accounts. Even if they have your password, they won’t be able to log in without the second factor.
How are the Additional Factors Provided?
There are three main categories of additional factors that can be used:
-
Something you know – This could be a PIN security question, or one-time password provided via email text, or an authentication app.
-
Something you have – This refers to possession of a physical device like a security token, smartphone, or FIDO security key
-
Something you are – This uses biometric authentication such as fingerprint facial, or iris recognition.
Some common examples of second factors:
- One-time code sent via text message or authentication app
- Push notification to your smartphone that you tap to approve
- Fingerprint scan on your smartphone
- Security code from a hardware token device
- Answering a security question
Why is MFA So Important for Security?
Adding a second form of identity verification makes it exponentially harder for bad actors to access your accounts. If a hacker gets ahold of your password through a data breach, phishing, or malware, they would also need physical possession of your phone or security token to get into the account.
Of course, no security is foolproof. But multifactor authentication adds some important hurdles that greatly minimize the chances of compromising accounts. According to a study by Microsoft, enabling MFA can reduce the risk of attacks by 99.99%.
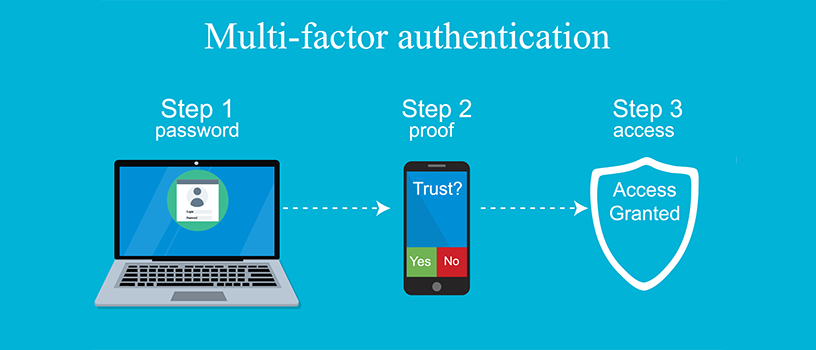
How Does MFA Actually Work When Logging In?
When logging into an account with MFA enabled, it works like this:
-
You enter your username and password as usual.
-
After submitting, you are prompted to provide the second factor of authentication.
-
You get the additional verification code (via text, app, etc.) and enter it.
-
After submitting the code, access is granted to your account.
On subsequent logins from the same device, you will often only need to provide the password and bypass the second factor, since the service recognizes your device. The additional authentication is only required periodically or if you try to login from a new, unrecognized device.
MFA Methods: Text Messages vs. Authentication Apps
There are two very common methods services use for the additional authentication factor:
-
Text messages – A one-time code is sent via SMS to your phone. This is convenient since it doesn’t require any apps, but SMS codes can be intercepted by hackers.
-
Authentication apps – Apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator generate time-sensitive codes that refresh every 30 seconds. This is more secure than SMS and works even without cell service.
Authentication apps are generally the preferred method these days because of enhanced security. The codes are generated locally on the device without having to be transmitted, meaning there’s no risk of interception.
Setting Up MFA on Your Accounts
Enabling MFA is usually simple and takes just a couple minutes. Most major services like Google, Facebook, Apple, and Microsoft make it easy to turn it on in your account settings.
You’ll be prompted to download an authentication app or enter a phone number to receive SMS codes. As long as you follow the steps, it takes just a minute or two to complete the setup.
The minor hurdle of setting MFA up is worth it for the major security benefits of keeping your accounts protected. Think of it as putting an extra lock on your front door – it requires remembering to use the key, but provides much more peace of mind.
MFA Drawbacks: Usability vs. Security
There’s no doubt multifactor authentication enhances security and provides important protection for online accounts. However, there are some usability tradeoffs that come with it:
-
Having to get a code and enter it adds more steps to logging in. This can sometimes be inconvenient, especially when using lots of different accounts with MFA enabled.
-
Getting locked out of accounts can happen more easily if you lose your phone or authentication device. It takes extra effort to get back into accounts.
-
Inputting codes may not be accessible for people with certain disabilities. Workarounds have to be used.
-
SMS text messages don’t always work reliably for delivering codes if you have spotty cell service.
The extra few seconds and steps to log in may be annoying, but the massive security upside makes it worth dealing with minor inconveniences. And authentication methods are continually improving to make MFA both more secure and easier to use.
The Future of MFA: Passwordless and Biometric Login
Multi-factor authentication is evolving beyond passwords and code-based verification. Some emerging methods that are growing in usage:
-
Passwordless login – Users can login to accounts by tapping a push notification on their phone rather than entering passwords and codes. Services like Microsoft and Apple support this.
-
Biometric authentication – Using fingerprint or facial recognition as a second factor provides enhanced security and convenience for users. It’s already widely adopted on smartphones.
These new methods maintain the multiple factors of identity verification but in a more seamless way for users. They represent the future of how multi-factor authentication will work.
Given how easy passwords are compromised in today’s digital world, taking a few seconds to use multifactor authentication is more than worth it to lock down your online identity and sensitive data. The next time you’re given the option to enable it on an account, take a minute to turn it on. Your security is worth it!
How Does MFA work?
MFA works by requiring additional verification information (factors). One of the most common MFA factors that users encounter are one-time passwords (OTP). OTPs are those 4-8 digit codes that you often receive via email, SMS or some sort of mobile app. With OTPs a new code is generated periodically or each time an authentication request is submitted. The code is generated based upon a seed value that is assigned to the user when they first register and some other factor which could simply be a counter that is incremented or a time value.
What’s the Difference between MFA and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
MFA is often used interchangeably with two-factor authentication (2FA). 2FA is basically a subset of MFA since 2FA restricts the number of factors that are required to only two factors, while MFA can be two or more.
How does Multifactor Authentication work? | MFA and privacy explained
What is multi-factor authentication?
Any combination of two or more factors qualifies as multi-factor authentication. The use of only two factors may also be referred to as two-factor authentication. Multi-Factor Authentication: How It Works A multi-factor authentication method is typically categorized in one of three ways:
What is an authentication factor?
An authentication factor is a category of credential used for identity verification. For MFA, each additional factor is intended to increase the assurance that an entity involved in some kind of communication or requesting access to a system is who — or what — it says it is.
What is the difference between multi-factor authentication and 2FA?
Multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication are both security measures that provide an additional layer of protection to your online accounts beyond just a username and password. While MFA combines any number of authentication factors to verify someone’s identity, the most common type is 2FA.
Is multi-factor authentication (MFA) worth it?
Explore Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) products. While some feel like this process is a minor inconvenience, or it takes too long to set up, it’s worth it in the long run to have a higher level of security. Every other day we hear about accounts and records being compromised worldwide. MFA can help prevent this.