Effective leadership is essential for any successful organization But with so many approaches to choose from, how do you know which style is right for your company?
In this comprehensive guide we’ll compare and contrast three of the most common leadership models – shared leadership, traditional leadership and team leadership.
Exploring the pros, cons, and situational appropriateness of each approach will provide the insights you need to determine the best leadership structure for your unique context.
What is Shared Leadership?
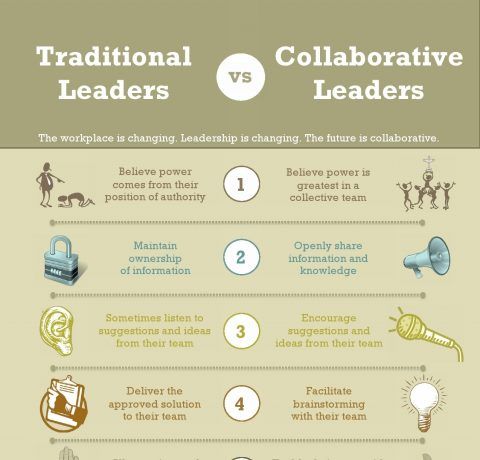
Shared leadership distributes power and influence across multiple team members rather than vesting authority solely in one designated leader. This collaborative model provides a Voice to all participants fosters joint decision making, and encourages mutual accountability.
With shared leadership:
- Leadership responsibilities are shared broadly
- Members have input into decisions
- Authority is distributed within the group
- There is no single decision maker
This egalitarian approach taps into the diverse skill sets and perspectives of the entire team. Shared leadership facilitates creativity, learning, and innovation through its emphasis on collaboration.
The Benefits of Shared Leadership
- Promotes democratic culture
- Facilitates collaboration
- Boosts engagement through inclusiveness
- Leverages diverse viewpoints
- Develops team capabilities through shared influence
- Fosters creativity and innovation
- Enhances commitment through participative decision making
When is Shared Leadership Most Appropriate?
Shared leadership tends to excel in these contexts:
- Highly competent teams: Skilled members can successfully share leadership duties
- Creative or complex projects: Diverse input facilitates innovation
- Egalitarian organizational cultures: Aligns well with democratic values
- Developmental objectives: Grows leadership skills across the team
- Tasks requiring collaboration: Joint participation enhances outcomes
However, shared leadership is less suitable in situations requiring rapid, unilateral decision making.
What is Traditional Leadership?
Traditional leadership concentrates authority and decision-making power in the hands of a single leader. This model features:
- A hierarchical structure with clear delineations of power
- A leader who directs the team and makes key decisions
- Followers who defer to the leader’s vision and judgment
This approach enables decisive action, consistency, and accountability through its centralized authority framework.
The Benefits of Traditional Leadership
- Enables speed and decisiveness
- Provides strong direction and vision
- Promotes efficiency through hierarchical structure
- Establishes clear accountability
- Suitable for specialized expertise areas
- Drives results through leader’s authority
When Does Traditional Leadership Work Best?
Traditional leadership thrives under these circumstances:
- Crisis situations: Quick, unilateral decisions are needed
- Specialized knowledge requirements: Reliance on leader’s expertise
- Complex regulatory environments: Hierarchy enhances compliance
- New, inexperienced teams: Leader provides guidance and oversight
- Period of transition: Leader steers change management
- Technical project focus: Leader provides vision and directives
However, traditional leadership can limit innovation and discourage critical input from team members.
What is Team Leadership?
Team leadership involves designating leadership duties to different team members based on their strengths and the needs of the project. While a formal hierarchical leader may still exist, leadership activities are distributed across the team.
With team leadership:
- Leadership shifts fluidly based on circumstances
- Different members lead based on their capabilities
- Collaborative decision making is emphasized
- There are fluid, shifting power dynamics
By leveraging members’ abilities, team leadership builds engagement and agility.
The Benefits of Team Leadership
- Capitalizes on members’ individual strengths
- Promotes engagement through leadership opportunities
- Develops member capabilities through leadership activities
- Enables versatility and agility in complex situations
- Fosters collective ownership of team direction
- Provides checks and balances on leader’s power
When Does Team Leadership Excel?
Team leadership works well under these conditions:
- Teams of highly competent specialists: Match leadership to expertise
- Complex or unpredictable environments: Flexibility aids adapting
- Creative projects: Inspires innovation through diverse leadership
- Development of future leaders: Growth opportunities for members
- Interdependent tasks: Collaboration enables success
- Large teams: Shared leadership prevents bottleneck
However, team leadership can result in confusion if coordination and communication are poor.
Key Differences Between the Models
| | Shared Leadership | Traditional Leadership | Team Leadership |
|-|
What Is shared leadership?
Shared leadership is when each employee within an organization takes ownership and responsibility for the part they play. In effect, shared leadership enables each employee to shoulder their work without the oversight from a command-and-control style manager.
It is a horizontal leadership model, where teams and employees make up the collective direction of the organization, as opposed to the traditional triangle model where vision and direction are dictated by an executive suite.
However, a critical aspect of shared leadership is that it is a gradient. This means shared leadership can take many forms and iterations. Here are two different examples that can both as ‘shared leadership.’
Example 2: Voted Leadership
Looking for a compromise between a rigid hierarchical structure and agile shared leadership is the Chinese appliance manufacturer, Haier, with their operational model: Rendanheyi.
Haier found that a traditional top-down hierarchical approach came with the lack of agility, but still wanted the visionary cohesion that a traditional leadership model comes with. The results with the Rendanheyi model, Haier found, were improved communication and productivity.
Essentially, the Rendanheyi is devised on, amongst other facets, micro-enterprises acting as smaller autonomous units within a larger company structure. The operational and tactical leadership within each unit is voted on by employees each year, while the visionary leadership is directed by upper management.
Thus, the Rendanheyi operational model is both shared and traditional leadership combined.

You will receive a list of questions along with a spreadsheet template to help you analyse your L&D strategy.
Concept of Shared Leadership For Lean (Shared Leadership Vs Traditional Top-Down Approach)
What is the difference between shared leadership and traditional leadership?
With traditional leadership, there is typically a clear hierarchy and chain of command that can lead to feelings of inequality among team members. Shared leadership often leads to more democratic decision making processes, which can result in greater buy-in and commitment from team members.
What is the difference between traditional leadership and traditional leadership?
This type of leadership can help to promote creativity and collaboration within a team. Traditional leadership, on the other hand, typically involves a leader who has sole decision-making power. While this type of leadership can be effective in some situations, it can also lead to stagnation and a lack of creativity.
Do groups with shared leadership styles have a primary leader?
While groups with shared leadership styles may still have a primary formal leader, it’s this manager’s or executive’s responsibility to share their authority with others to ensure that they’re not the only decision maker within the organization or team.
What is shared and team leadership?
Leadership approaches, such as shared and team leadership, encourage an open spread of information across an organization and rely on the dissemination of these details to ensure that all members of the company stay informed on important issues and initiatives.