- An operational amplifier is what? …
- Declare the premises used in the analysis of the perfect op-amp. …
- What does an op-voltage amp’s transfer curve mean? …
- What do a differential amplifier’s differential gain and common-mode gain mean? …
- Explain CMRR. …
- Why is an op-CMRR amp’s high?
Operational Amplifier questions and answers ¦OpAmp vivavoce!
Interview questions on OPAMP
1) What is CMRR?
Ans CMRR is defined as the ratio of differential voltage gain (Ad) to common mode voltage gain (Acm). The formula for CMRR is given below:
CMRR = Ad/Acm
2) What is characteristic of Ideal OPAMP? Important Interview questions on OPAMP
Ans Characteristic of ideal OPAMP are
1. Infinite voltage gain
2. Zero output impedance
3. infinite input impedance
4. Infinite slew rate
5. Characteristics not drifting with temperature
6. Infinite bandwidth
3) What is Amplifier? Important Interview questions on OPAMP
Ans Amplifier is a device that makes sound louder and signal level greater.
4) What is the Formula for Non Inverting Amplifier?
Ans The formula for non inverting amplifier is given as 1+Rf/R1
5) What is perfect balance in OPAMP? Important Interview questions on OPAMP
Ans Perfect balance is the characteristics of ideal OPAMP and if there is same input applied then we will get the output zero. In this condition it is known as perfect balance.
6)Which OPAMP don’t have feedback loop?
Ans Comparator OPAMP (operational amplifier) don’t have feedback loop.
7) Why OPAMP called direct coupled high differential circuit?
Ans OPAMP is called direct coupled because the input of one OPAMP is inserted into the input of another OPAMP. It is called high gain differential circuit because the difference of the two input is amplified.
8) Why OPAMP called operational Amplifier? Important Interview questions on OPAMP
Ans OPAMP it is a direct coupled high gain differential input amplifier. It is called operational amplifier because it is used for performing different functions like differentiation, addition, integration, subtraction. It has infinite voltage gain, infinite slew rate, infinite input impedance, zero output impedance, infinite bandwidth.
9) What is the output Differentiator and Integrator?
Ans If we give the sinusoidal input in differentiator we will get the output of differentiator as a square output. If we give the sinusoidal input in integrator we will get the output of integrator as a ramp output.
10) For the CMRR to be infinite what will be the condition?
Ans CMRR is defined as the ratio of differential voltage gain (Ad) to common mode voltage gain (Acm). The formula for CMRR is given below:
CMRR = Ad/Acm
If Acm will be zero then only it will be infinite.
Operational Amplifier op amp Viva Interview Questions and Answers
An operational amplifier is a direct coupled high-gain electronic amplifier with a differential input to which feedback is given to control its response characteristics at its single-ended output.
What is called a differential amplifier?
A differential amplifier is an amplifier circuit that amplifies the difference between two input signals but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. The output of the circuit is ideally proportional to the difference between the two signals.
What are the properties of an Ideal op-amp?
- Infinite input impedance
- Zero output impedance
- Infinite open loop voltage gain
- Infinite Bandwidth
- Zero input offset voltage
- Infinite output voltage
- Zero noise
- Infinite common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR)
- Infinite power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
- No temperature drift
What is an inverting and non-inverting operational amplifier?
Inverting Operational amplifier
Inverting amplifier has an inverted output which is 180 degrees out of phase with respect to the input. The output voltage changes in the opposite direction to the input voltage.
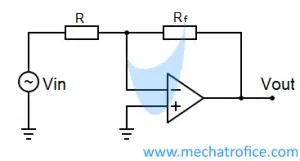
Non-inverting operational amplifier
Non Inverting amplifier has an in-phase output with respect to the input. The output voltage changes in the same direction as the input voltage.
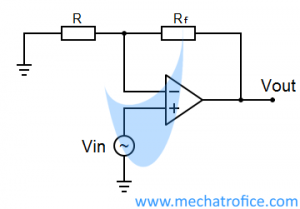
Write the Gain formula for an inverting and non-inverting op-amp.
Inverting Operational Amplifier Gain, A = – Rf / R
Non Inverting Operational Amplifier Gain, A = 1 + Rf/ R
List a few applications of the operational amplifier.
- Inverting amplifiers
- Non-inverting amplifiers
- Differential amplifiers
- Summing amplifiers
- Integrator
- Schmitt trigger
- Voltage followers
- Analog to Digital converter
- Digital to Analog converter
- Filter circuits
- Instrumentation amplifiers
- Oscillator circuits
What is called input offset voltage of an Op-amp?
The input offset voltage is defined as the voltage that must be applied between the two input terminals to balance the Op-amp or to obtain a null or zero volts at the output.
What is called output offset voltage of an Op-amp?
The output offset voltage is the DC voltage present at the output of the op-amp when the two input terminals are grounded or shorted.
Define CMRR.
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) of a differential amplifier is the ratio of the common-mode gain to differential-mode gain. It is the ability of the amplifier to reject common-mode signals.
Why OPAMP called operational Amplifier? Important Interview questions on OPAMP OPAMP it is a direct coupled high gain differential input amplifier. It is called operational amplifier because it is used for performing different functions like differentiation, addition, integration, subtraction. It has infinite voltage gain, infinite slew rate, infinite input impedance, zero output impedance, infinite bandwidth.
When the difference of the two inputs applied to the two terminals of a differential amplifier is amplified, the resultant gain is termed as differential gain. But when the two input terminals are connected to the same input source then the gain established by the differential amplifier is called the common mode gain.
