In today’s digitally driven world, a properly functioning IT infrastructure is absolutely crucial for any organization. Even minor IT issues can disrupt productivity and operations. That’s why having an effective IT service desk is a must. But what exactly is an IT service desk, and how does it benefit your business? This comprehensive guide provides all the key details you need to know.
Defining the IT Service Desk
An IT service desk is a central point of contact within the IT department that provides assistance and support to end users and customers. It serves as the “face” of IT operations by handling user queries, troubleshooting tech problems, resolving incidents, managing service requests, and more.
The service desk helps ensure the smooth delivery of IT services and a positive user experience. It may be a physical desk with technicians, a virtual team accessible by phone and online, or a sophisticated software platform. Most modern service desks involve a blend of people, processes, and technology.
Key functions of an IT service desk include:
-
Incident management – Restoring normal service as quickly as possible after an unplanned disruption or outage.
-
Service request management – Handling user requests for standard IT services like password resets, new hardware, or software access.
-
Problem management – Investigating the root causes of incidents to prevent recurrences.
-
Change management – Planning and implementing IT changes with minimal impact on operations.
-
Knowledge management – Documenting resolutions and best practices in a searchable knowledge base
-
Self-service – Enabling users to find information and resolve basic issues independently.
-
Reporting – Tracking IT metrics like incident volume, resolution time, user satisfaction, and cost
Benefits of a Service Desk
An optimized service desk provides tremendous value for both IT teams and the wider business, including:
-
Improved user productivity – Fast and effective issue resolution means less downtime for users Self-service also enables users to get back to work quickly,
-
Cost efficiency – Automation, knowledge sharing, and self-service reduce manual effort so staff can focus on high-value tasks.
-
Greater IT transparency – Service desks provide metrics and insights that help align IT with business objectives.
-
Enhanced customer service – Positive user experiences improve satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Proactive incident prevention – Identifying patterns helps address underlying problems before they disrupt service.
-
Faster innovation – With routine tasks automated, IT has more capacity to work on improvements and new capabilities.
-
Regulatory compliance – Change management and knowledge retention facilitates audit readiness.
Clearly, service desks are a strategic necessity, not just a technical support function. They maximize IT’s capability to deliver the services the business needs.
Service Desk vs. Help Desk
Service desk and help desk are sometimes used interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts:
Help Desk
-
Tactical function focused on resolving incidents
-
Limited scope: resetting passwords, troubleshooting issues, basic how-to support
-
Reactive: responds to user requests as they arise
Service Desk
-
Strategic function managing full lifecycle of service delivery
-
Broader scope: service requests, change management, problem prevention, self-service, knowledge management
-
Proactive: seeks to prevent incidents and continuously improve service
The help desk is a subset of the service desk focused on day-to-day IT support and operations. The service desk takes a bigger-picture view aligned with business objectives and overall service management.
Key Elements of an Effective Service Desk
World-class service desks share some vital characteristics:
1. Single Point of Contact
Having one easy-to-find place to get IT assistance provides a unified customer experience. This could be a phone number, email, website, chat platform, or within an internal app.
2. Service Catalog
A catalog of standard IT services helps users easily request what they need, like new hardware, software access, passwords, etc.
3. Knowledge Management
Reusable resolutions and documentation enable self-service and consistent support. Knowledge articles can assist with common issues or how-to queries.
4. Automation
AI chatbots, automatic ticket routing and escalation, and self-healing technology streamline service delivery.
5. Asset Management
Maintaining configuration details on all IT assets facilitates troubleshooting, compliance, and lifecycle management.
6. Change Management
Standard procedures minimize service disruption from IT changes like upgrades, migrations, and new releases.
7. Reporting and Metrics
Data on resolution time, uptime, costs, and satisfaction provides visibility and opportunities for improvement.
8. Problem Management
Root cause analysis of recurring incidents aims to prevent them proactively.
Implementing a Successful Service Desk
Follow these best practices when creating or improving an IT service desk:
Define goals and strategy – What key outcomes are you aiming for? Faster resolution? Lower costs? Improved satisfaction scores? Align to overall IT and business objectives.
Evaluate capabilities – Assess existing people, processes, and tools. Identify strengths to leverage and gaps to address.
Create service catalog – Document standard service offerings like hardware, software, access, configurations, training, and more.
Implement software – Choose user-friendly, customizable service desk software with robust functionality. Consider cloud vs. on-premises.
Integrate with ITSM processes – Connect service desk capabilities into broader incident, problem, change, and release management workflows.
Provide self-service options – Enable users to access knowledge, download software, reset passwords, and configure settings independently.
Improve knowledge management – Make resolving common problems faster and easier by capturing troubleshooting procedures, FAQs, and best practices.
Report on performance – Track KPIs like resolution time, uptime, costs per incident, and satisfaction to guide improvements.
Use automation – Escalate and route tickets automatically. Use chatbots for basic inquiries. Enable users to provision their own services.
Optimize team roles – Clarify responsibilities across first-, second- and third-line support teams.
Allow multi-channel contact – Phone, email, chat, self-service portal. Make it easy and convenient for users.
Gather user feedback – Survey end users and hold focus groups to identify areas for better meeting their needs.
IT Service Desk Models
There are three primary models for structuring an IT service desk:
Centralized – One unified service desk for the entire enterprise. Best for consistency, lower costs.
Decentralized – Multiple independent service desks for business units, regions, or functions. Better customization.
Hybrid – Combines overall centralized desk with some localized or specialized desks. Balances standardization with flexibility.
Determine the right approach based on your organization’s size, structure, locations, and specific requirements.
IT Service Desk Tools and Software
Specialized service desk software centralizes all the core capabilities:
-
Ticket management – Track, assign, escalate, categorize issues
-
Knowledge base – Document solutions with search and AI recommendations
-
Chat/Messaging – Communicate in real-time via chat, SMS, social media
-
Self-service portal – User forum, knowledge base, password resets, how-tos
-
Reporting and Metrics – Response times, uptime, costs, satisfaction
-
Change management – Plan, schedule, test, document changes
-
Asset management – Maintain inventory of all IT components
-
Automation – Chatbots, automatic ticket routing, and more
Leading options include ServiceNow, Freshdesk, BMC Helix, ManageEngine, Cherwell, IBM Cloud Pak for Watson AIOps, and more. Consider ease of use, ITSM integration, customization, mobility, security, and cost.
Many tools also integrate with other systems like IT asset management, automation platforms, and productivity software. AI capabilities like virtual agents and predictive analytics are growing capabilities. Cloud-based service desk software offers advantages like faster deployment, scalability, and lower TCO.
Making the Service Desk a Strategic Asset
Approaching the service desk as a purely technical function is short-sighted. Done right, it is a huge competitive advantage – delighting users with responsive, personalized support. Follow modern best practices and take advantage of automation, self-service, and integrated ITSM to transform your service desk from a cost center to a business accelerator.
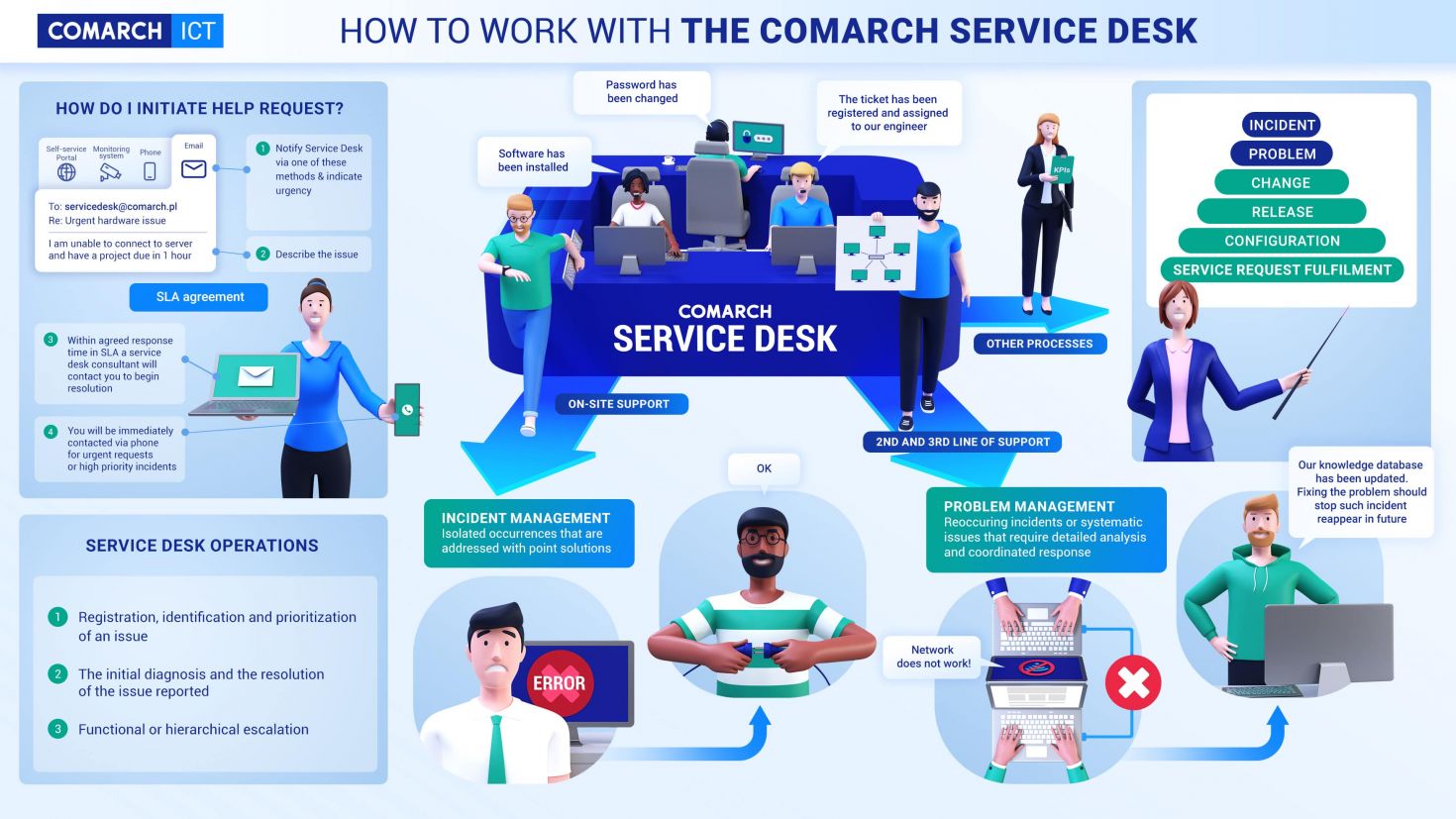
What is service desk?
An IT service desk is a communications center that provides a single point of contact (SPOC) between a company, its customers, employees and business partners.
The IT service desk assists throughout the entire product lifecycle and ensures that all users receive help promptly.
The benefits of a service desk
The IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a globally recognized collection of best practices for IT service management (ITSM).
This includes the set of processes used by IT teams for delivering the end product. ITIL defines the service desk as an essential ITSM tool that is part of the IT support ecosystem.
Service desks are designed to handle both incidents and service requests. An incident is an event that results in a disruption in service availability or quality. On the other hand, a service request seeks help with a routine task, such as helping a user change a password or getting a new user set up in work systems.
Other services provided may include change management, Release management and configuration-related tasks.
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) standard provides best practices for IT service management. It has evolved to address changing IT environments.
Service desks play a crucial role in business management. Here are some of the standard features and key benefits of a service desk:
- Ticketing system. Ticket management creates a ticket each time a user submits a support request. Service desk software also conducts ticket routing and automation. This helps in the organization and handling of queries.
- Customer service knowledge base. Service desks create a database of information that promotes self-service. This knowledge management ensures that customers can come here to get an answer to common queries.
- IT asset management. This refers to the organization of a companys assets for easier access to relevant information. It includes a configuration management database (CMDB) and asset valuation.
- Automation. Day-to-day tasks are automated and escalated such that the team members can focus on valuable work.
- Service-level agreement (SLA) management. Management of tickets based on SLAs provides an efficient workflow.
- Service catalog. This is an online catalog where the users have all the necessary information about the different services provided by the company.
- Incident management. This manages unplanned incidents such that the customer issues are resolved quickly, and the typical workflow can continue.
Popular ITSM frameworks include Six Sigma, ITIL and COBIT.
What is Service Desk Responsibility? | Organizing for Service Operation
What is the role of the IT service desk?
The multipurpose role of the IT service desk—which fulfills several objectives such as resolving issues quickly, nurturing user satisfaction, facilitating the efficiency of organizational processes, and providing actionable insights on organization productivity—demands a range of best practices that go well beyond traditional technical support.
What is an IT Help Desk?
An IT help desk is a component within the broader scope of IT service desks. IT service desks own and manage the IT service management processes, such as incident management, IT asset management, and more.
What is a service desk?
Service desks are the “face” of IT operations for employees, customers, suppliers, and business partners. They provide a centralized resource for getting help with IT incidents, as well as IT service requests like password resets or database access requests.
What is the difference between a service desk and a help desk?
The main focus of an IT help desk is on fixing issues, while a service desk is more broadly focused on delivering services to users. Therefore, the former is for tactical IT support, while the latter is more strategic. For example, the service desk also handles software licensing, service providers and third-party contracts related to ITSM.