Deciding whether to pursue an MBA or a more specialized Master’s degree in Economics or Finance can be a difficult choice. Both paths offer valuable skills and knowledge that can advance your career, but there are some key differences between these degrees that are worth considering. In this article we’ll explore the main distinctions between an MBA, Master’s in Economics and Master’s in Finance to help you determine which is the best fit for your goals and interests.
A Brief Overview of MBA, Economics, and Finance Degrees
An MBA is a broad business degree that covers topics like marketing, accounting, management, finance, and more The curriculum provides a big picture view of business operations MBAs are often sought by those interested in management, executive, or entrepreneurial career paths.
A Master’s degree in Economics involves more specialized training in economic theory, research methods, statistical analysis, and forecasting. Graduates pursue roles as professional economists in the public and private sectors.
A Master’s in Finance focuses specifically on financial management topics like investments, corporate finance, risk management, and securities analysis. It prepares students for careers as financial analysts, managers, or advisors.
Comparing the Core Differences
Scope of Curriculum
The most fundamental difference between an MBA and specialized Master’s degrees lies in the scope of the curriculum.
MBA programs provide an overview of numerous business disciplines. The broad curriculum equips graduates to understand how different functions and teams interact within an organization.
Conversely, Master’s degrees in Economics and Finance offer an in-depth education in those specific fields. You’ll take advanced courses tailored to the niche you want to work in. The focused curriculum gives you specialized expertise in applying economic and financial models, theories, and analytical tools.
Math and Statistics Requirements
Master’s degrees in Economics and Finance demand more proficiency in mathematics and statistics than most MBA programs.
MBAs require a basic background in algebra and statistics. The math is applied conceptually rather than theoretically.
Economics and Finance Master’s programs expect students to have taken higher level math like calculus and linear algebra. You’ll rely heavily on mathematical theories and statistical methods. Advanced analytics capabilities are essential for modeling economic forecasts or financial risks.
Career Paths
The different scopes of these degrees translate to different career trajectories.
An MBA provides versatile business training applicable across industries and functional areas. MBAs often pursue leadership, executive, or entrepreneurial roles. Their comprehensive business acumen helps them oversee cross-departmental initiatives and strategy.
A Master’s in Economics is ideal for public sector roles like economic policy analysis, forecasting, and research. Graduates may work for government agencies or think tanks informing policy decisions. The degree also qualifies graduates for private sector economist jobs.
A Master’s in Finance prepares students for jobs analyzing investments, preparing forecasts, managing risk, advising clients, or making strategic financial decisions for companies. Graduates are especially coveted within the finance industry.
Pros and Cons of Each Degree
Weighing the unique advantages and disadvantages of the MBA, Economics Master’s, and Finance Master’s can shed light on which is the best option for your goals.
MBA Degree
Pros:
- Broad business training applicable across roles and industries
- Develops leadership, communication, and strategic decision-making skills
- Versatile credential that signals management potential to employers
- Highest median salaries of the three degrees
Cons:
- Less specialized expertise in a particular discipline
- Does not provide technical skills for specific finance or economist roles
- Programs have higher tuition costs on average
Master’s in Economics
Pros:
- Focused training in advanced economic theories and models
- Builds highly technical analytical skills for modeling and forecasting
- Qualifies graduates for specialized economist roles in diverse industries
Cons:
- Not as broadly applicable across business functions
- Heavy quantitative focus requiring high math proficiency
- Fewer job prospects outside economic analysis and policy roles
Master’s in Finance
Pros:
- Develops specialized expertise in all aspects of finance management
- Prepares graduates for lucrative roles across the finance industry
- Builds technical modeling, analysis, and risk management skills
Cons:
- Less applicable to other business functions or industries
- Highly technical focus with intensive math requirements
- Typically lower salary potential than an MBA
Which Degree is the Right Fit For You?
Choosing between an MBA, Master’s in Economics, and Master’s in Finance depends largely on your career goals and interests.
The MBA is the most versatile option for general management roles across various businesses and industries. It offers the highest salary potential in many cases too.
A Master’s in Economics is ideal if you want to work as a professional, policy, or research economist. The heavy analytical focus prepares you for this specialized niche.
The Master’s in Finance is suited to those seeking technical finance positions like financial analyst, investment advisor, or fund manager. It provides targeted training for financial management careers.
Take time to reflect on your specific skills, interests, and aspirations. Weigh the pros, cons, and career paths associated with each degree. Talking to graduates, professors, and industry professionals can also provide helpful insights. Select the graduate program that aligns with your professional objectives and will provide the knowledge you need to excel in your chosen field.
With careful evaluation of these three promising options – MBA, Master’s in Economics, and Master’s in Finance – you can feel confident choosing the degree that will empower you to reach your full career potential.
Master of Science in Economics
Generally speaking, economics is a discipline that focuses primarily on the “big picture” of human behavior, including how that behavior influences labor, resource, and investment allocations. While economics is related to finance and often deals with financial topics, economics professionals focus less granularly on areas that are of the greatest interest to finance professionals. In some regards, economics has historically been seen as a theoretical field, but this perception is changing.
Some of the most in-demand economics-related careers include:
- Economist
- Securities Trader
- Financial Manager
- Business or Financial Lawyer
- Actuary
- Management Consultant
- Budget and Pricing Analyst
Typically, a relevant master’s degree, such as a Master of Science in Economics, is a prerequisite to working in these roles. This degree is designed to provide students with a broad but profound understanding of economic theory, quantitative methods, and economic analysis that will guide their careers.
At Northeastern, the Master of Science in Economics is designed as a terminal graduate degree for those wishing to work as professional economists, economic consultants, and government officials. The degree also provides a strong foundation for those interested in pursuing a PhD in Economics. The program concentrates on the real-world application of economic theory. By incorporating paid co-ops into the curriculum, students have the opportunity to gain hands-on experience and put their education into immediate practice.
Master of Science in Finance
While economics focuses broadly on a government’s approach to money, spending, and resources, the finance field concentrates on how individual people and companies manage money. Because this occurs within the broader economic context, financial professionals must still be familiar with economic theory and practice, but their day-to-day focus is typically on more granular issues of budgeting, cash-flow, and business development.
Some of the most popular finance jobs include:
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Financial Analyst
- Internal Auditor
- Insurance Underwriter
While a graduate degree is not strictly a requirement, earning a relevant master’s degree (such as a Master of Science in Finance) can make career advancement more likely, as it implies a certain level of expertise necessary to perform these jobs well. Though the specifics of such a degree will depend on the program that you enroll in, they tend to blend together economics, mathematics, and computer science along with financial theory and application.
At Northeastern, the Master of Science in Finance is designed to prepare students for new and emerging positions in the financial industry, including those which require FinTech experience and analytical capabilities. In addition, the curriculum pushes students to develop important “soft” or “human” skills such as effective communication and leadership to empower them to be more productive in their roles. This coursework is also designed to prepare students for a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, should they choose to pursue it.
Specialized Master’s vs. MBA | You need to know THIS before you make a decision
FAQ
Who earns more MBA or masters in finance?
|
|
MS in Finance
|
MBA
|
|
Salary Potential*
|
Average earning potential ranges from $80,000 to $141,000+
|
Average earning potential ranges from $63,000 to $160,000+
|
What’s the difference between an MBA and a Master’s in economics?
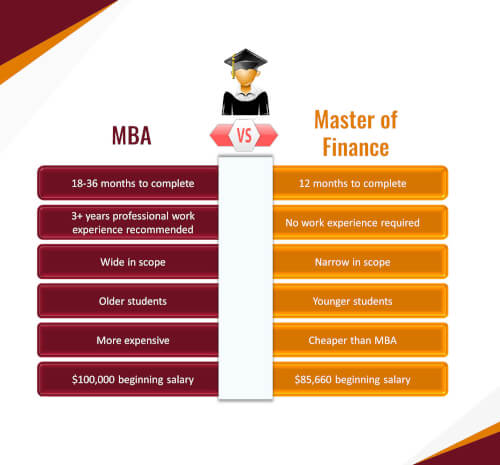
It comes down to figuring out the types of skills you are trying to get and what job you see yourself pursuing. MBAs are more expensive to obtain than a master’s in finance or economics. MBA programs are broader, while master’s programs in economics and finance are deeper.
What is the difference between a Master of Economics & Finance?
Here are some of the key differences and similarities between these programs to help you make your choice: The main difference between a Master of Economics or Finance and an MBA is the specialization and depth of studies in an economics or finance degree.
What is the difference between an MBA and a Master’s?
MBA programs cover a wide range of business topics, whereas master’s programs in economics and finance are more subject-focused. An MBA will cover finance and economics, but it will also cover other business topics. Learning about a wide range of fields, from marketing to accountancy and information technology, can be quite beneficial.
What’s the difference between an MBA and a finance degree?
Part of that difference can be explained by MBA graduates typically having more work experience, along with graduates in these programs pursuing different kinds of roles, even if they’re both in the realm of finance, according to information from the school.