An organization’s growth thrives on talent and the competencies of resources. With ever-increasing competition and demand for valued talent, leaders need to stay atop their game and utilize their workforce optimally.
For this, they must balance available resources with the ever-evolving demands of projects to ensure successful project delivery. Since this requires strategic foresight into resource capacity and demand, organizations must implement robust capacity planning solutions.
However, to manage capacity and improve resource utilization across the entire organization, one must first know how to measure resource capacity and demand.
Let’s take an in-depth understanding of some concepts that are imperative to measure Capacity and Demand.
With the dynamics of today’s business landscape, organizations must be nimble and responsive in aligning their resources. Effective operations and supply chain management demand strategic processes to match production output with customer demand. This brings us to two integral concepts – capacity planning and demand planning. While interrelated, there are fundamental differences between the two that organizations must recognize.
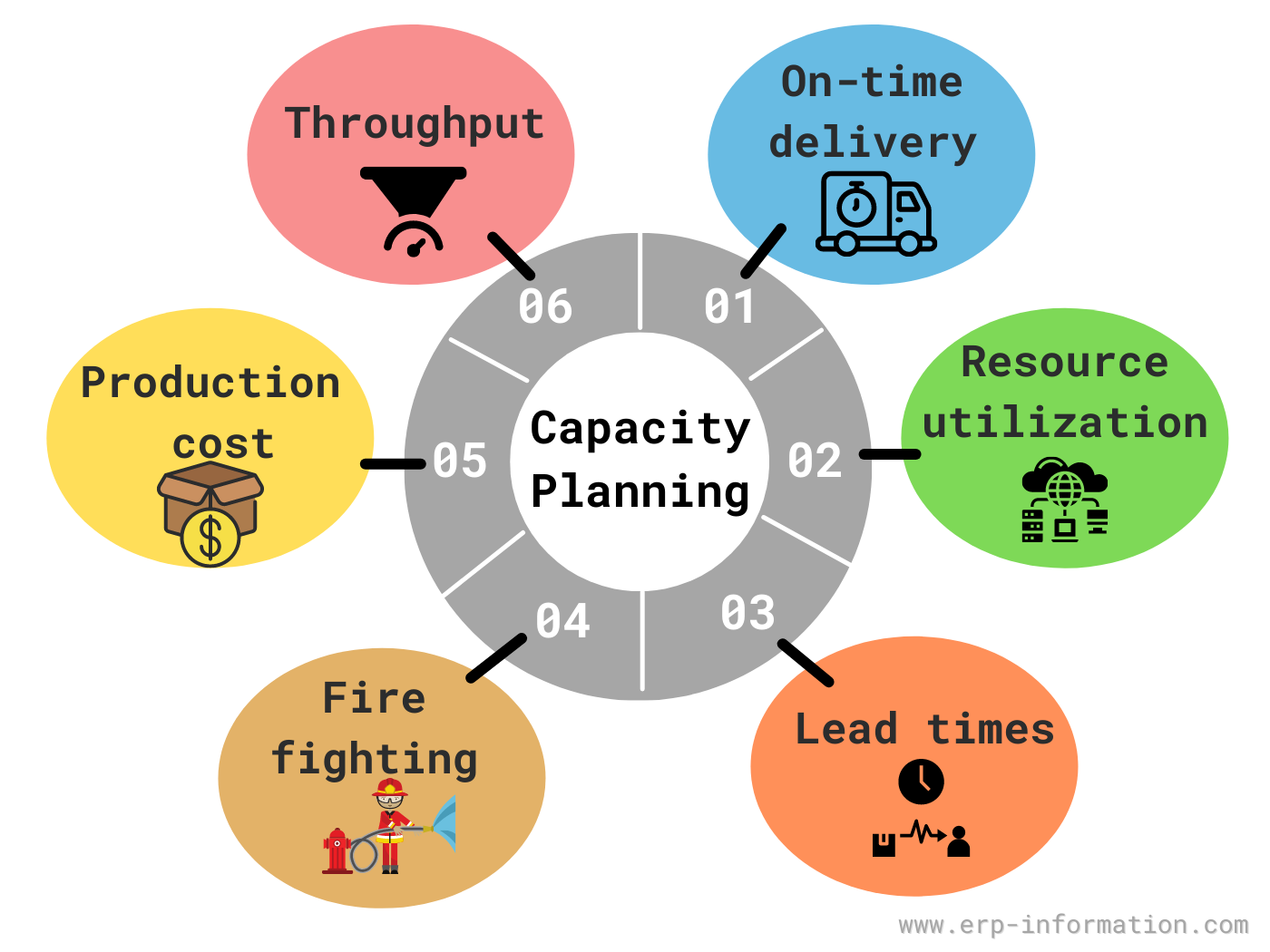
What is Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning is a strategic process of determining and aligning an organization’s resources to meet the anticipated demand for its products or services. It evaluates the workforce equipment facilities, and technology required to support planned production or operations.
The key aspects of capacity planning include:
-
Forecasting future demand – Using historical data, sales projections, and market analysis to estimate upcoming demand.
-
Assessing resource requirements – Identifying the workforce, tools, inventory, and other resources needed to meet the projected demand.
-
Analyzing current capacity – Evaluating existing capacity levels and constraints within the organization
-
Identifying capacity gaps – Comparing required capacity to current capacity to pinpoint shortages or excess.
-
Developing capacity strategies – Formulating plans to align capacity with demand, such as workforce hiring/training, adding equipment, process improvements etc.
The time horizon in capacity planning is generally medium to long term, from one year to five years. It enables organizations to make strategic decisions on scaling their resources to support growth objectives and prepare for variations in demand.
What is Demand Planning?
Demand planning focuses on accurately forecasting upcoming demand for products and services. It leverages historical data, predictive analytics, and inputs from multiple stakeholders to estimate consumer demand. The key elements include:
-
Demand forecasting – Developing quantitative projections for demand over a specified timeframe based on statistical models, predictive analytics, and qualitative insights.
-
Market intelligence – Continuous analysis of changing market conditions, trends, and competitive landscape that can impact demand.
-
Customer collaboration – Engaging with customers to gain insights into upcoming requirements, promotions, and demand fluctuations.
-
Integrated planning – Aligning with financial planning, supply planning, and S&OP (sales and operations planning) functions.
The time horizon for demand planning is usually short to medium term, ranging from one month to around 18 months. It enables organizations to improve forecast accuracy, reduce inventory costs, and enhance value chain collaboration.
Key Differences Between Capacity and Demand Planning
While capacity planning and demand planning are complementary disciplines, there are some notable differences:
| Capacity Planning | Demand Planning |
|---|---|
| Strategic process | Operational process |
| Assesses resource requirements | Forecasts customer demand |
| Considers constraints within the organization | Considers external market factors |
| Identifies gaps between capacity and demand | Seeks to improve forecast accuracy |
| Time horizon: 1-5 years | Time horizon: 1-18 months |
| Input for strategy and growth planning | Input for production planning and sales |
The Relationship Between Capacity and Demand Planning
Although distinct processes, capacity and demand planning work hand-in-hand to optimize organizational planning:
-
Demand forecasts from demand planning serve as a key input for capacity requirements during capacity planning.
-
By identifying capacity constraints, capacity planning provides inputs to refine demand forecasts to realistic levels.
-
Collaboration between capacity and demand planners enables integrated decision making, aligning resources and capabilities with projected demands.
-
Demand planning supports short to medium term production and sales planning while capacity planning guides long term strategic resource planning.
-
Effective capacity planning relies on accurate demand forecasts while demand planning helps avoid inefficient over or under capacity.
Best Practices for Capacity and Demand Planning
To leverage the synergy between capacity and demand planning, organizations should:
-
Promote cross-functional coordination – Ensure close collaboration between capacity planners, demand planners, and other teams for integrated planning.
-
Leverage data analytics – Use statistical forecasting models and predictive analytics to generate insights.
-
Maintain flexibility – Build in flexibility to adjust capacity or demand projections as market conditions evolve.
-
Refine continuously – Continuously monitor planning effectiveness and refine assumptions, data inputs, and algorithms accordingly.
-
Automate workflows– Use capacity planning and demand planning software to standardize processes and accelerate plan generation.
Capacity Planning Strategies
While balancing capacity and demand, organizations can consider three key strategies:
Lead Capacity Strategy
Increase capacity in advance to meet anticipated demand growth. This provides buffer for demand variability but risks excess capacity if forecasts are inaccurate.
Lag Strategy
Delay adding capacity until demand materializes. This minimizes excess capacity but can lead to reactive decisions and lost sales from stock-outs.
Matching Strategy
Add capacity incrementally to match current demand trends. This balanced approach requires accurate forecasting and nimble execution.
The optimal strategy depends on the organization’s operating environment, industry dynamics, and challenges faced.
Key Capacity Planning Challenges
Some common capacity planning challenges include:
- Insufficient data for accurate demand forecasts
- Long equipment lead times restricting quick capacity expansion
- Overestimation of capacity needs resulting in overcapacity
- Failure to account for external disruptions that alter demand
- Information disconnects between sales, marketing, and capacity planners
- Resource conflicts between legacy and new product capacity demands
Importance of Capacity and Demand Planning Alignment
When capacity and demand planning work in tandem, organizations can realize substantial benefits:
-
Improved customer service – Supply consistently matches demand to avoid stock-outs.
-
Reduced costs – Minimal waste from unused capacity or excess inventory holding.
-
Greater agility – Flexible capacity can quickly align with volatile customer demand.
-
Increased productivity – Smooth production throughput with minimal bottlenecks.
-
Optimized investments – Resources allocated for maximum ROI based on sound forecasts.
In today’s dynamic business climate, organizations must master strategic alignment of demand and resources. While capacity planning and demand planning have distinct scope and objectives, effective integration of the two is imperative for operational excellence. With cross-functional coordination, leveraging analytics, and continuous refinement, organizations can realize their full potential.
Best practices for calculating resource capacity and demand
This section explores how organizations can calculate resource capacity and demand to maintain a competitive edge. Let’s go through them one by one.
Our Insightful eBooks Just for You

Capacity Planning vs Demand Forecasting
What is capacity planning?
Capacity planning is a strategic, forward-looking process that aims to align an organization’s resources with its projected demand. It involves a comprehensive analysis of workforce capabilities, tool availability, and production capacities to ensure that the right resources are in place to meet future customer requirements.
What is demand planning & capacity planning?
Demand planning is a process that enables an organization to predict the demand for products so they can ensure they have enough supplies, or skilled team members, to deliver to consumers. The goal is to have a balance between producing enough inventory and not having a surplus. Demand planning and capacity planning are often used interchangeably.
How does capacity planning differ across industries?
Capacity planning can vary significantly across industries given the differences in demand patterns, production processes, and resource requirements. Despite these differences, the underlying goal of capacity planning remains consistent: focusing on aligning resources with demand to optimize operational performance.
What is the difference between capacity planning and resource planning?
Time Horizon: Capacity planning is a long-term endeavor, often spanning months or years, as it involves forecasting future demand and adjusting resource levels accordingly. Resource planning, however, typically operates on a shorter time horizon, dealing with the allocation of existing resources over weeks or months.