In today’s fast-paced corporate world, businesses often require 24/7 coverage to meet customer demands. Many companies adopt rotating shifts to ensure seamless operations as part of their workforce management strategy.
How do you schedule your staff if your company is open for fourteen, sixteen, or twenty-four hours daily? Do you assign one team to work only at night and the other to work only during the day? When do your staff have a vacation? When you consider the mechanics, it’s easy to see how scheduling may quickly devolve into a chaotic nightmare. Fortunately, a simple solution to this quandary is the rotating shift.
This blog post will explore rotating shifts, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and best practices for implementing them effectively. As a leading provider of workforce management solutions, Celayix understands the importance of optimizing schedules to maximize productivity while prioritizing employee well-being.
Rotating shifts refer to a workforce scheduling practice where employees work different shifts at different times of the day or week. This approach ensures that staffing needs are met throughout the day, ensuring continuous operations without overburdening employees or incurring excessive overtime costs. According to a study by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, an estimated 2.4% of the working population works rotating shifts.
Rotational shift work, commonly known as rotating shifts, is a dynamic scheduling system where employees follow a cyclical pattern of working various shifts, including the day, night, and any necessary swing shifts. This approach allows businesses to maintain 24/7 coverage efficiently while promoting employee satisfaction and productivity.
On the other hand, fixed schedules follow a different model, where different groups of employees are assigned to work specific shifts consistently. For instance, one group handles the day shift, another the night shift, and a third group manages the swing shift. The fixed schedule remains unchanged unless intentional shifts are made to individual employees’ assignments.
Rotating shift schedules where employees rotate through different work shifts rather than working a fixed schedule are becoming increasingly common. While rotating shifts offer some benefits for employers and employees, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
In this article, we’ll explore the key pros and cons of using a rotating shift schedule to help you determine if it’s the right approach for your workplace.
What Are Rotating Shift Schedules?
With a rotating shift schedule employees periodically transition between different shifts rather than working the same hours every day or week.
Common rotating shifts include:
- Day shift – Typically 8am to 4pm
- Evening shift – Often 4pm to midnight
- Night shift or graveyard shift – Midnight to 8am is most common
Employees rotate through these various shifts on a fixed weekly, monthly, or other recurring schedule. For example, an employee might work mornings for a week, then evenings the next week before transitioning to overnights.
The cycle then repeats, so the employee continues transitioning between the allotted shift times. The goal is to cover staffing needs throughout a 24-hour period by having employees work at varied times.
Now let’s explore the potential advantages and disadvantages of using rotating shifts.
The Pros of Rotating Shift Schedules
There are several reasons why rotating shifts can be an effective approach, including:
1. Flexible Coverage
Having employees work at different times makes it easier to ensure you have enough staff whenever needed. You can match staff levels to busier periods while minimizing unnecessary overtime costs.
2. Fulfilling 24/7 Staffing Requirements
Some roles, like healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, require round-the-clock staffing. Rotating shifts allow you to cover all hours without hiring more staff.
3. Accommodating Employee Needs
Rotating shifts can provide flexibility to employees. Those with personal obligations like childcare can work shifts that fit their schedules. Employees seeking more variety can gain experience working different hours.
4. Reduced Employee Burnout
By rotating shifts, employees avoid the exhaustion of working undesirable shifts for too long. Frequent changes provide a break from particularly draining shift times.
5. Broadened Employee Perspectives
Working various shifts exposes employees to different aspects of a role. They interact with unique coworkers and customers while handling distinctive tasks. This can broaden perspectives and skills.
6. Improved Morale From Schedule Equity
When shifts rotate, every employee must work the less desirable shifts instead of pushing those consistently onto a few employees. The equitable schedule can improve morale.
As you can see, rotating shift schedules offer several potential upsides for employers aiming to meet staffing needs while accommodating employees. However, there are also some drawbacks to consider.
The Cons of Rotating Shift Schedules
While rotating shifts provide benefits, the frequent schedule changes can also create challenges, such as:
1. Disrupted Sleep Schedules
Frequently alternating between day and night shifts makes it hard for employees to maintain consistent sleep patterns. This can lead to increased fatigue.
2. Communication Challenges
When employees work different shifts, it can be difficult to communicate and coordinate plans. This makes smooth operations more complex.
3. Decreased Productivity From Fatigue
Working overnight shifts often causes significant fatigue. Productivity and work quality frequently decline when employees are exhausted.
4. Higher Employee Turnover
Some employees struggle to adapt to rotating shifts, especially overnight assignments. The schedule challenges increase turnover risk.
5. Difficulty Planning Life Outside Work
Frequent shift changes make scheduling childcare, school, and other obligations complicated. Employees’ personal lives can suffer under shifting schedules.
6. Challenging Schedule Creation
It takes significant effort and skill to create equitable rotating shifts meeting staffing needs while incorporating employee preferences. Doing this well is difficult.
As you can see, rotating shifts can present productivity, morale, and logistical difficulties. However, the impact varies based on implementation and management strategies.
Best Practices for Effective Rotating Shift Schedules
While rotating shifts have drawbacks, following best practices can help maximize the benefits while minimizing the pitfalls:
- Provide as much schedule consistency and advance notice as possible. This helps employees plan.
- Build in transition days between certain shift changes to allow the body to adjust.
- Avoid scheduling more than 3-4 consecutive overnight shifts, which causes extreme fatigue.
- Periodically gather employee feedback on the rotating shifts to identify issues.
- Offer shift swapping flexibility so employees can adjust schedules when needed.
- Provide training for managers on supporting employees working various shifts.
- Analyze productivity data by shift to catch any emerging issues.
- Offer wellness resources like sleep hygiene education to support employee health.
Key Considerations When Evaluating Rotating Shifts
Assess the following to determine if rotating shifts are the right fit for your organization:
- Staffing requirements – Do you need 24/7 staff coverage? Are shift hours driven by customer needs?
- Employee flexibility – Do employees want schedule variability and option to change hours?
- Work duties – Do tasks require specialized training that would make rotating difficult?
- Management capabilities – Do you have skillsets needed to create complex rotating schedules?
- Company culture – Will expected fatigue and communication issues negatively impact operations?
Carefully weighing the pros and cons of rotating shifts for your unique environment is key to deciding whether implementing them makes strategic sense.
Creating a Rotating Shift Schedule
If you determine rotating shifts are the best fit, follow these steps to build an effective schedule:
- Gather input. Survey employees on shift preferences and constraints to inform creation.
- Define shifts. Determine the daily shifts and hours based on business needs while considering laws regarding shift length and rest between shifts.
- Build the rotation. Create equitable, alternating cycles that avoid excessive overnight assignments and allow transition time between drastic shift changes.
- Accommodate requests. Work to incorporate employee preferences and obligations as much as possible.
- Communicate schedules. Provide the rotating schedule well in advance and outline shift swap options.
- Continuously improve. Gather regular feedback to identify needed changes to improve schedule effectiveness.
At their best, rotating shift schedules allow you to meet 24/7 staffing needs while providing employees schedule flexibility and variability. However, fatigue, communication issues, and personal disruption are possible drawbacks.
Carefully weigh the pros and cons for your workplace. If you move forward with implementation, effective management and communication are key to maximizing benefits and minimizing problems. With strategic execution, rotating shifts can be a win-win for both company and employees.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
Implementing rotating shifts can foster teamwork and collaboration among employees. Exposing team members to diverse colleagues with varying expertise and perspectives encourages knowledge sharing and mutual learning, leading to a more cohesive and innovative work environment. A study published in the Journal of Applied Psychology found that teams with higher levels of diversity demonstrated a 45% increase in decision-making efficiency compared to less diverse teams.
Types of Rotating Shifts
Human resource specialists have developed several sorts of rotational schedules over the years. Depending on management practices, your organization may profit from one or more rotating shifts. Human resource managers should become acquainted with several forms of rotating shifts.
This allows them to comprehend several staff rotation plans and select the one that works best for their organization.
Employees on the Pitman shift pattern receive every other weekend off to attend family and social gatherings during regular hours. The ships here are 12 hours long and have four crews rotating around. Workers usually work up to three days in a row to prevent overworking them.
Here’s an example of a Pitman shift schedule:
Two days of work followed by two days off
Two shifts on, then three days off
Three days of work followed by two days off
When the two-week cycle ends, workers exchange shifts, beginning with night shifts and ending with day shifts.
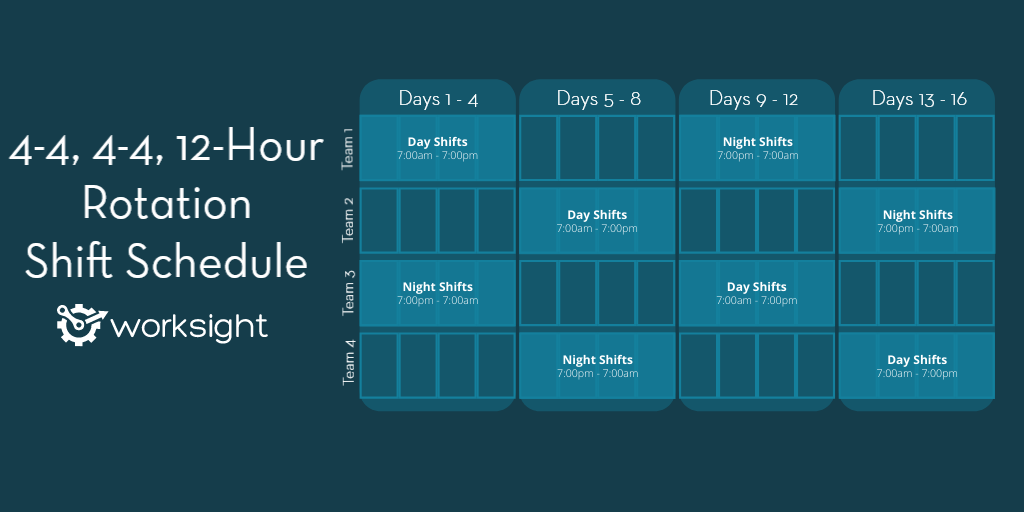
The 2-2-3-2-2-3 schedule is a 28-day cycle with a rotating shift. The 12-hour shifts in this schedule are alternated in the following pattern:
- Three-day workweeks
- Two days off
- 2-day shifts
- Three days of vacation
- Shifts of two nights
- Two days off
- Shifts of three nights
- Two days off
- Shifts of two nights
- Three days of vacation
- 2-day shifts
- Two days off

The advantage of this rotating schedule is that workers may take regular breaks without working more than three consecutive days. Employees in the construction and healthcare industries have rigorous 12-hour hours followed by many days off, as examples of this style’s rotating shift pattern.
Like the Pitman rotating shift, the DuPont shift schedule has four teams working 12-hour shifts, but the personnel rotation schedule is a bit more complicated. This shift changes from day to night in a four-week rotation at DuPont. Here’s an illustration:
- Four-night shifts followed by three days off
- Three days of work, followed by one day off
- Three nights of work, followed by three days off
- Four-day shifts followed by seven days off
There are consecutive offs here since the schedule may be a little stressful, but the DuPont system offers workers adequate time to recoup by having numerous days off. These days off culminate in a week-long break at the end of the cycle.
Managers should use caution when it comes to the DuPont shift schedule. Workers here have more flexibility in their everyday lives and spend more time with family and friends, but the trade-off is longer work hours. It could fit certain country employees who don’t mind working harder instead of taking more time off.
Ask Jim: Is It Better to Work Only Night Shifts, or Bounce Back and Forth?
What are the pros and cons of rotating shift schedules?
The pros and cons of rotating shift schedules can vary depending on where you work and the duties you handle. You may notice these schedules commonly in industries that perform work or provide services outside of standard business hours because they can help distribute non-standard business hour shifts equally.
What are the disadvantages of rotating shift work?
While rotating shifts bring certain benefits, this type of work schedule has its downsides too. According to an article on the effects of shift work on employees’ lives, health-related problems are one of the main drawbacks of shift work as rotational shift work can disrupt circadian rhythms.
Are fixed shifts better than rotating shifts?
Simply put, employees who work a fixed shift always work the same shift. Still, fixed shift schedules do not provide much flexibility to employees as they always work the same hours, while with rotating shift schedules, employees have a chance to choose when they work. What industries use rotating shifts?
Do rotating shifts offer less routine consistency for employees?
Rotating shifts may offer less routine consistency for employees because their work schedule can change from week to week or month to month. However, there are ways you can help promote routine consistency by planning rotating schedules to ease employees into working shifts at different times.