Budgeting is an essential function of any business, necessary for both financial planning and growth. A master budget gathers a company’s lower-level budgets and incorporates them into one central document for ease of reference. Keep reading for a closer look at what’s included in a master budget, as well as how to use it.
A master budget is one of the most important tools businesses use to plan and manage their finances. But what exactly does a master budget include? This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key components of a master budget, how to prepare one, and why it’s so critical for business success.
What Is a Master Budget?
A master budget is a detailed forecast of a company’s revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows over a specific time period, usually one year. It integrates all the organization’s individual functional budgets into one consolidated financial plan.
The master budget serves as a roadmap for a company’s operations and strategic goals. It helps managers coordinate activities across departments and ensures that the company’s departments are aligned in meeting financial objectives.
Why Is a Master Budget Important?
A master budget provides numerous benefits for an organization
-
It forces managers to think ahead, anticipate changes, and develop concrete plans.
-
It coordinates activities across departments and business units
-
It helps allocate resources efficiently based on forecasted needs.
-
It enables measurement of actual financial results against planned results.
-
It aids in cash flow management, cost control, and profit planning.
Who Is Involved in Preparing the Master Budget?
While the financial controller or CFO typically oversees master budget preparation, multiple departments are involved in the process:
-
Sales department: Provides the sales forecast that determines anticipated revenues.
-
Production department: Prepares production budgets and schedules.
-
Procurement department: Prepares purchase budgets.
-
Human resources department: Develops the labor budget.
-
Department managers: Estimate their own department’s expenses.
-
Finance department: Consolidates all the functional budgets into the master budget.
This cross-departmental involvement helps ensure that the master budget is accurate, realistic, and reflective of the entire organization’s needs.
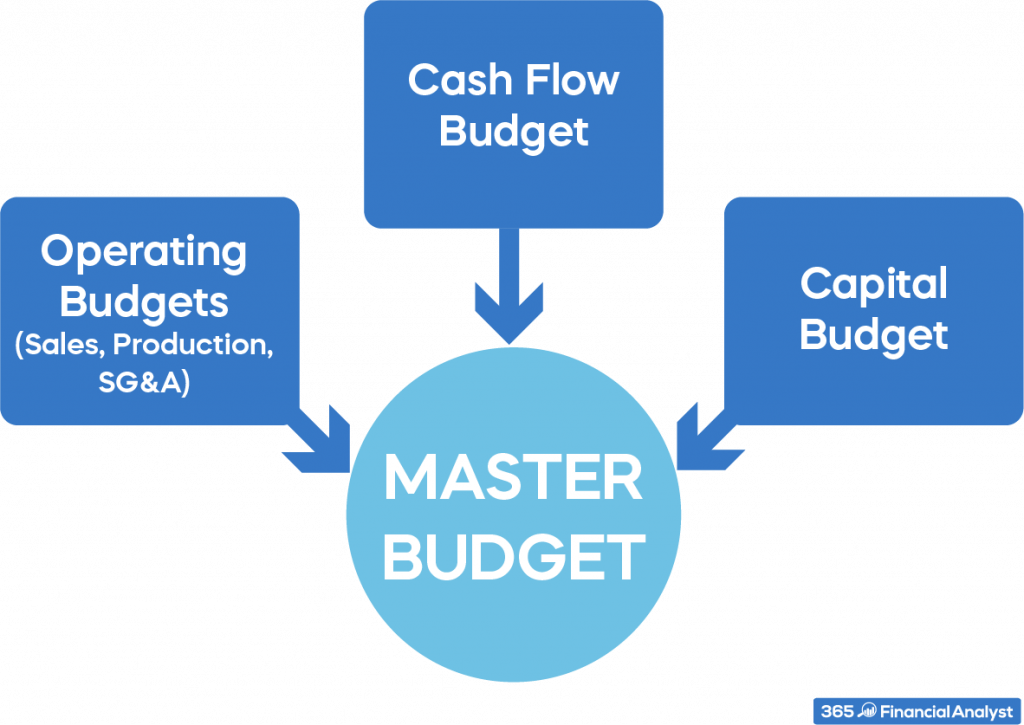
What Are the Key Components of a Master Budget?
A master budget comprises several distinct components. Here are some of the most common elements:
1. Sales Budget
The sales budget is typically the starting point for the master budget. It projects total sales volume and revenues based on the sales forecast. The sales budget determines production levels and provides the foundation for the overall budget.
2. Production Budget
The production budget outlines the number of units that must be manufactured to meet the sales forecast. This budget balances projected sales volume and the inventories needed to avoid stock-outs.
3. Direct Material Budget
This budget projects the quantity and cost of raw materials required for production based on sales estimates. It accounts for desired ending inventory levels.
4. Direct Labor Budget
The direct labor budget estimates the time and cost of labor required to produce the number of units in the production budget. This includes staff directly involved in manufacturing.
5. Manufacturing Overhead Budget
This budget covers production costs other than direct materials and labor, such as utilities and equipment depreciation. Overhead costs are allocated to units produced.
6. Selling and Administrative Expense Budget
This budget forecasts expenses unrelated to production, such as marketing, sales commissions, and general administration. It is based on historical data.
7. Cash Budget
The cash budget helps manage cash inflows and outflows. It projects cash receipts from sales, cash disbursements for expenses, and the resulting cash surplus or deficit.
8. Budgeted Income Statement
This statement presents the anticipated revenues, expenses, and net income for the budget period based on all the budget components above. It shows whether a profit or loss is expected.
9. Budgeted Balance Sheet
The budgeted balance sheet shows the expected assets, liabilities, and equity accounts at the end of the budget period. It is based on the changes projected in the various budgets.
How Do You Create a Master Budget?
Here is an overview of the steps involved in developing a master budget:
-
Set budget objectives: Define the purpose and goals you want to achieve, based on company strategy.
-
Make forecasting assumptions: Project economic factors like demand, costs, and availability of resources.
-
Create functional budgets: Have each department prepare its own budget projections.
-
Consolidate departmental budgets: Integrate all budgets into a consolidated master budget.
-
Senior management approval: Review, adjust, and approve the final master budget.
-
Monitoring and updating: Assess budget vs. actual results and revise projections as needed.
Master Budget Example
Let’s look at a simplified example to understand how a master budget comes together:
-
The sales department projects $1 million in sales.
-
The production department determines 800 units must be manufactured to support $1 million in sales.
-
Direct materials are estimated at $200,000 for 800 units.
-
Direct labor is estimated at $150,000 for 800 units.
-
Manufacturing overhead totals $100,000 based on historical averages.
-
Selling expenses are forecast at $200,000 based on projected sales.
-
Administrative expenses are budgeted at $150,000.
-
The total master budget compiled from these projections forecasts $1 million in sales revenue, $600,000 in production costs, $350,000 in operating expenses, and $50,000 in net income.
This example shows how consolidating all the individual functional budgets allows analysis of revenues, costs, and profits across the organization.
Challenges in Master Budgeting
While master budgets are invaluable management tools, preparing them can be difficult:
-
Sales forecasts may be overly optimistic or pessimistic.
-
It’s challenging to accurately predict costs and expenses.
-
Lack of coordination across departments can skew projections.
-
Sudden competitive or market changes can quickly render budgets obsolete.
-
People may intentionally underestimate costs or overestimate sales.
To address these challenges, budgets must contain enough flexibility to adapt to changing conditions. Financial managers also need contingency plans for different scenarios.
Tips for Effective Master Budgeting
Here are some tips to create accurate, useful master budgets:
-
Involve operations personnel in the forecasting process to improve buy-in.
-
Use rolling budgets that are updated periodically rather than static annual budgets.
-
Build in contingencies for cost overruns and revenue shortfalls.
-
Use multiple data sources to make sales forecasts more precise.
-
Analyze variances between actual and budgeted figures, and adjust projections accordingly.
-
Use budgeting software tools to improve efficiency and accuracy.
The Bottom Line
A well-developed master budget is vital for aligning strategy, coordinating plans, allocating resources, and monitoring performance across an organization. While budgeting has its challenges, proper preparation and participation can lead to budgets that provide immense business value. Master budgets enable data-driven decisions and keep companies financially on-track in the short and long term.
Are there any challenges to using a master budget?
As you can see, the master budget is quite comprehensive, giving a detailed account of all expected cash inflows, outflows, and wider expenses. However, it’s not always entirely accurate. One issue that can crop up is the fact that some figures are more difficult to estimate than others. For example, net change in working capital can fluctuate, particularly during periods of rapid growth. Budgeting for inventory can also present a challenge. With more sales, there’s a higher need for more inventory – which can lead to negative cash flows before the resulting payments come in.
These are factors that need to be considered when calculating the master budget. Another is the use of the master budget for employee goal setting and incentives. If management incentivizes sticking to the budget with bonuses, it could drive employees to low-ball their estimated sales and go too high with estimated expenses. This gives more room for error than necessary in meeting these targets. It’s important to keep this in mind when gauging the accuracy of any master budget – particularly if it involves input from multiple departments.
GoCardless helps you automate payment collection, cutting down on the amount of admin your team needs to deal with when chasing invoices. Find out how GoCardless can help you with ad hoc payments or recurring payments.
How does a master budget work?
Master budgets are prepared as part of small business accounting, usually on a monthly or quarterly basis to cover the full fiscal year. Companies might tack on extra months to the end of the budget to keep it rolling forward, a process called continuous budgeting.
In addition to the budgeted financial statements, the master budget also showcases a financing plan and cash flow forecast. Some businesses will include a statement of purpose to explain how the master budget fits into the business’s future financial goals. There is a great deal of flexibility within the document, as it’s used by the company’s management to make planning decisions. The budget director is responsible for maintaining this document, using input from various departments and employees.
The Master Budget
What are the components of a Master Budget?
The components of a master budget include: The planned operating budget may include these items: Sales budget: The sales budget includes a forecast of how many units the company plans to sell during the year and how much income that would generate.
What is a Master Budget?
These are a planned operating budget, which details how much the organization projects for its income, and a financial budget, which details how much it plans to spend and on what. The individual budgets and level of detail to use for your master budget depend on the company’s size and level of complexity. The components of a master budget include:
How to create a Master Budget?
Preparation of a master budget happens later in the financial planning process when the company has already decided its goals and expectations for sales and investments. After the company completes its initial data gathering, it creates a master budget with these steps: 1. Create individual budgets
What does a Master budget look like?
This is not the case for the master budget, which looks very much like a standard set of financial statements. The income statement and balance sheet will be in the normal format mandated by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or International Financial Reporting Standards.